Abstract
Acute hyperadrenergic stressor states are accompanied by cation dyshomeostasis, together with the release of cardiac troponins predictive of necrosis. The signal-transducer-effector pathway accounting for this pathophysiological scenario remains unclear. We hypothesized that a dyshomeostasis of extra- and intracellular Ca2+ and Zn2+ occurs in rats in response to isoproterenol (Isop) including excessive intracellular Ca2+ accumulation (EICA) and mitochondrial [Ca2+]m-induced oxidative stress. Contemporaneously, the selective translocation of Ca2+ and Zn2+ to tissues contributes to their fallen plasma levels. Rats received a single subcutaneous injection of Isop (1 mg/kg body wt). Other groups of rats received pretreatment for 10 days with either carvedilol (C), a β-adrenergic receptor antagonist with mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter-inhibiting properties, or quercetin (Q), a flavonoid with mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant properties, before Isop. We monitored temporal responses in the following: [Ca2+] and [Zn2+] in plasma, left ventricular (LV) apex, equator and base, skeletal muscle, liver, spleen, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), indices of oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses, mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening, and myocardial fibrosis. We found ionized hypocalcemia and hypozincemia attributable to their tissue translocation and also a heterogeneous distribution of these cations among tissues with a preferential Ca2+ accumulation in the LV apex, muscle, and PBMC, whereas Zn2+ declined except in liver, where it increased corresponding with upregulation of metallothionein, a Zn2+-binding protein. EICA was associated with a simultaneous increase in tissue 8-isoprostane and increased [Ca2+]m accompanied by a rise in H2O2 generation, mPTP opening, and scarring, each of which were prevented by either C or Q. Thus excessive [Ca2+]m, coupled with the induction of oxidative stress and increased mPTP opening, suggests that this signal-transducer-effector pathway is responsible for Isop-induced cardiomyocyte necrosis at the LV apex.
Keywords: catecholamines, mitochondria, oxidative stress, fibrosis
patients hospitalized with acute bodily injury often present with ionized hypocalcemia and hypozincemia, together with elevated plasma catecholamines and parathyroid hormone (15, 17–20, 22, 24, 26, 29, 38). The degree of these disturbances is related to the extent of injury and therefore serves as a prognostic marker. The accompanying hyperadrenergic state can be associated with elevation in plasma cardiac troponins, indicative of cardiomyocyte necrosis (10, 28, 54). Pathophysiological responses invoked by an acute stressor state involving the signal-transducer-effector pathway mechanistically account for the dyshomeostasis of Ca2+ and Zn2+, serving as prooxidant and antioxidant, respectively, and appearance of cardiomyocyte necrosis, all of which are the focus of our ongoing investigative effort.
In rats with an acute hyperadrenergic state induced by isoproterenol (Isop), a synthetic catecholamine, Rona et al. (55) reported on cardiomyocyte necrosis and the unusual propensity of the left ventricular (LV) apex to develop more extensive necrosis relative to its equator or base. Later, Fleckenstein and coworkers (30, 31) characterized the catecholamine-induced intracellular Ca2+ overloading as the signal-transduction pathway initiating cardiomyocyte necrosis and predicted that associated mitochondrial dysfunction with reduced ATP synthetic activity is responsible for consequent cardiotoxicity. Subsequent studies have demonstrated that intracellular Ca2+ overloading is coupled to induction of oxidative stress and serves as a transducer in the involved myocardium, where the rate of reactive oxygen species generation overwhelms the rate of their elimination by endogenous antioxidant defenses that include a rise in intracellular free Zn2+ concentration ([Zn2+]i) (21, 46, 49).
In addition to cardiac-related pathophysiology of a hyperadrenergic state that accompanies bodily injury, there is a systemic response involving diverse tissues, such as skeletal muscle, liver, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC; lymphocytes and monocytes), which includes intrinsically coupled Ca2+ and Zn2+ dyshomeostasis (1, 18–20, 65).
On the basis of these cumulative findings, we hypothesized that, in rats with Isop-induced acute stressor state, a dyshomeostasis of extra- and intracellular Ca2+ and Zn2+ ensues in the myocardium and systemic tissues. In the heart, excessive intracellular Ca2+ accumulation (EICA) and consequent increased mitochondrial [Ca2+]m preferentially target the endocardium of the LV apex, leading to the induction of oxidative stress and opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pores (mPTP). A simultaneous fall in Zn2+ may exacerbate this oxidative stress because of its critical role in the activity of Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase. The ensuing necrosis of cardiomyocytes results in a reparative fibrosis at this site. In our experiments, two groups of age- and sex-matched rats also received pretreatment with either carvedilol, a β-adrenergic receptor antagonist with mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter inhibitor properties, or quercetin, a naturally occurring flavonoid found in fruit with mitochondrial antioxidant properties. In a series of strategically designed targeted interventions described in materials and methods, we monitored and contrasted plasma and tissue levels of Ca2+ and Zn2+, regions of LV that included its apex, equator, and base, skeletal muscle, PBMC, liver, and spleen, together with indices of oxidative stress, antioxidant defenses, and mPTP opening of subsarcolemmal cardiac mitochondria to elucidate the mechanism(s) of action at play for these observed iterations.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animal Model
Eight-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats were used throughout this series of experiments approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center. Untreated age- and sex-matched rats served as controls. Treatment consisted of rats given Isop (1 mg/kg) as a single subcutaneous injection. According to the specific aims of our studies, rats were killed at various time points (vide infra) following Isop treatment. Two separate groups of rats received pretreatment with either carvedilol (5 mg/kg per day) or quercetin (25 mg/kg per day), given by gavage once daily for 10 days before Isop injection.
