Abstract
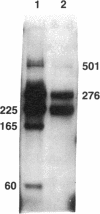
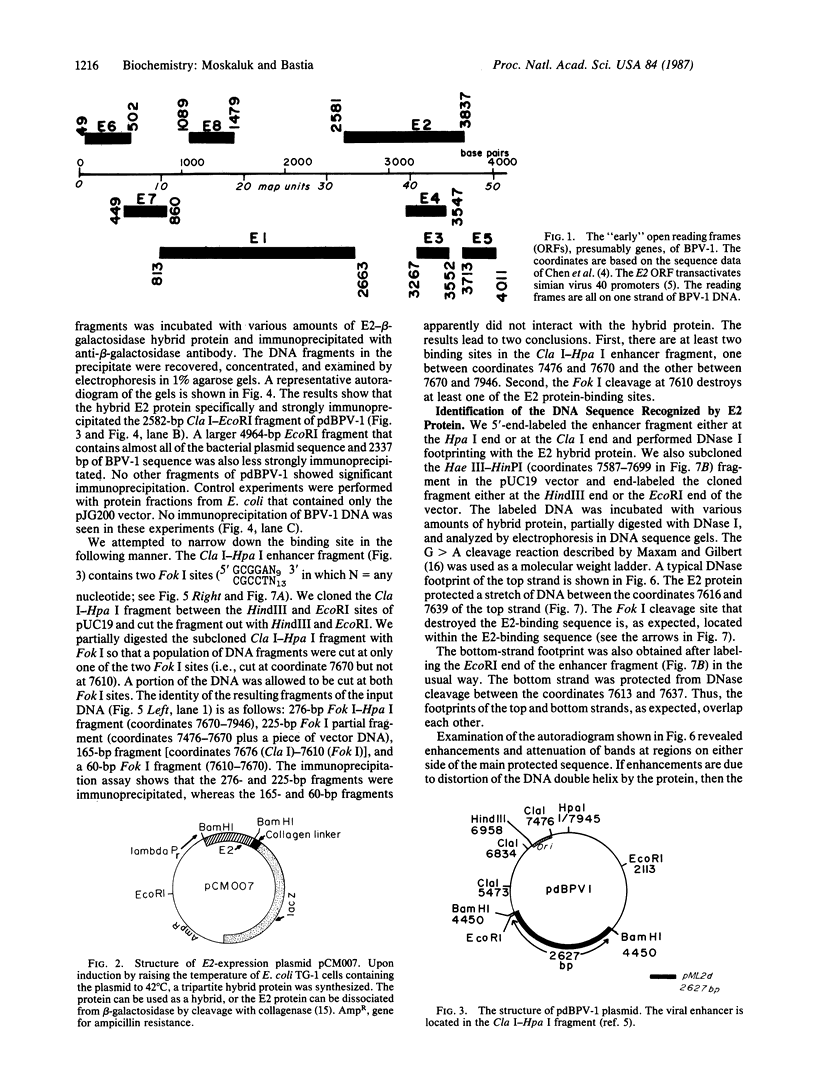
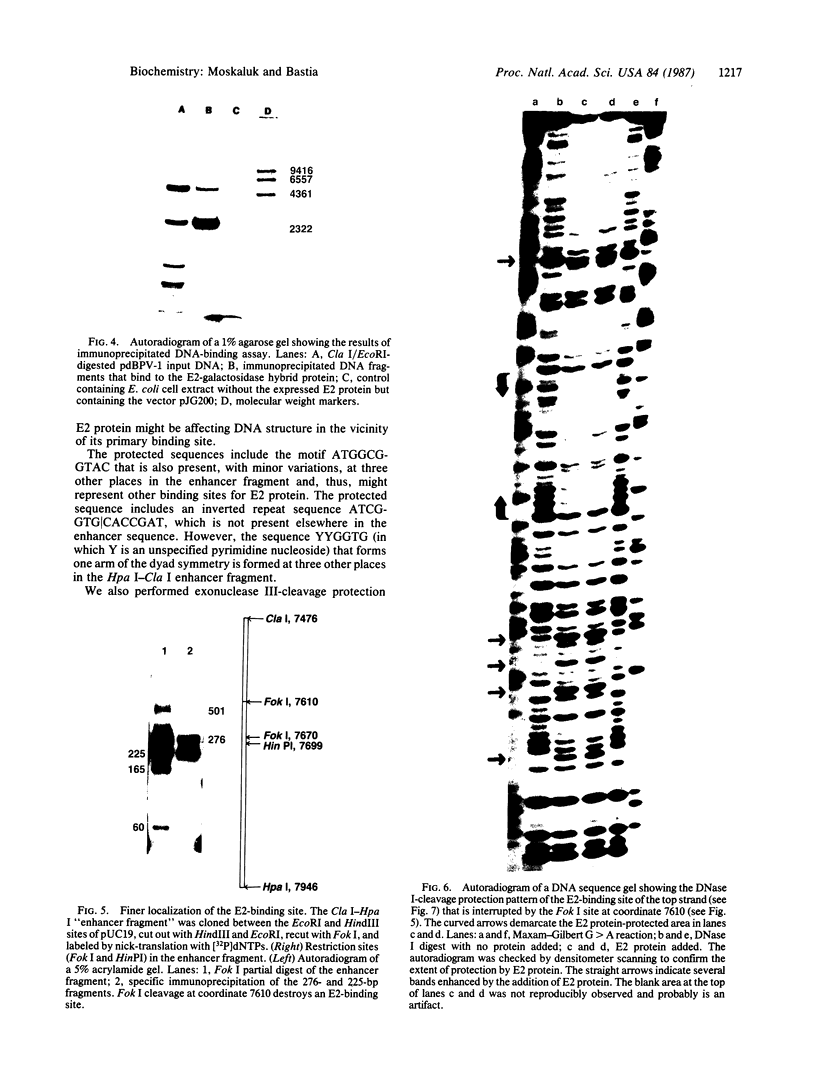
The E2 early open reading frame (presumably gene) of bovine papillomavirus-1 was fused in frame with the collagen-beta-galactosidase-encoding region of the vector pJG200 and was expressed in and partially purified from Escherichia coli. The hybrid protein specifically bound to the enhancer region of bovine papillomavirus at several sites. DNase I-cleavage protection analysis of one such site revealed the protected sequence. A comparison of the protected sequence with the remainder of the DNA sequences that also have affinity for the protein revealed a consensus sequence having the motif AATTGGCGGNNCG, in which N is any nucleotide. The protected region also includes a sequence with 2-fold rotational symmetry--ATCGGTG/CACCGAT.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg L. J., Singh K., Botchan M. Complementation of a bovine papilloma virus low-copy-number mutant: evidence for a temporal requirement of the complementing gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):859–869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P., Bedouelle H., Winter G. Improved oligonucleotide site-directed mutagenesis using M13 vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4431–4443. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Howley P. M., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H. The primary structure and genetic organization of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 genome. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):529–534. doi: 10.1038/299529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Engel L. W., Chen E. Y., Yaniv M., Howley P. M. Comparative analysis of the human type 1a and bovine type 1 papillomavirus genomes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):557–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.557-566.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino J., Bastia D. Rapid purification of a cloned gene product by genetic fusion and site-specific proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4692–4696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino J., Bastia D. The replication initiator protein of plasmid R6K tagged with beta-galactosidase shows sequence-specific DNA-binding. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Schenborn E. T., Lund E., Byrne J. C., Dahlberg J. E. The bovine papillomavirus distal "enhancer" is not cis essential for transformation or for plasmid maintenance. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3310–3315. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Sharp P. A. Transcription control by oncogenes. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko J. L., Dalie B. L., Goldman E., Harter M. L. Adenovirus-2 early region IA protein synthesized in Escherichia coli extracts indirectly associates with DNA. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1645–1651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. DNA-binding site of major regulatory protein alpha 4 specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster W. D. Apparent lack of integration of bovine papillomavirus DNA in virus-induced equine and bovine tumor cells and virus-transformed mouse cells. Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Howley P. M. Mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus contain only extrachromosomal viral DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2727–2731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Law M. F., Engel L., Howley P. M. In vitro tumorigenic transformation by a defined sub-genomic fragment of bovine papilloma virus DNA. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):72–74. doi: 10.1038/287072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Berg L., Weiher H., Botchan M. Bovine papilloma virus contains an activator of gene expression at the distal end of the early transcription unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1108–1122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Genetic analysis of bovine papillomavirus type 1 trans-acting replication factors. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):955–965. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.955-965.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Transactivation of a bovine papilloma virus transcriptional regulatory element by the E2 gene product. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]