Abstract
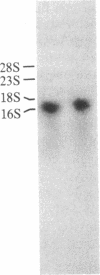
Arginase (EC 3.5.3.1) catalyzes the last step of the urea cycle in the liver of ureotelic animals. Inherited deficiency of the enzyme results in argininemia, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by hyperammonemia. To facilitate investigation of the enzyme and gene structures and to elucidate the nature of the mutation in argininemia, we isolated cDNA clones for human liver arginase. Oligo(dT)-primed and random primer human liver cDNA libraries in lambda gt11 were screened using isolated rat arginase cDNA as a probe. Two of the positive clones, designated lambda hARG6 and lambda hARG109, contained an overlapping cDNA sequence with an open reading frame encoding a polypeptide of 322 amino acid residues (predicted Mr, 34,732), a 5'-untranslated sequence of 56 base pairs, a 3'-untranslated sequence of 423 base pairs, and a poly(A) segment. Arginase activity was detected in Escherichia coli cells transformed with the plasmid carrying lambda hARG6 cDNA insert. RNA gel blot analysis of human liver RNA showed a single mRNA of 1.6 kilobases. The predicted amino acid sequence of human liver arginase is 87% and 41% identical with those of the rat liver and yeast enzymes, respectively. There are several highly conserved segments among the human, rat, and yeast enzymes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berüter J., Colombo J. P., Bachmann C. Purification and properties of arginase from human liver and erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):449–454. doi: 10.1042/bj1750449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizikes G. J., Spector E. B., Cederbaum S. D. Cloning of rat liver arginase cDNA and elucidation of regulation of arginase gene expression in H4 rat hepatoma cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Jul;12(4):375–384. doi: 10.1007/BF01570732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt R., Mecke D. Permissive effect of dexamethasone on glucagon induction of urea-cycle enzymes in perifused primary monolayer cultures of rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):29–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. D., Knox W. E. Arginase isozymes of rat mammary gland, liver, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5785–5789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzfeld A., Raper S. M. The heterogeneity of arginases in rat tissues. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):469–478. doi: 10.1042/bj1530469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch-Kolb H., Greenberg D. M. Molecular characteristics of rat liver arginase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6123–6129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNAN A. L., COHEN P. P. Ammonia detoxication in liver from humans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jan;106:170–173. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto S., Amaya Y., Oda T., Kuzumi T., Saheki T., Kimura S., Mori M. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of cDNA for arginase of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):955–961. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers W. H., Mooren P. G., De Graaf A., Charles R. Perinatal development of the liver in rat and spiny mouse. Its relation to altricial and precocial timing of birth. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):475–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. C., Snodgrass P. J., Rabier D. Induction of urea cycle enzymes by glucagon and dexamethasone in monolayer cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5061–5067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penninckx M., Simon J. P., Wiame J. M. Interaction between arginase and L-ornithine carbamoyltransferase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Purification of S. cerevisiae enzymes and evidence that these enzymes as well as rat-liver arginase are trimers. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 15;49(2):429–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T. Adaptive characteristics of urea cycle enzymes in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:459–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrzypek-Osiecka I., Robin Y., Porembska Z. Purification of rat kidney arginases A1 and A4 and their subcellular distribution. Acta Biochim Pol. 1983;30(1):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumrada R. A., Cooper T. G. Nucleotide sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae arginase gene (CAR1) and its transcription under various physiological conditions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1078–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1078-1087.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarrab R., Rodríguez J., Huitrón C., Palacios R., Soberón G. Molecular forms of rat-liver arginase. Isolation and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 15;49(2):457–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vielle-Breitburd F., Orth G. Rabbit liver L-arginase. Purification, properties, and subunit structure. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1227–1235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]