Experimental Protocol
To test our hypothesis, a series of sequential interventions were carried out, and major findings are summarized herein. First, we examined the accumulation and distribution of Ca2+ that appeared within the heart at 8 h after Isop treatment, including the base, equator, and apex of the LV. This study demonstrated the preferential Ca2+ overloading in the LV apex compared with other regions. Thereafter, our follow-up studies focused on the LV apex only.
We next addressed the temporal responses in tissue Ca2+ and Zn2+ in plasma, LV apex, skeletal muscle (rectus femoris), PBMC, liver, and spleen at 2, 4, 8, and 24 h and at 7 days after Isop treatment. We also addressed the perturbations in prooxidant:antioxidant equilibrium present in LV apex and muscle at these time points on the basis of respective rise in 8-isoprostane and levels of total antioxidant capacity.
Third, and having identified LV apex as the site of predominant intracellular Ca2+ overloading and inferring that 2 h after Isop treatment coincided with the onset of cardiomyocyte necrosis (9), we focused our attention only to this time point and the apical region of the LV for the isolation of subsarcolemmal cardiac mitochondria to determine their responses in [Ca2+]m and mPTP opening.
Finally, two subgroups of rats received either carvedilol or quercetin as pretreatment before Isop administration to address the specific impact of these mechanistically targeted interventions on mitochondrial free [Ca2+]m and mPTP opening at 2 h after Isop.
Plasma Ionized Calcium and Plasma Zinc
Plasma ionized [Ca2+]o was measured by direct ion-selective electrode technique using a Nova 8 Analyzer (Nova Biomedical, Waltham, MA) and expressed in mmol/l as we previously reported (23, 64). Plasma total Zn2+ was measured by atomic absorption spectroscopy and expressed in μg/dl as we previously reported (5, 11).
Tissue Calcium and Zinc
Total Ca2+ and Zn2+ contents in heart, skeletal muscle, liver, and spleen were measured using atomic absorption spectroscopy as we previously reported (43, 62) and expressed as nEq/mg fat-free dry tissue (FFDT) and ng/mg FFDT, respectively.
PBMC were isolated, and their cytosolic free [Ca2+]i concentration in nM was measured using a ratiometric method and fluorescent molecular probe Fura-2 (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) as we previously reported (3, 4, 23). PBMC cytosolic-free [Zn2+]i concentration in nM was measured by flow cytometry (BD FACS Calibur; Becton Dickson, Franklin Lakes, NJ) using a Zn2+-specific probe (FluoZin3; Invitrogen, Eugene, OR) according to Hasse et al. (37) and as we previously reported (3, 4, 23).
Differential and regional heterogeneity in cardiac tissue Ca2+ and Zn2+ distribution were addressed by sectioning the LV transversely into three coronal sections representing the base, equator, and apex with each LV section further subdivided to distinguish between epicardium and endocardium.
Metallothionein-1 Expression
Metallothionein-1 (MT-1) protein levels in heart and liver were measured by Western blot as previously reported (62). The relative abundance of protein present was measured by a computer image analysis system (NIH Image, version 1.6).
Oxidative Stress: Prooxidants
Total 8-isoprostane.
This biomarker of lipid peroxidation (free and esterified) was measured in plasma, heart, skeletal muscle, and PBMC from control rats and those after Isop treatment using a competitive enzyme immunoassay kit (Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI) as we previously reported (32).
H2O2 production.
The H2O2 generation within mitochondria, stimulated by succinate, was monitored using the Amplex Red (Invitrogen) protocol of Mohanty et al. (50) as we previously reported (43).
Oxidative Stress: Antioxidants
Total antioxidant capacity.
The total antioxidant capacity found in plasma, heart, and skeletal muscle was measured using a commercially available reagent kit (Cayman Chemical) as we previously reported (41).
Isolation of Cardiac Mitochondria
Subsarcolemmal cardiac mitochondria were isolated from the LV apex by differential centrifugation of whole myocardial homogenates. The purity of mitochondrial preparation was assessed by flow cytometry and mitochondria-specific dye, Mito Tracker Red (Invitrogen), as we previously reported (32). Given the paucity of mitochondrial population density in endothelial and smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts, we presume that these cells may contribute as a very miniscule source of contamination, if any.
Mitochondrial Free [Ca2+]m and Total [Zn2+]m
Free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]m) in cardiac mitochondria was determined by ratiometric method using Fura-2 and expressed in nM as we previously reported (3, 4). Mitochondrial total Zn2+ concentration ([Zn2+]m) was determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy as we previously reported (64).
mPTP Opening
Opening potential of the mPTP was stimulated by Ca2+-induced swelling of isolated cardiac mitochondria and measured according to Baines et al. (6) with the addition of 40 μl of 200 μM CaCl2, thus providing a reproducible and stable decline in mitochondrial optical density as we previously reported (41). This decrease in optical density measured by change in absorption at 560 nm was completely prevented by preincubation of the organelles with 30 nM cyclosporine A, thus confirming the specificity of our mPTP opening assay, as previously reported.
