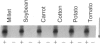Abstract
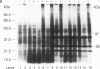
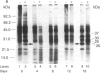
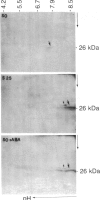
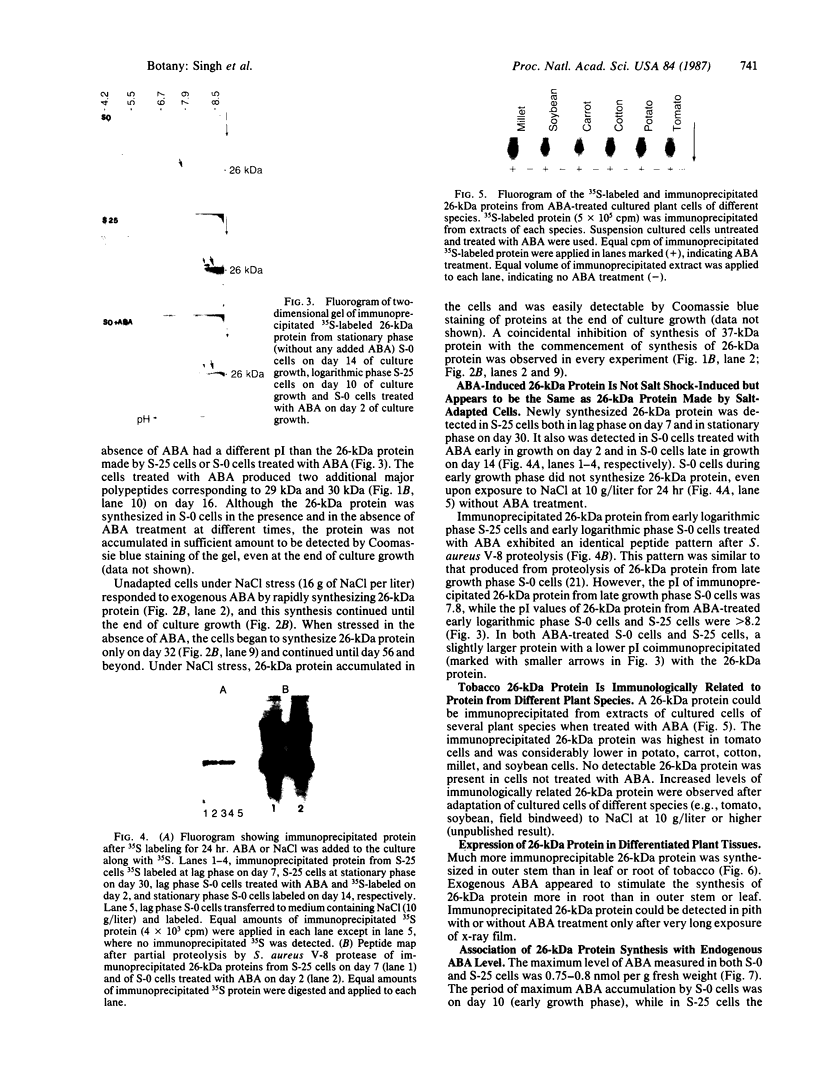
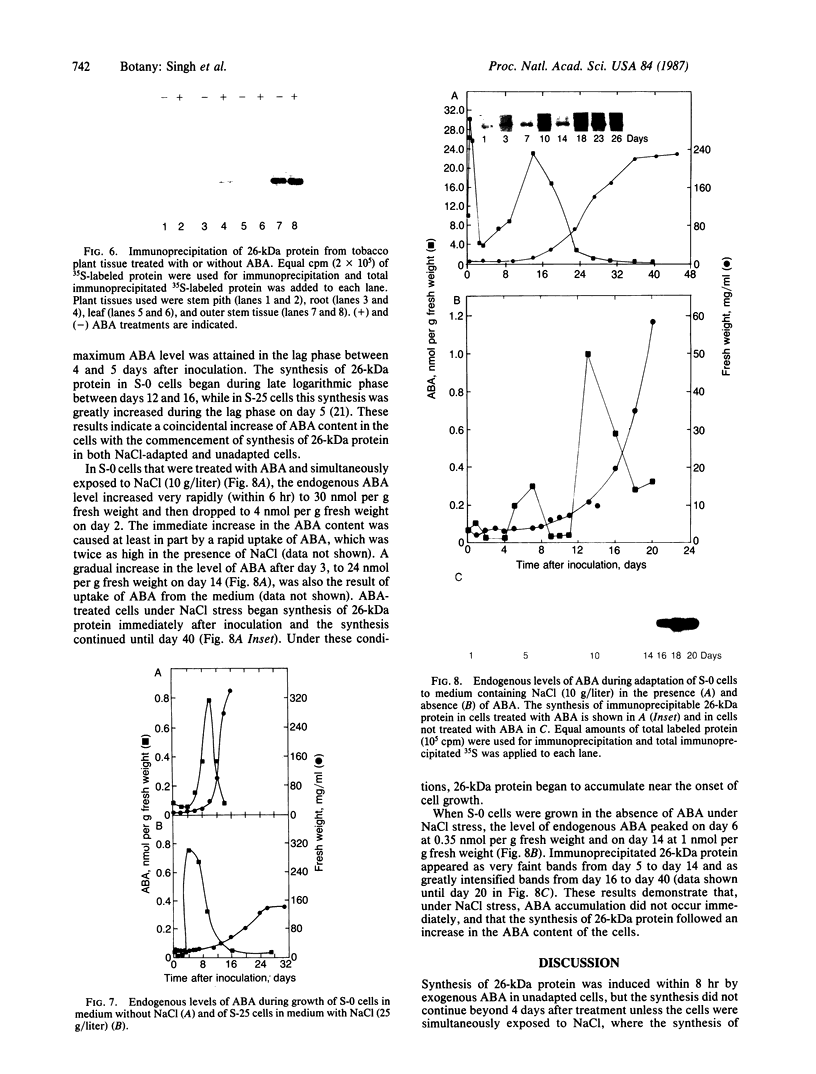
Cultured tobacco cells (Nicotiana tabacum L. cv. Wisconsin 38) synthesize a predominant 26-kDa protein upon exposure to abscisic acid (ABA). ABA also accelerates the rate of adaptation of unadapted cells to NaCl stress. The ABA-induced 26-kDa protein is immunologically cross-reactive to, and produces a similar pattern of peptides after partial proteolysis as, the major 26-kDa protein associated with NaCl adaptation. Both have pI values of >8.2. The synthesis of the ABA-induced 26-kDa protein is transient unless the cells are simultaneously exposed to NaCl stress. There is an association between increased intracellular accumulation of ABA during cell growth and commencement of synthesis of the 26-kDa protein. ABA induces the synthesis of an immunologically cross-reactive 26-kDa protein in cultured cells of several plant species. In tobacco plants, synthesis of the 26-kDa protein could be detected in several tissues but the highest level of expression was seen in outer stem tissue. In root tissues, exogenous ABA greatly stimulated the synthesis of 26-kDa protein as compared to outer stem tissue and leaf. We suggest that ABA is involved in the normal induction of the synthesis of 26-kDa protein and that the presence of NaCl is necessary for the protein to accumulate.
Keywords: abscisic acid, cultured plant cells, NaCl adaptation, 26-kDa protein
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binzel M. L., Hasegawa P. M., Handa A. K., Bressan R. A. Adaptation of Tobacco Cells to NaCl. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):118–125. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray E. A., Beachy R. N. Regulation by ABA of beta-Conglycinin Expression in Cultured Developing Soybean Cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):746–750. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dure L., 3rd, Greenway S. C., Galau G. A. Developmental biochemistry of cottonseed embryogenesis and germination: changing messenger ribonucleic acid populations as shown by in vitro and in vivo protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4162–4168. