Abstract
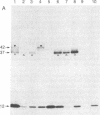
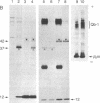
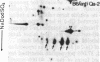
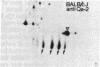
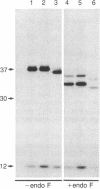
Treatment of supernates of labeled C57BL/6 mouse lymphocytes with antibodies against beta 2-microglobulin reveals the presence of two different soluble class I molecules. One molecule (Mr, 37,000) is found in supernates of both 125I surface-labeled and [35S]methionine biosynthetically labeled cells and reacts with antibodies against Qa-2 antigens. The other molecule (Mr, 42,000) is found labeled only in supernates of [35S]methionine-labeled cells and reacts with antibodies against Qb-1. Analysis of mutant and recombinant mouse strains demonstrates that both soluble class I molecules are encoded in the Qa region. Pulse-chase experiments show that the Qa-2 molecules are released more slowly than Qb-1. It is proposed that Qb-1 molecules are secreted directly, whereas Qa-2 is first expressed on the cell surface and then processed to a soluble form.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Devlin J. J., Lew A. M., Flavell R. A., Coligan J. E. Secretion of a soluble class I molecule encoded by the Q10 gene of the C57BL/10 mouse. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):369–374. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03638.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin J. J., Weiss E. H., Paulson M., Flavell R. A. Duplicated gene pairs and alleles of class I genes in the Qa2 region of the murine major histocompatibility complex: a comparison. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3203–3207. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobberstein B., Garoff H., Warren G., Robinson P. J. Cell-free synthesis and membrane insertion of mouse H-2Dd histocompatibility antigen and beta 2-microglobulin. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):759–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Alexander S. endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4540–4544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogarth P. M., Crewther P. E., McKenzie I. F. Description of a Qa-2 like alloantigen (Qa-m2). Eur J Immunol. 1982 May;12(5):374–379. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincade P. W., Flaherty L., Lee G., Watanabe T., Michaelson J. Qa antigen expression on functional lymphoid, myeloid, and stem cells in adult mice. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2879–2885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S. Secretion of HLA-A and -B antigens via an alternative RNA splicing pathway. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1173–1190. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., Cosman D., Khoury G., Jay G. Secretion of a transplantation-related antigen. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Peterson P. A. Radioimmunoassay determinations of murine beta 2-microglobulin and an H-2 antigen-like serum component. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Dec;9(12):991–996. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830091214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew A. M., Maloy W. L., Coligan J. E. Characteristics of the expression of the murine soluble class I molecule (Q10). J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):254–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor A. L., Antoniou J., Robinson P. J. Structure and expression of genes encoding murine Qa-2 class I antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5920–5924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor A. L., Weiss E. H., Kress M., Jay G., Flavell R. A. A nonpolymorphic class I gene in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson J., Flaherty L., Bushkin Y., Yudkowitz H. Further biochemical data on Qa-2. Immunogenetics. 1981;14(1-2):129–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00344306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natori T., Tanigaki N., Pressman D. A mouse plasma substance carrying beta2-microglobulin activity and lacking in H-2 alloantigenic activity. J Immunogenet. 1976 Apr;3(2):123–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1976.tb00563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Russo C., Allison J. P. HLA antigens in serum. Methods Enzymol. 1984;108:614–624. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)08122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan L., Rogers M. J., Robinson E. A., Hearing V. J., Tanigaki N., Appella E. Biochemical analysis of a 40,000 mol. wt mouse serum protein which binds beta 2-microglobulin and has serological cross-reactivity with H-2 antigens. Mol Immunol. 1982 Sep;19(9):1075–1086. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss C. S., Evans G. A., Margulies D. H., Seidman J. G., Burakoff S. J. Allospecific and virus-specific cytolytic T lymphocytes are restricted to the N or C1 domain of H-2 antigens expressed on L cells after DNA-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2709–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J. Qb-1, a new class I polypeptide encoded by the Qa region of the mouse H-2 complex. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(3):285–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00404488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J., Schirrmacher V. Differences in the expression of histocompatibility antigens on mouse lymphocytes and tumor cells: immunochemical studies. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jan;9(1):61–66. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada A., Nathenson S. G. Murine histocompatibility-2 (H-2) alloantigens. Purification and some chemical properties of soluble products from H-2b and H-2d genotypes released by papain digestion of membrane fractions. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4048–4062. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloski M. J., Vernachio J., Einhorn G., Lattimore A. Qa gene expression: biosynthesis and secretion of Qa-2 molecules in activated T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2949–2953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Winoto A., Minard K., Hood L. Clusters of genes encoding mouse transplantation antigens. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada N., Kimura S., Hatzfeld A., Hämmerling U. Ly-m11: the H-3 region of mouse chromosome 2 controls a new surface alloantigen. Immunogenetics. 1980;11(5):441–449. doi: 10.1007/BF01567813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Golden L., Fahrner K., Mellor A. L., Devlin J. J., Bullman H., Tiddens H., Bud H., Flavell R. A. Organization and evolution of the class I gene family in the major histocompatibility complex of the C57BL/10 mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):650–655. doi: 10.1038/310650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama K., Nathenson S. G. Intramolecular organization of Class I H-2 MHC antigens; localization of the alloantigenic determinants and the beta 2 m binding site to different regions of the H-2 Kb glycoprotein. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1419–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]