Cardiac Pathology
The presence of myocardial scarring, a footprint of cardiomyocyte necrosis, was elucidated in hearts harvested at 7 days after Isop treatment using a collagen-specific picrosirius red stain applied to coronal sections (6 μm) of the ventricles and examined by light microscopy as previously reported (61).
Statistical Analysis
Group data are presented as means ± SE. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA in SPSS software (version 18.0; SPSS, Chicago, IL). Multiple-group comparisons were made by Scheffé's F-test. Significant differences between individual group means were assigned for P values <0.05.
RESULTS
Regional Responses in Cardiac Tissue Ca2+ and Zn2+ After Isoproterenol
Tissue Ca2+.
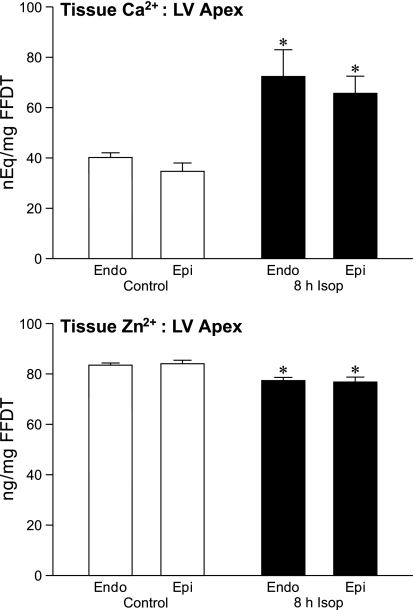
We examined myocardial Ca2+ and Zn2+ concentrations in different regions of the rat myocardium in control tissue and those occurring at 8 h of Isop treatment. This included the LV, further subdivided into its basal, equatorial, and apical segments, and in their corresponding epi- and endocardial regions. As seen in the control tissue in Fig. 1 (top), there was no significant difference in baseline Ca2+ concentration between the LV apex and its endo- and epicardium. Furthermore, there were no differences between the endo- and epicardium of the LV apex and its equator or base.
Fig. 1.
Tissue Ca2+ and Zn2+ from the left ventricular (LV) apex for endocardium (endo) and epicardium (epi) found in control hearts and those harvested 8 h following isoproterenol (Isop) injection. *P < 0.05 vs. controls. FFDT, fat-free dry tissue.
At 8 h after Isop treatment, a marked rise (P < 0.01) in tissue Ca2+ was seen in the LV apex contrasting to the LV equator and base. In the endocardium of LV apex tissue, Ca2+ rose significantly, as was the case for the apical epicardium, whereas tissue Ca2+ concentrations at the endo- and epicardium of the LV equator and base remained unaltered from control levels after Isop treatment.
Tissue Zn2+.
In contrast to Ca2+ overloading of the LV apex that appeared at 8 h after Isop, a decline (P < 0.01) in tissue Zn2+ occurred at this site (see Fig. 1, bottom). In control tissue, Zn2+ concentrations did not differ between the LV apex and its endo- or epicardium or the LV equator and LV base. At 8 h following Isop, however, tissue Zn2+ fell (P < 0.01) in the apical LV endocardium (P < 0.01) and epicardium. In contrast, tissue Zn2+ levels found at the endo- and epicardium of the LV equator and base remained unchanged from control levels after Isop treatment.
Temporal Responses in Ca2+ and Zn2+ Dyshomeostasis After Isoproterenol
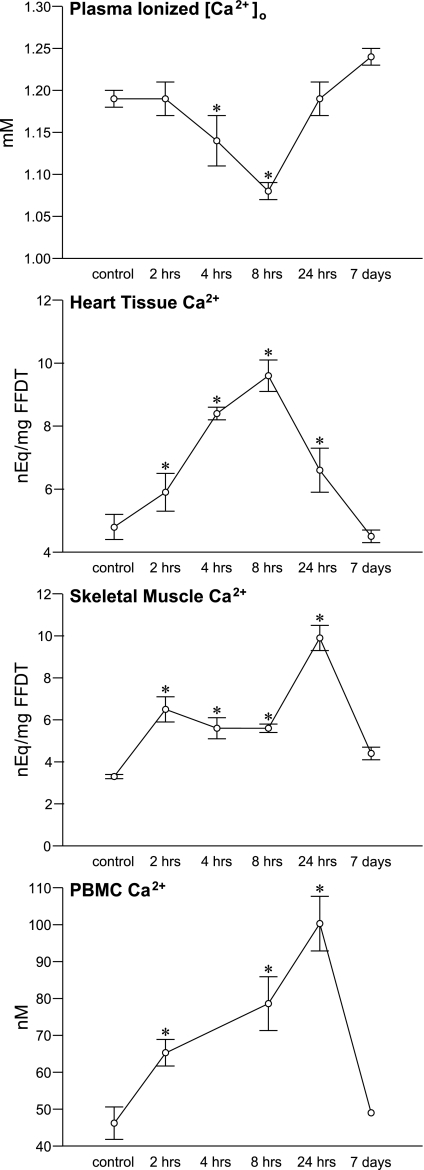
As seen in Fig. 2 (top) and compared with controls, plasma ionized [Ca2+]o was unchanged at 2 h, but fell (P < 0.05) at 4 h after Isop and continued to fall at 8 h before returning to control levels at 24 h and 7 days. This early and significant ionized hypocalcemia was coupled to the precipitous hypozincemia (see Fig. 3) that appeared at 4 h compared with control levels and remained subnormal at 8 h before returning to control levels at 24 h and 7 days.