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerton R. W., Ho T. H. Hormonal regulation of the development of protease and carboxypeptidase activities in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):692–697. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila J. J., Papp J. E., Schultz G. A., Bewley J. D. Induction of heat shock protein messenger RNA in maize mesocotyls by water stress, abscisic Acid, and wounding. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):270–274. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. T. Response of barley aleurone layers to abscisic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1976 Feb;57(2):175–178. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V., Hanson A. D., Chandler P. C. Water stress enhances expression of an alpha-amylase gene in barley leaves. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):350–359. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larosa P. C., Handa A. K., Hasegawa P. M., Bressan R. A. Abscisic Acid accelerates adaptation of cultured tobacco cells to salt. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):138–142. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. S., Ho T. H. Mode of action of abscisic Acid in barley aleurone layers : induction of new proteins by abscisic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):289–297. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozer T. J. Control of protein synthesis in barley aleurone layers by the plant hormones gibberellic acid and abscisic acid. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N. K., Handa A. K., Hasegawa P. M., Bressan R. A. Proteins Associated with Adaptation of Cultured Tobacco Cells to NaCl. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):126–137. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeevaart J. A. Sites of Abscisic Acid Synthesis and Metabolism in Ricinus communis L. Plant Physiol. 1977 May;59(5):788–791. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.5.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwar J. A., Hooley R. Hormonal Regulation of alpha-Amylase Gene Transcription in Wild Oat (Avena fatua L.) Aleurone Protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):459–463. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]