Fig. 5.
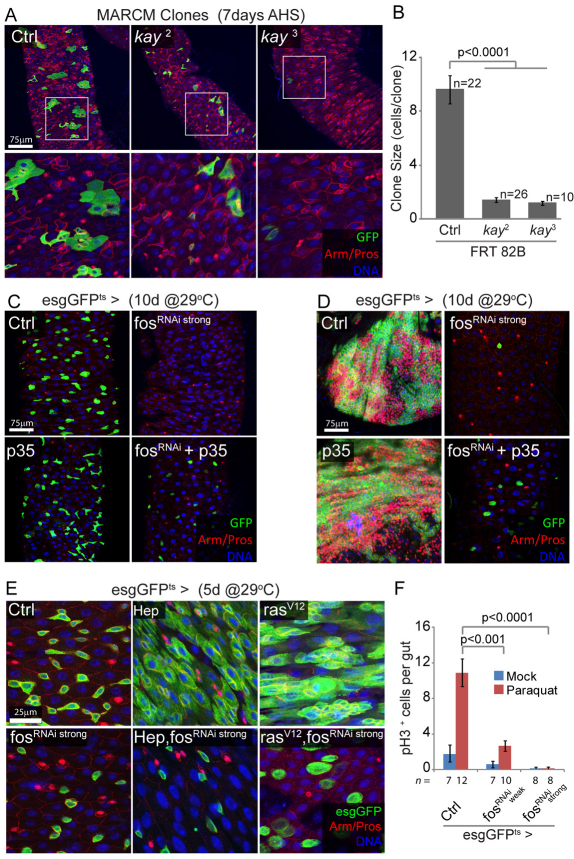
FOS is required for stem cell survival and proliferation, downstream of JNK and RAS. (A,B) FOS is required in ISCs for clone formation. Posterior midguts showing MARCM clones homozygous for fos (kay) loss-of-function alleles, 7 days after induction. Mutant clones remain smaller than controls, often limited to single stem cells, and are recovered less frequently for the kay3 allele. Boxed areas are enlarged in lower panels. Clone size (number of cells per clone) is quantified in B. FRT 82B, MARCM using Flip recombination target at 82B. (C) Prolonged inhibition of FOS results in ISC death by apoptosis. Expression of the fosRNAi construct that causes strong knockdown of FOS expression, using the esgGFPts driver, leads to the disappearance of esg+ cells. This phenotype is rescued when the anti-apoptotic protein p35 is co-expressed, whereas expression of p35 alone has no effect. (D) A similar experiment performed in N loss-of-function background demonstrates that p35 expression rescues cell death but is unable to restore NRNAi-induced proliferation and tumor formation, suggesting that FOS affects both survival and proliferative capacity of ISCs. (E) FOS is required for HEP- and RAS-induced ISC proliferation. Intestines 5 days after induction of HEP or rasV12 together with fosRNAi, using the temperature-sensitive esgGal4 driver. The HEP- and rasV12-induced expansion of esg+ cells is entirely blocked by fosRNAi, demonstrating that FOS is required downstream of JNK and RAS. Note that knocking down FOS does not block RAS-induced cell growth. (F) Paraquat-induced ISC proliferation requires FOS. Expression of two different fosRNAi constructs, using esgGFPts (for 2 days at 29°C prior to treatment), significantly reduces Paraquat-induced proliferation in the intestinal epithelium, as shown by the limited number of pH3+ cells per gut 48 hours after paraquat exposure. In A, C and D GFP is shown in green, armadillo (Arm) outlines cell boundaries (red), prospero (Pros) identifies EEs (nuclear red), DNA is shown in blue. AHS, after heat shock; EE, enteroendocrine cells; ISC, intestinal stem cell; MARCM, mosaic analysis with a repressible cell marker.