Fig. 2.
The temporal responses in plasma ionized [Ca2+]o and tissue Ca2+ for the LV apex, skeletal muscle, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) at 2, 4, 8, and 24 h and 7 days after a single subcutaneous dose of isoproterenol. *P < 0.05 vs. controls.
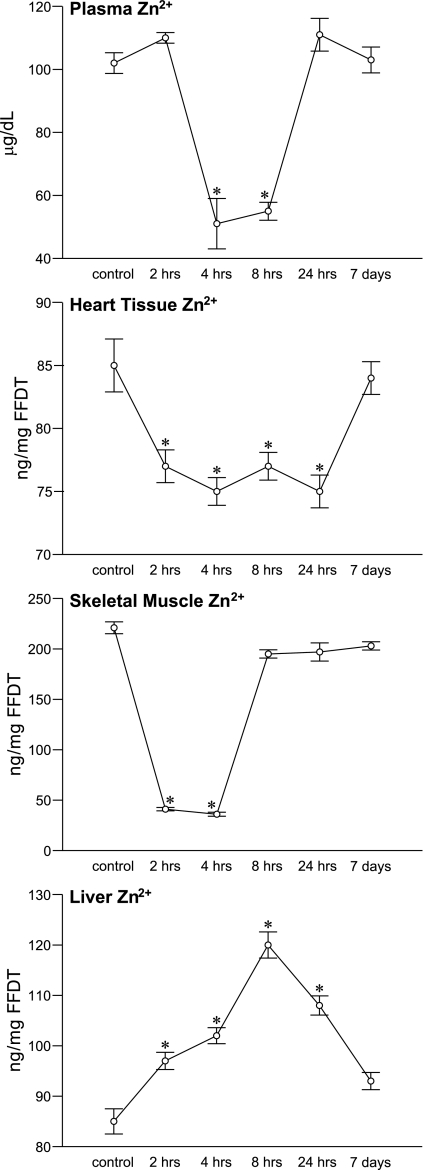
Fig. 3.
The temporal responses in plasma Zn2+ and tissue Zn2+ for the LV apex, skeletal muscle and liver after isoproterenol administration. *P < 0.05 vs. controls.
In LV apical tissue, a marked rise (P < 0.0001) in Ca2+ above controls was found at 2 and 4 h, reaching a peak at 8 h, thereafter declining at 24 h and returning to control levels at 7 days.
Contemporaneous to Ca2+ overloading of the LV apex, a progressive rise (P < 0.05) in tissue Ca2+ appeared in skeletal muscle and PBMC at 2 h and continued thereafter over 24 h before returning to control levels at 7 days (see Fig. 2). In rectus femoris tissue, total tissue Ca2+ rose (P < 0.0001) above control levels at 2 h and reached a peak at 24 h, thereafter returning to control levels at 7 days. In PBMC, cytosolic free [Ca2+]i was elevated (P < 0.01) above control levels at 2 h, continuing to rise at 8 h and reaching a peak at 24 h. No significant change in tissue Ca2+ content was found either in the liver or spleen over the various time points (data not shown).
Unlike the rise in total Ca2+ concentration that appeared in multiple tissues and likely accounted for ionized hypocalcemia following Isop treatment, the precipitous hypozincemia that appeared was associated with a variable response in total tissue Zn2+ concentration (see Fig. 3). A fall in tissue Zn2+ was seen in the heart over 24 h and in muscle over 4 h. In LV apex, tissue Zn2+ decreased from controls at 2 and 4 h and remained equally low at 8 and 24 h before returning to control levels at 7 days. The fall in skeletal muscle Zn2+ was even more marked, declining from control levels and then slowly returning to normal range by 7 days.
In contrast, there was a progressive increase in liver Zn2+ over 24 h rising from control levels at 2 and 4 h and reaching a peak at 8 h before declining at 24 h and falling to near control levels at 7 days. This hepatospecific sequestration of Zn2+ to the liver was accompanied by an increased hepatic upregulation of MT-1, a Zn2+-binding protein, before returning to basal levels at 7 days. Corresponding change in the MT-1 expression was not found in the heart at any time point. Splenic tissue Zn2+ was unchanged following Isop over the course of the study (data not shown), whereas cytosolic free Zn2+ concentration in PBMC increased at 2 h before returning to control levels, and it remained there thereafter.
