Abstract
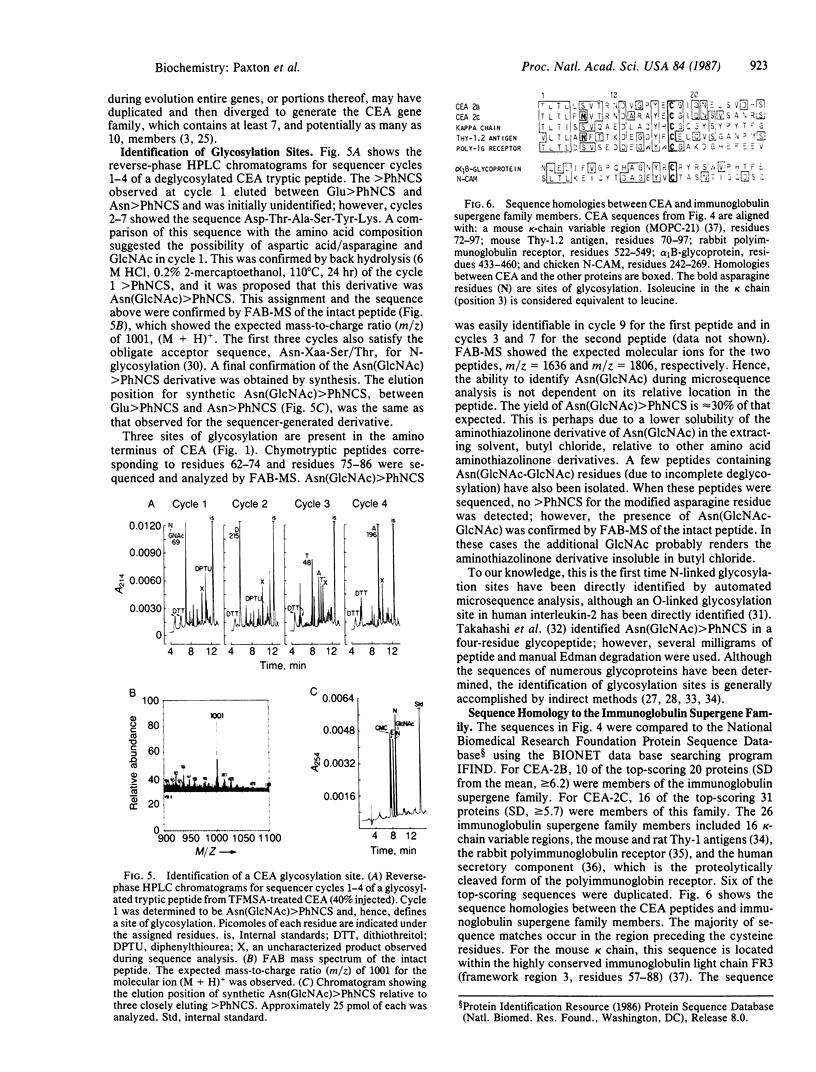
A direct method for the determination of N-linked glycosylation sites in highly glycosylated proteins is described. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and a nonspecific crossreacting antigen (NCA) were chemically deglycosylated, and peptide maps were prepared by reverse-phase HPLC. The peptides were sequenced on a gas-phase microsequencer, and glycosylation sites were identified as the phenylthiohydantoin derivative of N-acetylglucosaminylasparagine. The sequences were confirmed by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Highly homologous, extended amino-terminal sequences were determined for CEA and two NCAs, NCA-95 and NCA-55. Cysteine-containing sequences for CEA and NCA-95 show up to 95% sequence homology, and the CEA sequences also show internal sequence homologies. A comparison of the CEA sequences with known protein sequences suggests that CEA may be a member of the immunoglobulin supergene family. The protein sequence data have been used to identify a genomic DNA clone for one of the NCA antigens [Thompson, J., Pande, H., Paxton, R. J., Shively, L., Padma, A., Simmer, R. L., Todd, C. W., Riggs, A. D. & Shively, J. E. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, in press] and a cDNA clone for CEA [Zimmermann, W., Ortlieb, B., Friedrich, R. & von Kleist, S. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, in press].
