Abstract
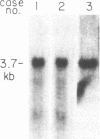
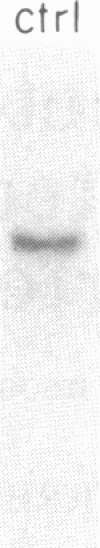
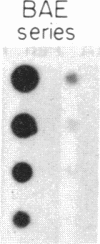
Arterial smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation is thought to be an essential aspect of the development of human atherosclerotic lesions. In this study we posed the question, could a growth factor gene be transcriptionally active in atherosclerotic tissue? We found that transcripts from the sis gene, which encodes one of the two chains of platelet-derived growth factor, were present in surgically removed human carotid artery lesions at levels 5-fold greater than the low level of constitutive expression detected in normal artery. This demonstrates that a growth factor could be synthesized endogenously within human atherosclerotic lesions. Although atherosclerotic lesions are composed predominantly of SMC, large numbers of infiltrating macrophages, T cells, and endothelial cells can also be present, raising the possibility that one of these secondary cell types, rather than SMC, could be responsible for the sis transcripts. Human macrophages activated in culture contained 2- to 4-fold more sis RNA, per micrograms of total cellular RNA, than lesions, whereas T cells activated in culture did not contain significant levels. Cultured human endothelial cells expressed sis transcripts at higher levels than macrophages. Since human arterial SMC in culture express receptors for and are mitogenically responsive to platelet-derived growth factor, transcription of the sis gene by cells within lesions, whether these cells are SMC themselves, macrophages, endothelial cells, or another cell type, suggests that an autocrine and/or paracrine proliferative mechanism is important in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amasino R. M. Acceleration of nucleic acid hybridization rate by polyethylene glycol. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. B., Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M., McDougall J. K., Benditt E. P. Expression of the sis gene by endothelial cells in culture and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6772–6774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Benditt J. M. Evidence for a monoclonal origin of human atherosclerotic plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1753–1756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes A. W., Reidy M. A., Clowes M. M. Kinetics of cellular proliferation after arterial injury. I. Smooth muscle growth in the absence of endothelium. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):327–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCorleto P. E., Bowen-Pope D. F. Cultured endothelial cells produce a platelet-derived growth factor-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1919–1923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelmann E. P., Petri E., Cetta A., Wong-Staal F. Deletions of specific regions of the simian sarcoma-associated virus genome are found in defective viruses and in the simian sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):593–604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.593-604.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G. The role of the monocyte in atherogenesis: II. Migration of foam cells from atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1981 May;103(2):191–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn K. C., Ross R. Human monocyte-derived growth factor(s) for mesenchymal cells: activation of secretion by endotoxin and concanavalin A. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson L., Holm J., Skalli O., Bondjers G., Hansson G. K. Regional accumulations of T cells, macrophages, and smooth muscle cells in the human atherosclerotic plaque. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):131–138. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Proper J. A., Goustin A. S., Shipley G. D., DiCorleto P. E., Moses H. L. Induction of c-sis mRNA and activity similar to platelet-derived growth factor by transforming growth factor beta: a proposed model for indirect mitogenesis involving autocrine activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinet Y., Bitterman P. B., Mornex J. F., Grotendorst G. R., Martin G. R., Crystal R. G. Activated human monocytes express the c-sis proto-oncogene and release a mediator showing PDGF-like activity. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):158–160. doi: 10.1038/319158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornex J. F., Martinet Y., Yamauchi K., Bitterman P. B., Grotendorst G. R., Chytil-Weir A., Martin G. R., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous expression of the c-sis gene and release of a platelet-derived growth factorlike molecule by human alveolar macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):61–66. doi: 10.1172/JCI112574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss N. S., Benditt E. P. The ultrastructure of spontaneous and experimentally induced arterial lesions. II. The spontaneous plaque in the chicken. Lab Invest. 1970 Sep;23(3):231–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson J., Sjölund M., Palmberg L., Thyberg J., Heldin C. H. Arterial smooth muscle cells in primary culture produce a platelet-derived growth factor-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4418–4422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn A., Garte S. J., Warren L., Nesta D., Mindich B. Transforming gene in human atherosclerotic plaque DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7951–7955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Josephs S. F., Jarrett R., Reitz M. S., Jr, Wong-Staal F. Nucleotide sequence of transforming human c-sis cDNA clones with homology to platelet-derived growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5007–5018. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R. A., Schwartz S. M., Bowen-Pope D. F. Developmentally regulated production of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecules. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):669–671. doi: 10.1038/311669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokado K., Raines E. W., Madtes D. K., Barrett T. B., Benditt E. P., Ross R. A significant part of macrophage-derived growth factor consists of at least two forms of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. N., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R., Reidy M. A. Production of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecules by cultured arterial smooth muscle cells accompanies proliferation after arterial injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7311–7315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield M. D., Scrace G. T., Whittle N., Stroobant P., Johnsson A., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor is structurally related to the putative transforming protein p28sis of simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):35–39. doi: 10.1038/304035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]