Prooxidant: Antioxidant Responses After Isop
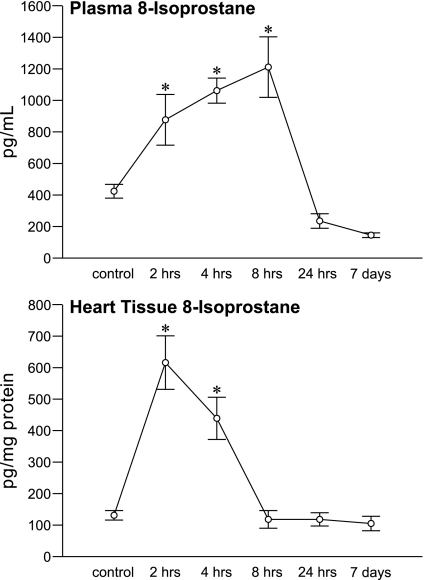
Figure 4 depicts the results on total 8-isoprostane for plasma and heart. A marked rise (P < 0.0001) in cardiac tissue 8-isoprostane occurred at 2 h and remained elevated at 4 h before returning to controls levels at 8 and 24 h and 7 days. This sudden burst in oxidative stress in the heart virtually mirrored the rise in cardiac tissue Ca2+ seen at 2 and 4 h (see Fig. 2) and the continuing fall in cardiac Zn2+ that was present over 24 h (see Fig. 3). A contemporaneous rise (P < 0.05) in muscle 8-isoprostane levels was also seen at 2 and 4 h and in PBMC at 2 h before each returned to control values. The rapid induction of oxidative stress in these multiple tissues led to a temporal and progressive rise (P < 0.001) in plasma 8-isoprostane at 2, 4, and 8 h after Isop compared with controls (see Fig. 4) and returned to basal values at 24 h and 7 days.
Fig. 4.
The temporal responses for 8-isoprostane in plasma and LV apical tissue after isoproterenol administration. *P < 0.05 vs. controls.
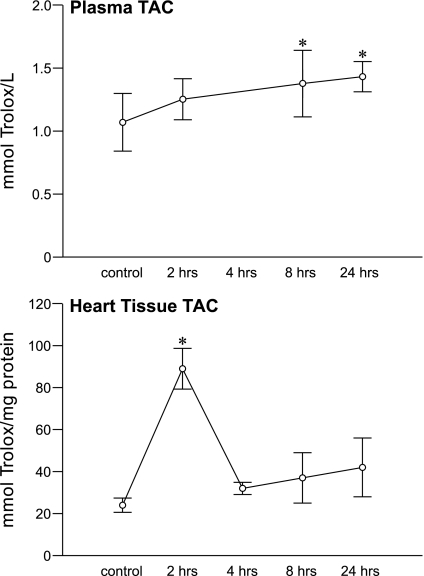
Total antioxidant capacity embodies cumulative antioxidant defenses derived from nonenzymatic low molecular weight antioxidants and vitamins A, C, and E. The response in this biomarker in plasma and heart is shown in Fig. 5, in which a sustained rise (P < 0.05) in these antioxidant defenses was found in both tissue over the course of 24 h.
Fig. 5.
The temporal responses in total antioxidant capacity (TAC) for plasma and LV apical tissue after isoproterenol administration. *P < 0.05 vs. controls.
Cardiac Pathology
In hearts harvested 7 days after Isop treatment, the appearance of myocardial fibrosis was evident within the LV, in which it appeared primarily within the endocardium of the LV apex (not shown). These findings are consistent with those reported by others (9, 13, 36, 40).
Mitochondrial Free [Ca2+]m and Total [Zn2+]m
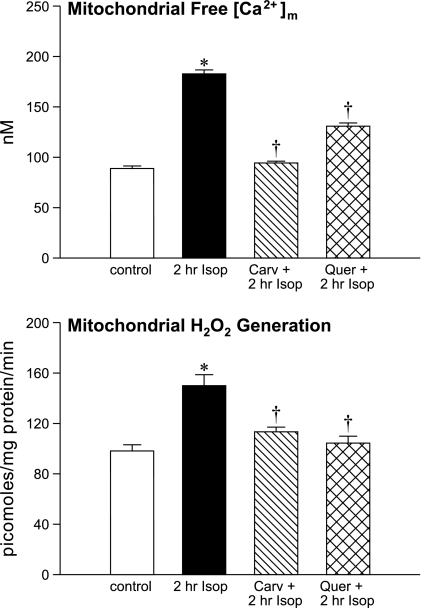
At 2 h after Isop treatment, [Ca2+]m rose (P < 0.01) from control levels (see Fig. 6, top), whereas mitochondrial [Zn2+]m remained unchanged (not shown).
Fig. 6.
Responses in cardiac mitochondrial free [Ca2+]m and H2O2 generation in organelles harvested from the LV apex of controls, 2 h after Isop treatment alone, or at 2 h Isop treatment combined with pretreatment using either carvedilol (Carv) or quercetin (Quer). *P < 0.05 vs. controls; †P < 0.05 vs. 2 h Isop.
Mitochondrial 8-Isoprostane and H2O2 Production
The rise in [Ca2+]m at 2 h after Isop treatment was accompanied by increased (P < 0.005) mitochondrial 8-isoprostane levels compared with controls.
As seen in Fig. 6, (bottom), succinate-stimulated mitochondrial H2O2 generation was increased (P < 0.05) from control levels following Isop.
