Abstract
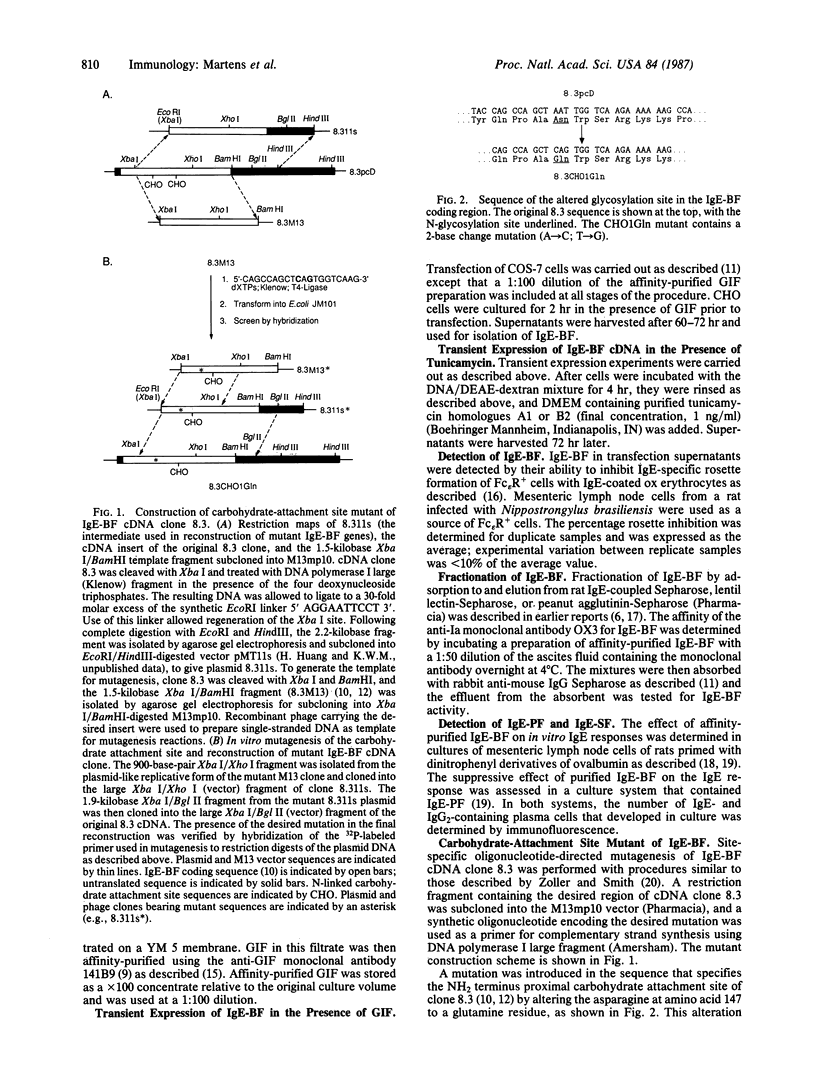
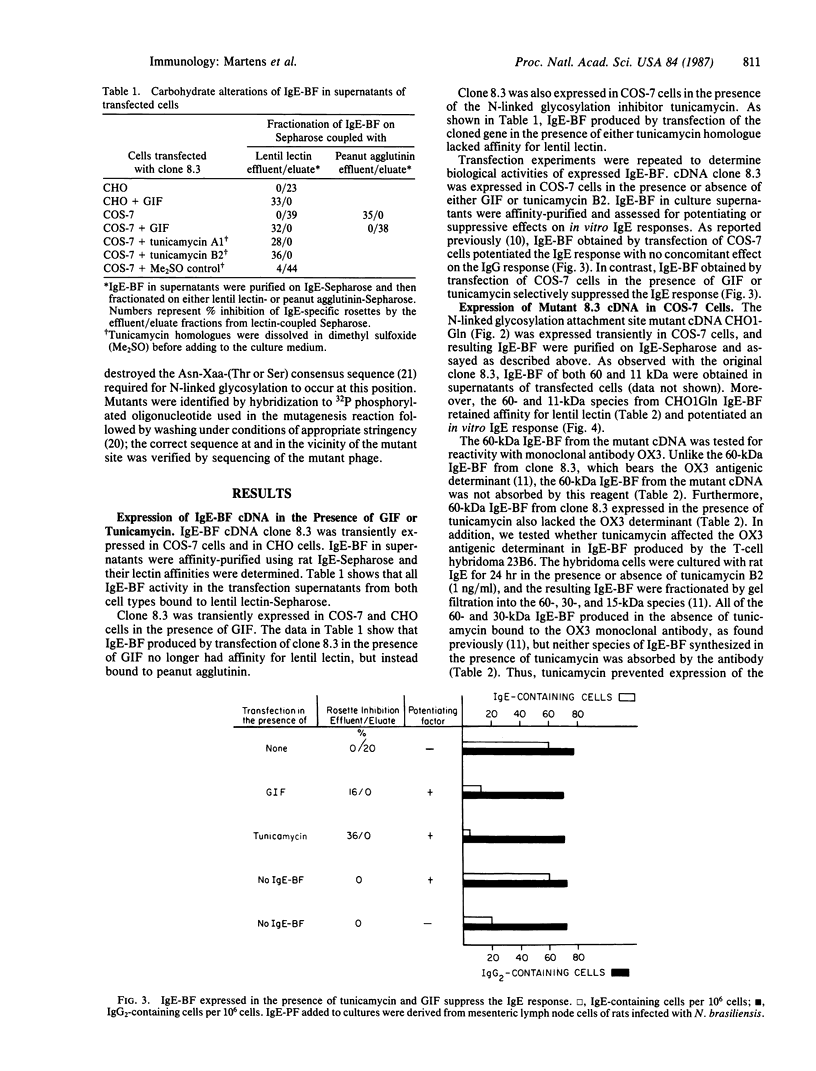
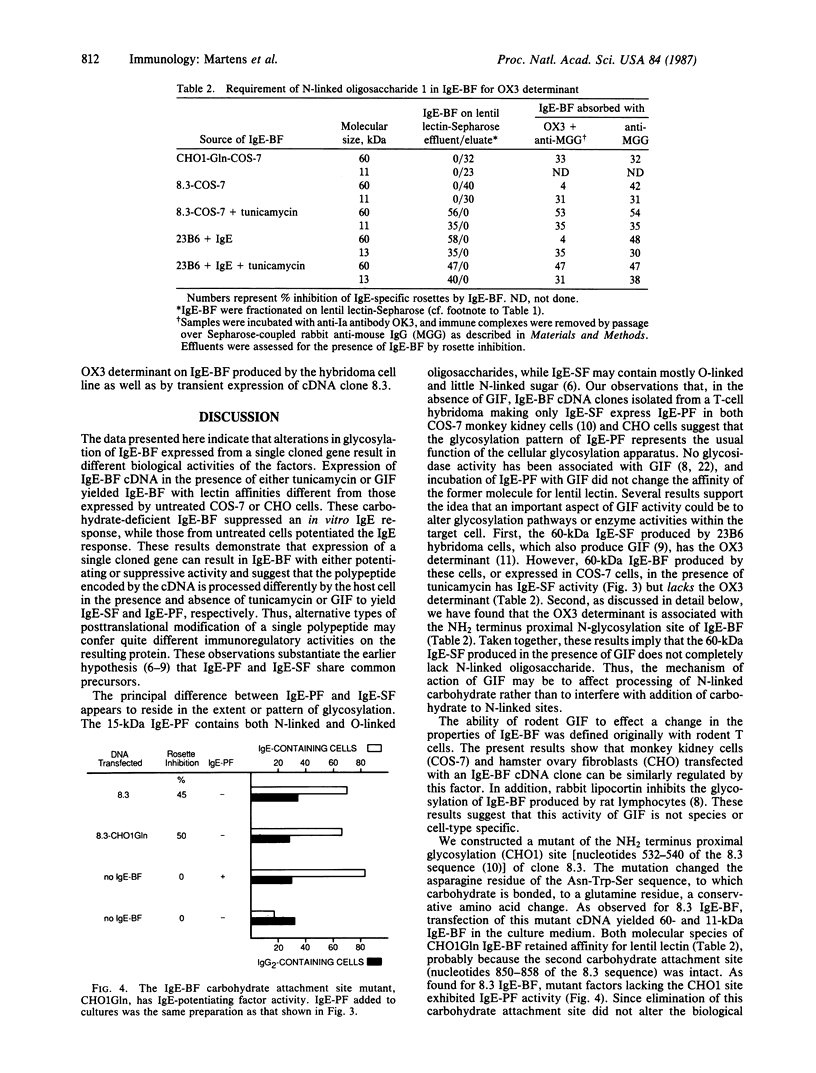
We have investigated expression of an IgE-binding factor (IgE-BF) cDNA in both COS-7 monkey kidney cells and Chinese hamster ovary cells. Transient expression of the IgE-BF clone in either cell type yielded IgE-BF, which potentiated an in vitro IgE response and had an affinity for lentil lectin. In contrast, when the transient expression experiments were carried out in the presence of tunicamycin, the factors no longer bound to lentil lectin. Moreover, IgE-BF expressed under these conditions suppressed an in vitro IgE response. IgE-BF lacking affinity for lentil lectin and suppressing the IgE response also resulted from transient expression of the IgE-BF gene in the presence of glycosylation inhibiting factor, a phospholipase inhibitory protein. Thus, IgE-BF that either potentiate or suppress the IgE response can be expressed from a single cloned gene; the difference in biological activities appears to be determined principally by the type of glycosylation of the common polypeptide chain. Previous work showed that IgE-BF bears an antigenic determinant recognized by the anti-Ia monoclonal antibody OX3. IgE-BF produced in the presence of tunicamycin, and IgE-BF expressed from a mutant cDNA lacking one of two carbohydrate-attachment sites, lacked the OX3 determinant. Thus, the OX3 determinant on IgE-BF appears to be associated with a site of N-linked glycosylation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akasaki M., Jardieu P., Ishizaka K. Immunosuppressive effects of glycosylation inhibiting factor on the IgE and IgG antibody response. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3172–3179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman W. H., Rabourdin-Combe C., Neauport-Sautes C., Gisler R. H. Characterization and function of T cell Fc gamma receptor. Immunol Rev. 1981;56:51–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb01047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins T. J., Parish C. R. Extraction of the carbohydrate-defined class of Ia antigens from murine spleen cells and serum. Mol Immunol. 1980 Aug;17(8):1065–1073. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima M., Yodoi J., Huff T. F., Ishizaka K. Formation of IgE-binding factors by rat T lymphocytes. III. Mechanisms of selective formation of IgE-suppressive factors by treatment with complete Freund's adjuvant. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1810–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima M., Yodoi J., Ishizaka K. Regulatory role of IgE-binding factors from rat T lymphocytes. III. IgE-specific suppressive factor with IgE-binding activity. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1442–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff T. F., Uede T., Ishizaka K. Formation of rat IgE-binding factors by rat-mouse T cell hybridomas. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff T. F., Uede T., Iwata M., Ishizaka K. Modulation of the biologic activities of IgE-binding factors. III. Switching of a T cell hybrid clone from the formation of IgE-suppressive factor to the formation of IgE-potentiating factor. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1090–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff T. F., Yodoi J., Uede T., Ishizaka K. Presence of an antigenic determinant common to rat IgE-potentiating factor, IgE-suppressive factor, and Fc epsilon receptors on T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):406–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Huff T. F., Ishizaka K. Modulation of the biologic activities of IgE-binding factor. V. The role of glycosylation-enhancing factor and glycosylation-inhibiting factor in determining the nature of IgE-binding factors. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1286–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardieu P., Moore K., Martens C., Ishizaka K. Relationship among IgE-binding factors with various molecular weights. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2727–2734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono H., Mosteller-Barnum L. M., Pitts A. M., Williamson S. I., Michalek S. M., McGhee J. R. Isotype-specific immunoregulation. IgA-binding factors produced by Fc alpha receptor-positive T cell hybridomas regulate IgA responses. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):731–747. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwy I., Brezin C., Neauport-Sautes C., Theze J., Fridman W. H. Isotype regulation of antibody production: T-cell hybrids can be selectively induced to produce IgG1 and IgG2 subclass-specific suppressive immunoglobulin-binding factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2323–2327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens C. L., Huff T. F., Jardieu P., Trounstine M. L., Coffman R. L., Ishizaka K., Moore K. W. cDNA clones encoding IgE-binding factors from a rat-mouse T-cell hybridoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2460–2464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Identification of Ia glycoproteins in rat thymus and purification from rat spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):426–433. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., Jardieu P., Mietz J. A., Trounstine M. L., Kuff E. L., Ishizaka K., Martens C. L. Rodent IgE-binding factor genes are members of an endogenous, retrovirus-like gene family. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4283–4290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabourdin-Combe C., Dorf M. E., Guimezanes A., Fridman W. H. T cell-produced immunoglobulin binding factor (IBF) bears determinants coded for by the I region of the major histocompatibility complex and lacks allogeneic restriction. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):237–242. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suemura M., Shiho O., Deguchi H., Yamamura Y., Böttcher I., Kishimoto T. Characterization and isolation of IgE class-specific suppressor factor (IgE-TsF) I. The presence of the binding site(s) for IgE and of the H-2 gene products in IgE-TsF. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):465–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suemura M., Yodoi J., Hirashima M., Ishizaka K. Regulatory role of IgE-binding factors from rat T lymphocytes. I. Mechanism of enhancement of IgE response by IgE-potentiating factor. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):148–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uede T., Hirata F., Hirashima M., Ishizaka K. Modulation of the biologic activities of IgE-binding factors. I. Identification of glycosylation-inhibiting factor as a fragment of lipomodulin. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):878–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yodoi J., Hirashima M., Ishizaka K. Regulatory role of IgE-binding factors from rat T lymphocytes. II. Glycoprotein nature and source of IgE-potentiating factor. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1436–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yodoi J., Hirashima M., Ishizaka K. Regulatory role of IgE-binding factors from rat T lymphocytes. V. The carbohydrate moieties in IgE-potentiating factors and IgE-suppressive factors. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):289–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yodoi J., Ishizaka K. Lymphocytes bearing Fc receptors for IgE. IV. Formation of IgE-binding factor by rat T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1322–1329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. C., Leung D. Y., Geha R. S. Production of IgE-potentiating factor in man by T cell lines bearing Fc receptors for IgE. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):871–878. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