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abuharfeil N., Grunert F., von Kleist S. Non-specific crossreacting antigen (NCA) does not contain methionine. Tumour Biol. 1984;5(6):339–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchegger F., Schreyer M., Carrel S., Mach J. P. Monoclonal antibodies identify a CEA crossreacting antigen of 95 kD (NCA-95) distinct in antigenicity and tissue distribution from the previously described NCA of 55 kD. Int J Cancer. 1984 May 15;33(5):643–649. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtin P., Chavanel G., Hirsch-Marie H. Characterization of a second normal antigen that cross-reacts with CEA. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1926–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge A. S., Faltynek C. R., Hof L., Reichert L. E., Jr, Weber P. Deglycosylation of glycoproteins by trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiffert H., Quentin E., Decker J., Hillemeir S., Hufschmidt M., Klingmüller D., Weber M. H., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstruktur der menschlichen freien Sekretkomponente und die Anordnung der Disulfidbrücken. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 Dec;365(12):1489–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Shively J. E., Wrann M. Isolation and characterization of the normal crossreacting antigen: homology of its NH2-terminal amino acid sequence with that of carcinoembryonic antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLD P., FREEDMAN S. O. DEMONSTRATION OF TUMOR-SPECIFIC ANTIGENS IN HUMAN COLONIC CARCINOMATA BY IMMUNOLOGICAL TOLERANCE AND ABSORPTION TECHNIQUES. J Exp Med. 1965 Mar 1;121:439–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassman J. N., Todd C. W., Shively J. E. Chemical deglycosylation of carcinoembryonic antigen for amino acid sequence studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):209–216. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold P., Freedman S. O. Specific carcinoembryonic antigens of the human digestive system. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):467–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunert F., AbuHarfeil N., Schwarz K., von Kleist S. Two CEA and three NCA species, although distinguishable by monoclonal antibodies, have nearly identical peptide patterns. Int J Cancer. 1985 Sep 15;36(3):357–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawke D. H., Harris D. C., Shively J. E. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. V. Design and performance of a novel gas-liquid-solid phase instrument. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jun;147(2):315–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemperly J. J., Murray B. A., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the polysialic acid-rich and cytoplasmic domains of the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3037–3041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Kronenberg M., Hunkapiller T. T cell antigen receptors and the immunoglobulin supergene family. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishioka N., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Amino acid sequence of human plasma alpha 1B-glycoprotein: homology to the immunoglobulin supergene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2363–2367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler M. J., Shively J. E., Pritchard D. G., Todd C. W. Isolation, immunological characterization, and structural studies of a tumor antigen related to carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer Res. 1978 Apr;38(4):1041–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki M., Kuroki M., Koga Y., Matsuoka Y. Monoclonal antibodies to carcinoembryonic antigen: a systematic analysis of antibody specificities by using related normal antigens and evidence for allotypic determinants on carcinoembryonic antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2090–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier J., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Purification of cyanogen bromide fragments from beta-2-glycoprotein I by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1983 Aug 26;266:545–554. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)90925-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach J. P., Pusztaszeri G. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA): demonstration of a partial identity between CEA and a normal glycoprotein. Immunochemistry. 1972 Oct;9(10):1031–1034. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D. Glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:673–702. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort A. J., Lamport D. T. Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride deglycosylates glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):289–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Friedlander M., Blobel G. The receptor for transepithelial transport of IgA and IgM contains multiple immunoglobulin-like domains. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):37–43. doi: 10.1038/308037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumaier M., Fenger U., Wagener C. Delineation of four carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) related antigens in normal plasma by transblot studies using monoclonal anti-CEA antibodies with different epitope specificities. Mol Immunol. 1985 Nov;22(11):1273–1277. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumaier M., Fenger U., Wagener C. Monoclonal antibodies for carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as a model system: identification of two novel CEA-related antigens in meconium and colorectal carcinoma tissue by Western blots and differential immunoaffinity chromatography. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3604–3609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard D. G., Todd C. W. Purification of carcinoembryonic antigen by removal of contaminating mucopolysaccharides. Cancer Res. 1976 Dec;36(12):4699–4701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Kutny R. M., Panico M., Morris H. R., Chowdhry V. Amino acid sequence and post-translational modification of human interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6486–6490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Beatty J. D. CEA-related antigens: molecular biology and clinical significance. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1985;2(4):355–399. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(85)80008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Kessler M. J., Todd C. W. Amino-terminal sequences of the major tryptic peptides obtained from carcinoembryonic antigen by digestion with trypsin in the presence of Triton X-100. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2199–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenberg T., Hammarström S., Hedin A. Purification and properties of biliary glycoprotein I (BGP I). Immunochemical relationship to carcinoembryonic antigen. Mol Immunol. 1979 Apr;16(4):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Yasuda Y., Kuzuya M., Murachi T. The amino acid sequence of glycopeptides isolated from stem bromelain. J Biochem. 1969 Nov;66(5):659–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry W. D., Henkart P. A., Coligan J. E., Todd C. W. Structural studies of the major glycoprotein in preparations with carcinoembryonic antigen activity. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):200–204. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetaert D., Takahashi N., Putman F. W. Purification of glycopeptides of human ceruloplasmin and immunoglobulin D by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):430–437. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxdal M. J., Konigsberg W. H., Henley W. L., Edelman G. M. The covalent structure of a human gamma G-immunoglobulin. II. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide fragments. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1959–1966. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Gagnon J. Neuronal cell Thy-1 glycoprotein: homology with immunoglobulin. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):696–703. doi: 10.1126/science.6177036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kleist S., Chavanel G., Burtin P. Identification of an antigen from normal human tissue that crossreacts with the carcinoembryonic antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2492–2494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]