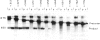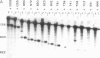Abstract
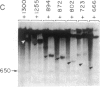
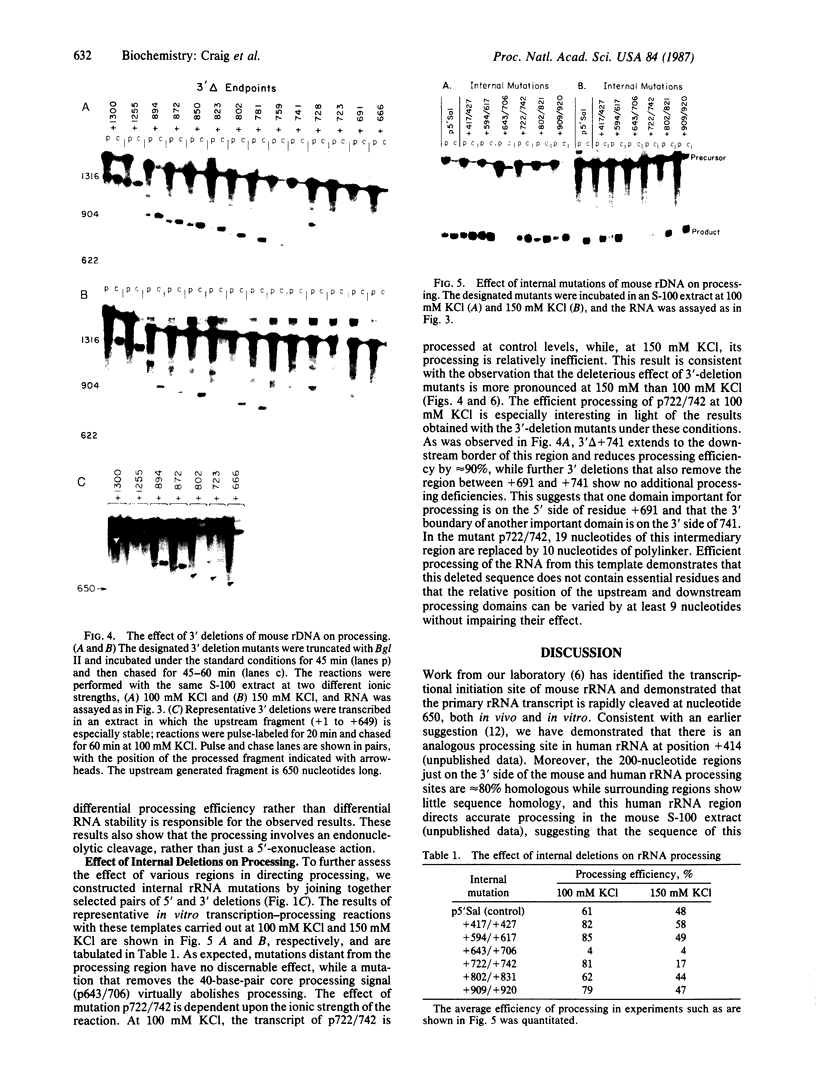
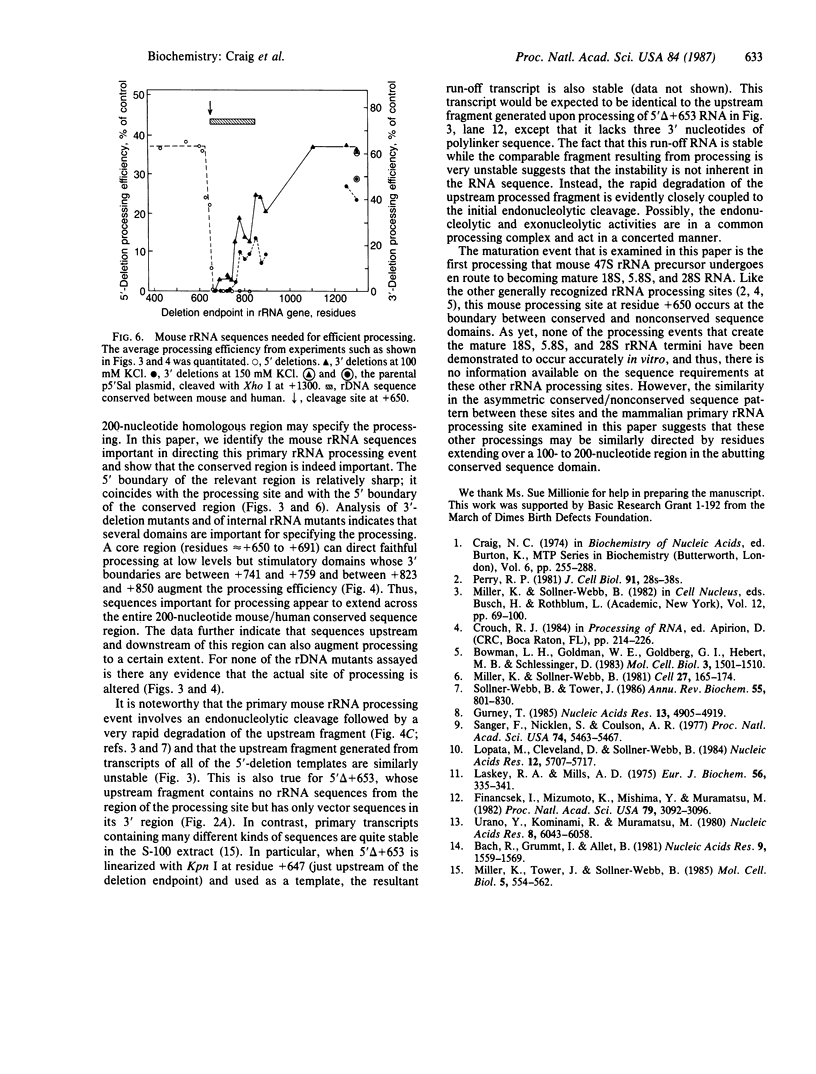
The first step in the processing of 47S precursor rRNA in mouse cells is reproduced in vitro in an S-100 transcription reaction and consists of an endonucleolytic cleavage at residue +650 of the primary transcript followed by rapid degradation of the fragment upstream from residue +650. An analogous processing occurs in human rRNA. The mouse and human rRNA sequences are approximately equal to 80% conserved for 200 nucleotides on the 3' side of these processing sites, suggesting that this conserved region may be important in specifying the processing. To test this hypothesis, we constructed a systematic series of deletion mutants approaching the mouse rDNA processing region from both the 5' and 3' directions and analyzed the processing of their transcripts in vitro. The 5' boundary of the region required for processing is quite sharp and corresponds to the rRNA cleavage site at the 5' end of the conserved sequence region. The 3' boundary is more complex: The 3' deletions extending to between 250 and 130 nucleotides beyond the processing site cause about a 50% decrease in the amount of the processed RNA. A 3' deletion that extends to 109 nucleotides beyond the processing site greatly reduces the processing efficiency. Deletions to or beyond 91 nucleotides on the 3' side of the processing site virtually eliminate processing. Under altered ionic conditions, transcripts of 3' deletions extending to only 41 nucleotides beyond the processing site can still direct a low level of accurate processing. These results demonstrate that the mouse/human conserved sequence just on the 3' side of the primary rRNA processing site consists of several domains that direct and/or augment both the initial endonucleolytic cleavage and the closely coupled selective degradation of the upstream fragment that together constitute the primary rRNA processing event.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach R., Grummt I., Allet B. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation region of the ribosomal transcription unit from mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1559–1569. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman L. H., Goldman W. E., Goldberg G. I., Hebert M. B., Schlessinger D. Location of the initial cleavage sites in mouse pre-rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1501–1510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Human ribosomal RNA gene: nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region and comparison of three mammalian genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney T., Jr Characterization of mouse 45S ribosomal RNA subspecies suggests that the first processing cleavage occurs 600 +/- 100 nucleotides from the 5' end and the second 500 +/- 100 nucleotides from the 3' end of a 13.9 kb precursor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4905–4919. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. A complex control region of the mouse rRNA gene directs accurate initiation by RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):554–562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. RNA processing comes of age. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):28s–38s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.28s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano Y., Kominami R., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. The nucleotide sequence of the putative transcription initiation site of a cloned ribosomal RNA gene of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6043–6058. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]