Ten days of pretreatment with either carvedilol or quercetin before Isop administration attenuated (P < 0.01) both the rise in [Ca2+]m and H2O2 production that followed in these organelles harvested from the LV apex (see Fig. 6).
mPTP Opening
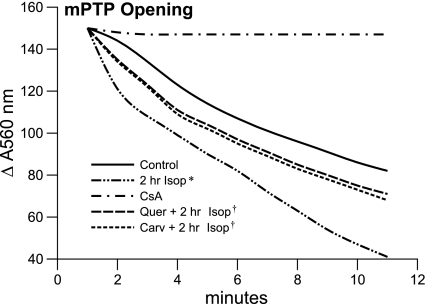
In cardiac mitochondria harvested from the LV apex in control tissue and 2 h after Isop treatment, opening of a nonspecific pore in the inner mPTP is followed by an abnormal and abrupt rise in permeability to solutes (molecular weight <1,500 Da) and osmotic swelling. This was assessed by the reduction in absorbance, measured spectrophotometrically at 560 nm, and with pore opening induced by 40 μl of 200 μM CaCl2. The response in mPTP opening is shown in Fig. 7 for mitochondria harvested from the LV apex in control tissue and after 2 h Isop treatment alone. As presented, there is an increase in mPTP opening in response to this hyperadrenergic state (ΔA560 118.0 ± 3.6) compared with 70.1 ± 2.3 in controls, whereas this propensity to mPTP opening was attenuated by pretreatment with either carvedilol or quercetin.
Fig. 7.
Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening potential of cardiac mitochondria harvested from the LV apex of controls, 2 h after Isop treatment, or 2 h Isop treatment together with either Carv or Quer pretreatment. The abrupt rise in mitochondrial permeability to solutes and ensuing osmotic swelling is assessed by the reduction in absorbance measured spectrophotometrically at 560 nm following mPTP opening induced by CaCl2. *P < 0.05 vs. controls; †P < 0.05 vs. 2 h Isop. CsA, cyclosporine A.
DISCUSSION
Our study led to several major findings. First, the acute stressor state induced in young adult male Sprague-Dawley rats by a single subcutaneous dose of the synthetic catecholamine, Isop, was accompanied by a dyshomeostasis of extra- and intracellular Ca2+ and Zn2+ involving diverse tissues. In plasma, the appearance of ionized hypocalcemia and hypozincemia was concordant with each appearing within 4 h and remaining subnormal for 8 h before returning to control levels at 24 h and 7 days. The presence of ionized hypocalcemia would inevitably provoke the parathyroid glands to secrete parathyroid hormone, which we documented to be the case throughout weeks 1–4 of aldosterone/salt treatment (23). As we and others have shown, this calcitropic hormone promotes intracellular Ca2+ overloading (see Fig. 8) (23, 59, 64). We envisaged that the single subcutaneous dose of Isop would quickly raise its plasma concentration, peaking within 20 min and lasting over 60 min or less, thereafter rapidly metabolizing within the liver by catechol-O-methyltransferase and monoamine oxidase (39). However, metabolites of Isop may remain active for longer duration. As we have demonstrated with plasma concentrations of Ca2+ and Zn2+ and with their temporal responses within the heart and systemic tissues (vide infra), the carryover effects to this hyperadrenergic burst appeared to have lasted for 24 h, at the very least.
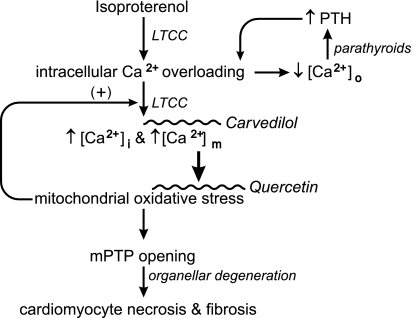
Fig. 8.
A schematic representation of the signal-transducer-effector pathway leading to cardiomyocyte necrosis and replacement fibrosis of myocardium following a single subcutaneous dose of isoproterenol given to simulate an acute hyperadrenergic stressor state. Catecholamine-induced intracellular Ca2+ overloading, expressed via increased Ca2+ entry through l-type Ca2+ channels (LTCC), leads to the rise in cytosolic [Ca2+]i and mitochondrial [Ca2+]m that contribute to an associated fall in plasma ionized [Ca2+]o. Ionized hypocalcemia provokes the Ca2+-sensing receptor of the parathyroid glands to promote the secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH). This calcitropic hormone further contributes to intracellular Ca2+ overloading. The excessive accumulation of [Ca2+]m accounts for the induction of oxidative stress in these organelles and increased opening potential of their inner membrane mPTP. The ensuing osmotic swelling and degeneration of these organelles, coupled with the loss of ATP synthesis, perpetuates cardiomyocytes necrosis and consequent replacement fibrosis, or scarring of myocardium. Reactive oxygen species further contribute to intracellular Ca2+ entry via LTCC.
