Abstract
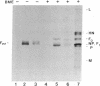
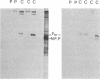
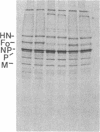
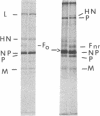
The fusion glycoprotein of Newcastle disease virus is synthesized as an inactive precursor, F0. During intracellular transport and maturation, F0 undergoes a conformational change resulting from the loss of intramolecular disulfide bonds. F0 is also cleaved to yield F1, F2, the active, membrane-fusing form of the protein. Two monoclonal antibodies were used to explore this conformational change and its relationship to cleavage. These antibodies failed to precipitate the pulse-labeled fusion protein but did precipitate the F0 and the F1, F2 forms of the "chase" fusion protein. Use of the inhibitors carbonylcyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone and monensin showed that the fusion protein acquired the ability to react with the monoclonal antibodies after it left the rough endoplasmic reticulum but before it left the medial Golgi membranes and before it was cleaved. The acquisition of antigenicity correlates with the disruption of intramolecular disulfide bonds during transit through the cell. This correlation was directly confirmed. The pulse-labeled fusion protein could be recognized by both monoclonal antibodies if the protein was first reduced. The formation and disruption of intramolecular disulfide bonds as a posttranslational modification of glycoproteins is discussed.
Full text
PDF

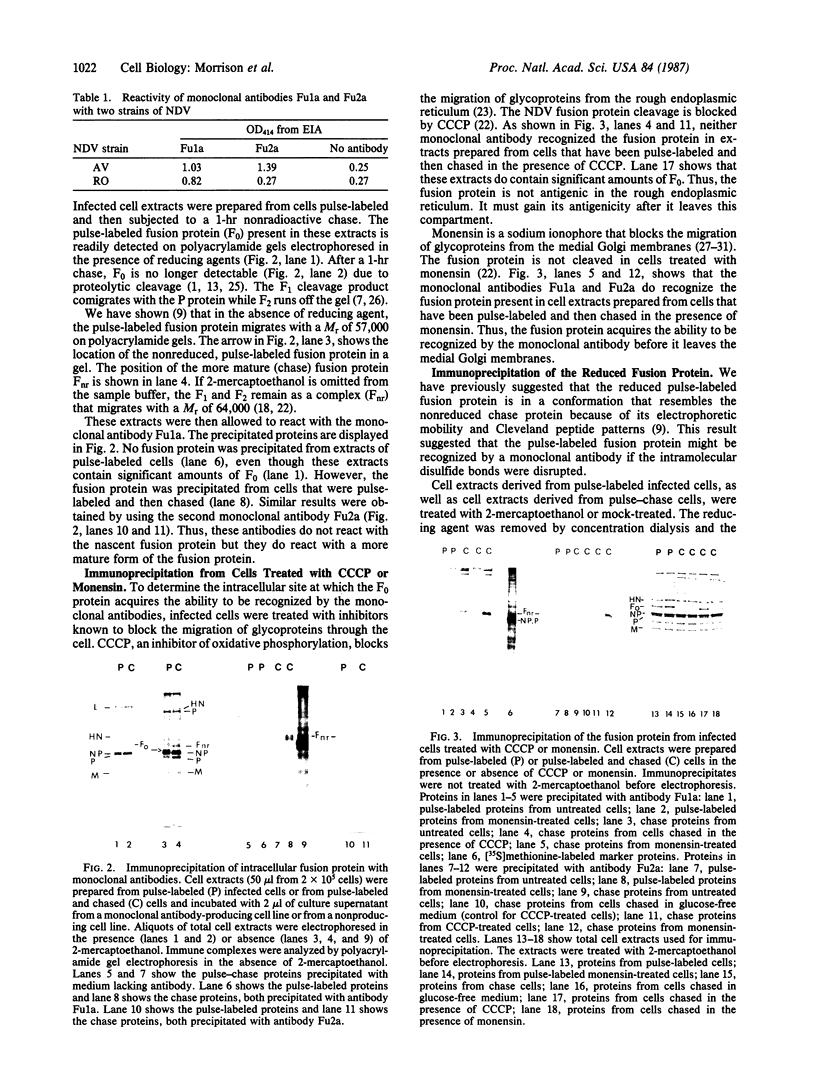


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergman L. W., Kuehl W. M. Formation of an intrachain disulfide bond on nascent immunoglobulin light chains. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8869–8876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Morrison T. G. Fatty acid modification of Newcastle disease virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):342–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.342-347.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Hightower L. E., Ball L. A. Transcription and translation of Newcastle disease virus mRNA's in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):324–336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.324-336.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries E., Rothman J. E. Transport of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein in a cell-free extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3870–3874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Quinn P., Warren G. Dissection of the Golgi complex. I. Monensin inhibits the transport of viral membrane proteins from medial to trans Golgi cisternae in baby hamster kidney cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):835–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E., Bratt M. A. Protein metabolism during the steady state of Newcastle disease virus infection. I. Kinetics of amino acid and protein accumulation. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):696–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.696-706.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Activation of the Sendai virus fusion protein (f) involves a conformational change with exposure of a new hydrophobic region. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3557–3563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Schlesinger M. J. Vesicular stomatitis virus and sindbis virus glycoprotein transport to the cell surface is inhibited by ionophores. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):407–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohama T., Garten W., Klenk H. D. Changes in conformation and charge paralleling proteolytic activation of Newcastle disease virus glycoproteins. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):364–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnes L. W., Morrison T. G. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the Newcastle disease virus fusion protein and comparisons of paramyxovirus fusion protein sequences. Virus Res. 1986 Sep;5(4):343–356. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnes L. W., Semerjian A., Morrison T. Conformational changes in Newcastle disease virus fusion glycoprotein during intracellular transport. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):341–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.341-348.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Ward L. J. Intracellular processing of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein and the Newcastle disease virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein. Virus Res. 1984;1(3):225–239. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T., Ward L. J., Semerjian A. Intracellular processing of the Newcastle disease virus fusion glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.851-857.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of the viral glycoproteins and its significance for the virulence of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):494–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Ogura H., Klenk H. Studies on the assembly of the envelope of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):523–538. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples M. E., Bratt M. A. UV irradiation analysis of complementation between, and replication of, RNA-negative temperature-sensitive mutants of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):965–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.965-973.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Käriäinen L. Incomplete complex oligosaccharides in semliki forest virus envelope proteins arrested within the cell in the presence of monensin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):213–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr, Davidson L. K. The biosynthesis of rat serum albumin. In vivo studies on the formation of the disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8847–8853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. The golgi apparatus: two organelles in tandem. Science. 1981 Sep 11;213(4513):1212–1219. doi: 10.1126/science.7268428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson A. C., Fox C. F. Precursor protein for Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):579–587. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.579-587.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele G., Jacoby R. Conformational changes associated with proteolytic processing of presecretory proteins allow glutathione-catalyzed formation of native disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12277–12282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Isolation and purification of the envelope proteins of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.263-271.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Two disulfide-linked polypeptide chains constitute the active F protein of paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):54–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe J. C., Hightower L. E. Maturation of the envelope glycoproteins of Newcastle disease virus on cellular membranes. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):947–957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.947-957.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto J. T., Garten W., Rott R. The site of cleavage in infected cells and polypeptides of representative paramyxoviruses grown in cultured cells of the chorioallantoic membrane. Arch Virol. 1981;67(1):19–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01314598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. Perturbation of vesicular traffic with the carboxylic ionophore monensin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1026–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M., Vassalli P. Plasma cell immunoglobulin secretion: arrest is accompanied by alterations of the golgi complex. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1332–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]