Abstract
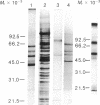
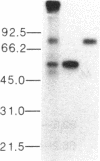
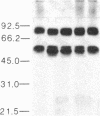
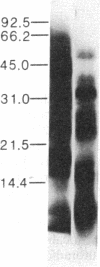
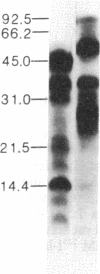
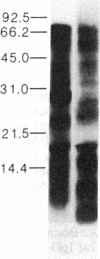
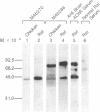
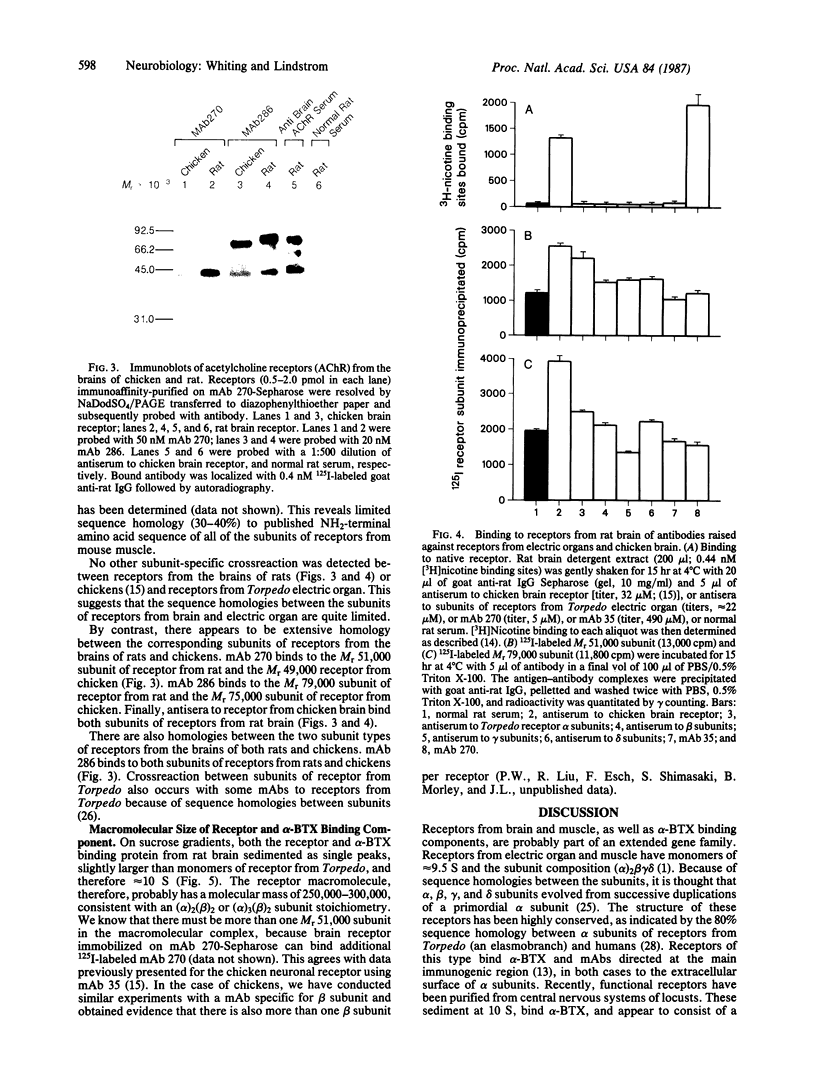
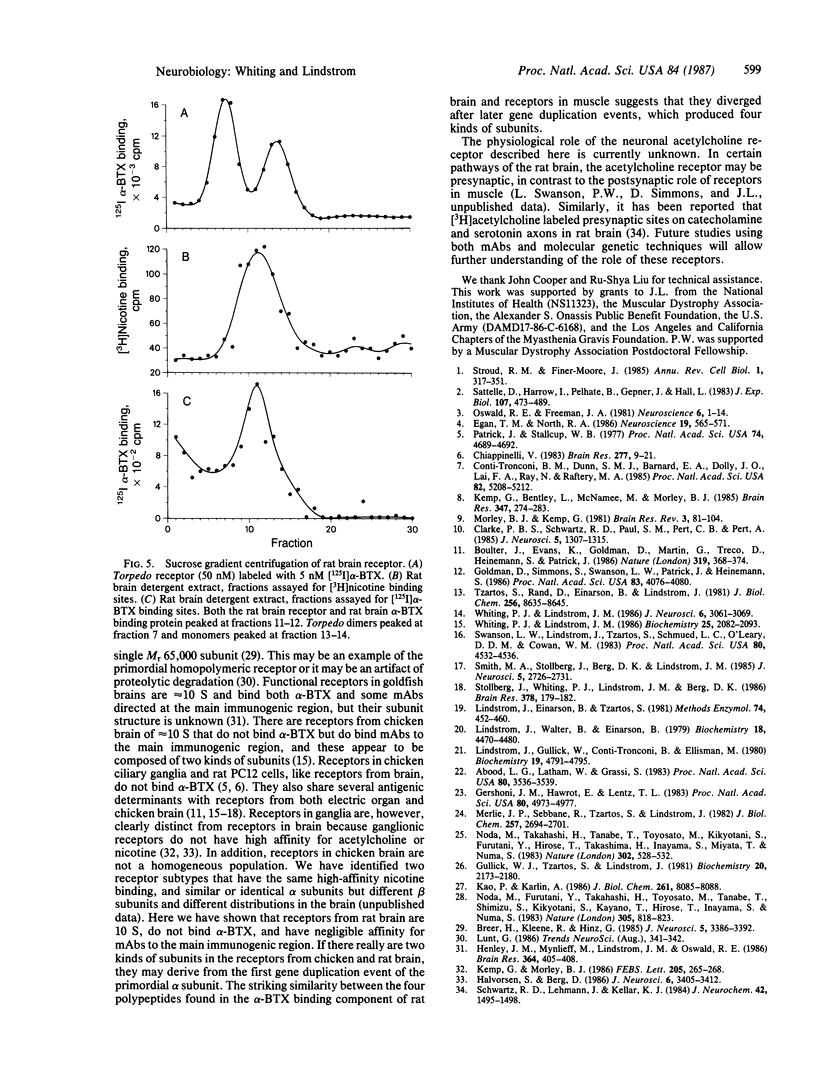
We previously reported the immunoaffinity purification of an acetylcholine receptor from chicken brain that did not bind alpha-bungarotoxin but did bind nicotine and other cholinergic agonists. Antisera and monoclonal antibodies raised against this receptor crossreacted with a receptor from rat brain that had similar pharmacological properties, and also bound to functional acetylcholine receptors in chicken ciliary ganglion cells and rat PC12 cells. Here we report purification of the receptor from rat brain using monoclonal antibody (mAb) 270 raised against receptor from chicken brain. This receptor, similar in size to monomers of receptor from Torpedo electric organ, contained two subunits--apparent Mr, 51,000 and 79,000. The Mr 51,000 subunit was bound by antisera to alpha subunits of receptor from Torpedo electric organ and by mAb 270, which is specific for the Mr 49,000 subunit analogue of receptor from chicken brain. Both subunits were bound by mAb 286, which also binds both subunits of receptors from chicken brain. The alpha-bungarotoxin binding component was purified from the same extracts. It consisted of four subunits of apparent Mr 44,700, 52,300, 56,600, and 65,200. The basic structure of receptors from muscle had evolved to an (alpha)2 beta gamma delta subunit stoichiometry by the time of primitive elasmobranches and is now little changed in mammals. The apparent (alpha)2(beta)2 or (alpha)3(beta)2 structure of the neuronal acetylcholine receptors that we have purified may derive from an early gene duplication event in the evolution of the extended gene family, which now also includes receptors from ganglia and muscle as well as neuronal alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abood L. G., Latham W., Grassi S. Isolation of a nicotine binding site from rat brain by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3536–3539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Evans K., Goldman D., Martin G., Treco D., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Isolation of a cDNA clone coding for a possible neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):368–374. doi: 10.1038/319368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breer H., Kleene R., Hinz G. Molecular forms and subunit structure of the acetylcholine receptor in the central nervous system of insects. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3386–3392. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03386.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiappinelli V. A. Kappa-bungarotoxin: a probe for the neuronal nicotinic receptor in the avian ciliary ganglion. Brain Res. 1983 Oct 24;277(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90902-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. B., Schwartz R. D., Paul S. M., Pert C. B., Pert A. Nicotinic binding in rat brain: autoradiographic comparison of [3H]acetylcholine, [3H]nicotine, and [125I]-alpha-bungarotoxin. J Neurosci. 1985 May;5(5):1307–1315. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-05-01307.