Second, the perturbations in Ca2+ and Zn2+ that followed Isop treatment differed considerably among the tissues examined. In myocardium, there was a discordance in which a preferential accumulation of Ca2+ occurred within the LV apex (vis-à-vis the LV equator and base), whereas the tissue Zn2+ content declined and remained subnormal for 24 h. This regional heterogeneity to intracellular Ca2+ accumulation that favors apical LV tissue is likely predestined by the high abundance of β1-adrenergic receptors present at this site and not attributable to a differential expression of l-type Ca2+ channels (34, 45, 51). An alternate explanation would suggest the binding affinity for β1 receptors is greater at the LV apex (63). In either scenario, we would speculate that this difference in β1 receptor density or affinity innately relates to the sequence of depolarization that occurs within the LV, involving apical to basal activation, with the concordant contraction and torsion (twisting) of myocardium along the vertical axis contributing to the efficient emptying and propulsion of blood from its chamber into the aorta (14, 56, 57).
In the case of skeletal muscle and liver, Ca2+ and Zn2+ responses were discordant with respect to one another. Total tissue Ca2+ rose in rectus femoris, a fast-twitch muscle, soon after Isop and remained so for 24 h, whereas the Zn2+ levels fell at 2 and 4 h before returning to control levels. In this context, slow-twitch muscles (e.g., soleus) are considered less susceptible to catecholamine-induced injury than fast-twitch muscles (16, 52). The temporal translocation of Ca2+ from blood to these tissues accounts for the early appearance of ionized hypocalcemia. Oxidative stress in skeletal muscle is manifested with mitochondrial Ca2+ overloading and myocyte necrosis associated with EICA, whether attributable to catecholamines, muscular dystrophy, prolonged ischemia, or electrical trauma (12, 16, 31, 35, 52). In liver, a conservation of Zn2+ and progressive rise in hepatic Zn2+ concentrations occurred, accounting for hypozincemia and in accordance with the upregulation of the Zn2+-binding protein MT-1 seen in other acute stressor states (8, 44, 66). Liver serves as a storage site for Zn2+, which becomes a repository when needed for wound healing (58). A persistent rise in [Ca2+]i was noted in PBMC over 24 h after Isop treatment. Intracellular Ca2+ overloading of PBMC mirrors that seen in the LV apex, raising the prospect that these cells could be monitored as a novel noninvasive surrogate biomarker for Ca2+ levels in heart tissue.
Third, the EICA associated with Isop-induced injury was accompanied by the induction of oxidative stress and early (2 hrs) rise in 8-isoprostane found in such diverse tissues as the LV apex, skeletal muscle, and PBMC, which contributed to the rise in plasma levels of this endogenous biomarker of lipid peroxidation. Also contributory to the appearance of oxidative stress, when the rate of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species overwhelm their rate of elimination by endogenous antioxidant defenses, including the increment in total antioxidant capacity of tissues, was the contemporaneous decline in tissue Zn2+ in heart, muscle, and plasma. The fall in cardiac tissue Zn2+ we observed in response to Isop has also been reported by others (2, 48). Intracellular Zn2+, acting as an antioxidant, is essential to the activity of Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase, a metalloenzyme integral to these defenses and degradation of cytotoxic oxygen-rich intermediaries that appear in these tissues in response to intracellular Ca2+ overloading. The fall in cardiac tissue Zn2+ following Isop treatment contrasted to its rise in Zn2+ in cardiomyocytes that occurs in response to ischemia/reperfusion and the appearance of chronic stressor state associated with aldosterone/salt treatment (21, 32, 43, 46, 49). This begs the question whether supplemental Zn2+ would be clinically useful if given soon after the acute hyperadrenergic state is set in motion following bodily injury. Relative to the heart, we do not believe this to be the case given that the activity of Zn2+ transporters needed for Zn2+ entry and intracellular Zn2+ accumulation would be lost to cardiomyocyte necrosis. This contrasts to ZnSO4 supplement given as pretreatment before Isop (25) or with the salutary responses to this supplement when given to prevent the chronic cardiotoxicity associated with diabetes or aldosterone/salt treatment (32, 42, 60). Finally, the rise in total antioxidant capacity found in heart and plasma, including those derived from vitamins A, C, and E, was not adequate to prevent the appearance of oxidative stress over the 24 h that followed Isop treatment.
The predilection for cardiac injury and myocardial scarring following Isop that involves the LV apex is related to a preferential Ca2+ overloading at this site. This importantly includes increased mitochondrial free [Ca2+]m and the associated induction of oxidative stress by these organelles, demonstrated by their increased H2O2 generation and 8-isoprostane concentration, leading to consequent mPTP opening and ensuing cardiomyocyte necrosis. In attenuating mitochondrial Ca2+ accumulation with carvedilol or mitochondrial oxidative stress with quercetin, the greater propensity for mPTP opening in response to Isop could be largely attenuated. Furthermore, when quercetin binds to Zn2+, forming a flavonoid-metal complex, it is an even more potent antioxidant than free quercetin (27). We would suggest that these responses represent a crucial pathophysiological overview confirming that this signal-transducer-effector pathway (see Fig. 8) preferentially begets cytotoxicity at the LV apex in response to hyperadrenergic stressor state.
It is intriguing to speculate on the relevance of this pathway in leading to the predilection for hypokinesia of the apical segment of LV myocardium, which has been clinically termed apical ballooning, “broken heart,” ampulla, or takotsubo cardiomyopathy that accompanies the hyperadrenergic state seen with profound emotional stress, pheochromocytoma, or dobutamine-stress echocardiography (33, 47, 67). In this context, carvedilol has been used to effectively treat apical ballooning cardiomyopathy (53).