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Dunn S. M., Barnard E. A., Dolly J. O., Lai F. A., Ray N., Raftery M. A. Brain and muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are different but homologous proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5208–5212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan T. M., North R. A. Actions of acetylcholine and nicotine on rat locus coeruleus neurons in vitro. Neuroscience. 1986 Oct;19(2):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Hawrot E., Lentz T. L. Binding of alpha-bungarotoxin to isolated alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo californica: quantitative analysis with protein blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4973–4977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Simmons D., Swanson L. W., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Mapping of brain areas expressing RNA homologous to two different acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4076–4080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of acetylcholine receptor structure. 1. Peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2173–2180. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorsen S. W., Berg D. K. Identification of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor on neurons using an alpha-neurotoxin that blocks receptor function. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3405–3412. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03405.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henley J. M., Mynlieff M., Lindstrom J. M., Oswald R. E. Interaction of monoclonal antibodies to electroplaque acetylcholine receptors with the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site of goldfish brain. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 5;364(2):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90857-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. N., Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor binding site contains a disulfide cross-link between adjacent half-cystinyl residues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8085–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp G., Bentley L., McNamee M. G., Morley B. J. Purification and characterization of the alpha-bungarotoxin binding protein from rat brain. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 18;347(2):274–283. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp G., Morley B. J. Ganglionic nAChRs and high-affinity nicotinic binding sites are not equivalent. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 15;205(2):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80910-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Einarson B., Tzartos S. Production and assay of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1981;74(Pt 100):432–460. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)74031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Gullick W., Conti-Tronconi B., Ellisman M. Proteolytic nicking of the acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4791–4795. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Walter B., Einarson B. Immunochemical similarities between subunits of acetylcholine receptors from Torpedo, Electrophorus, and mammalian muscle. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4470–4480. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sebbane R., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. Inhibition of glycosylation with tunicamycin blocks assembly of newly synthesized acetylcholine receptor subunits in muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2694–2701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley B. J., Kemp G. E. Characterization of a putative nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in mammalian brain. Brain Res. 1981 Aug;228(1):81–104. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(81)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Tanabe T., Shimizu S., Kikyotani S., Kayano T., Hirose T., Inayama S. Cloning and sequence analysis of calf cDNA and human genomic DNA encoding alpha-subunit precursor of muscle acetylcholine receptor. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):818–823. doi: 10.1038/305818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):528–532. doi: 10.1038/302528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald R. E., Freeman J. A. Alpha-bungarotoxin binding and central nervous system nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuroscience. 1981;6(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Stallcup W. B. Immunological distinction between acetylcholine receptor and the alpha-bungarotoxin-binding component on sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4689–4692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. D., Lehmann J., Kellar K. J. Presynaptic nicotinic cholinergic receptors labeled by [3H]acetylcholine on catecholamine and serotonin axons in brain. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1495–1498. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Stollberg J., Lindstrom J. M., Berg D. K. Characterization of a component in chick ciliary ganglia that cross-reacts with monoclonal antibodies to muscle and electric organ acetylcholine receptor. J Neurosci. 1985 Oct;5(10):2726–2731. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-10-02726.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollberg J., Whiting P. J., Lindstrom J. M., Berg D. K. Functional blockade of neuronal acetylcholine receptors by antisera to a putative receptor from brain. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 16;378(1):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M., Finer-Moore J. Acetylcholine receptor structure, function, and evolution. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:317–351. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Lindstrom J., Tzartos S., Schmued L. C., O'Leary D. D., Cowan W. M. Immunohistochemical localization of monoclonal antibodies to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in chick midbrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4532–4536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Rand D. E., Einarson B. L., Lindstrom J. M. Mapping of surface structures of electrophorus acetylcholine receptor using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8635–8645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting P. J., Lindstrom J. M. Purification and characterization of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor from chick brain. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2082–2093. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting P., Lindstrom J. Pharmacological properties of immuno-isolated neuronal nicotinic receptors. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):3061–3069. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-03061.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]