Our study of the acute hyperadrenergic stressor state induced by Isop and assessment of Ca2+ and Zn2+ dyshomeostasis and oxidative stress that appeared in the heart and systemic organs could be explored to further address other pertinent issues. For example, we did not specifically monitor stressor signaling pathways, such as the mitogen-activated kinases (p38MAPK, JNK and ERK), in each of these tissues. This family of enzymes will relay and propagate external stimuli using phosphorylation cascades to generate coordinated and adaptive cellular responses that target downstream substrates, such as redox-sensitive nuclear transcription factor (NF)-κB and the proinflammatory cytokines it regulates. In response to acute burn injury, p38MAPK activation importantly contributes to cytokine-mediated organ injury (7). In future studies, it will be important to critically examine and address many of these relevant issues, including their responses to targeted pharmacological interventions.
In summary, we demonstrated that a dyshomeostasis of Ca2+ and Zn2+ occurs in the heart and systemic tissues of rats in response to an acute hyperadrenergic stressor state induced by a single dose of Isop in which pathophysiological derangements persisted for many hours. In plasma, Ca2+ and Zn2+ responses were concordant, whereas in tissues these were both discordant and persistent. Within the heart the EICA was heterogeneous, favoring the LV apex (vis-à-vis the LV equator and base), whereas the total tissue Zn2+ levels fell early and remained subnormal over 24 h. Liver, on the other hand, with its upregulation of MT-1 served as a strategic repository for Zn2+. The Ca2+ overloading of heart, muscle, and PBMC was accompanied by the contemporaneous appearance of oxidative stress and the concordant rise in endogenous total antioxidant capacity although it was insufficient to completely abrogate cardiotoxicity. In mitochondria harvested from the LV apex, Ca2+ overloading was accompanied by increased H2O2 generation and opening potential of mPTP, resulting in myocardial necrosis and subsequent scarring. These iterations in mitochondrial Ca2+ and their corresponding pathological redox state could each be prevented by cotreatment with either carvedilol or quercetin.
We therefore would suggest that signal-transducer-effector pathway, leading to LV apical injury and scarring of the endocardium in response to catecholamine excess, involves Ca2+ overloading of cardiac mitochondria, induction of oxidative stress, and increased opening potential of their inner membrane mPTP.
GRANTS
This work was supported, in part, by NIH grants R01-HL73043 and R01-HL90867 (K. T. Weber).
DISCLOSURES
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The contents of this article are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
REFERENCES
- 1. Agay D, Anderson RA, Sandre C, Bryden NA, Alonso A, Roussel AM, Chancerelle Y. Alterations of antioxidant trace elements (Zn, Se, Cu) and related metallo-enzymes in plasma and tissues following burn injury in rats. Burns 31: 366–371, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Ahmad M, Salahuddin Mathew BM, Kumar S, Seth TD, Hasan MZ, Mahdi SQ. Effect of extent of myocardial damage on the behavior of myocardial zinc in albino rats. Adv Myocardiol 2: 171–176, 1980 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Ahokas RA, Sun Y, Bhattacharya SK, Gerling IC, Weber KT. Aldosteronism and a proinflammatory vascular phenotype. Role of Mg2+, Ca2+ and H2O2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Circulation 111: 51–57, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Ahokas RA, Warrington KJ, Gerling IC, Sun Y, Wodi LA, Herring PA, Lu L, Bhattacharya SK, Postlethwaite AE, Weber KT. Aldosteronism and peripheral blood mononuclear cell activation. A neuroendocrine-immune interface. Circ Res 93: e124–e135, 2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Arroyo M, LaGuardia SP, Bhattacharya SK, Nelson MD, Johnson PL, Carbone LD, Newman KP, Weber KT. Micronutrients in African-Americans with decompensated and compensated heart failure. Transl Res 148: 301–308, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Baines CP, Song CX, Zheng YT, Wang GW, Zhang J, Wang OL, Guo Y, Bolli R, Cardwell EM, Ping P. Protein kinase Cε interacts with and inhibits the permeability transition pore in cardiac mitochondria. Circ Res 92: 873–880, 2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Ballard-Croft C, White DJ, Maass DL, Hybki DP, Horton JW. Role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in cardiac myocyte secretion of the inflammatory cytokine TNF-α. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280: H1970–H1981, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Banni M, Messaoudi I, Said L, El Heni J, Kerkeni A, Said K. Metallothionein gene expression in liver of rats exposed to cadmium and supplemented with zinc and selenium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56: 513–519, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Benjamin IJ, Jalil JE, Tan LB, Cho K, Weber KT, Clark WA. Isoproterenol-induced myocardial fibrosis in relation to myocyte necrosis. Circ Res 65: 657–670, 1989 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Bertinchant JP, Polge A, Mohty D, Nguyen-Ngoc-Lam R, Estorc J, Cohendy R, Joubert P, Poupard P, Fabbro-Peray P, Monpeyroux F, Poirey S, Ledermann B, Raczka F, Brunet J, Nigond J, de la Coussaye JE. Evaluation of incidence, clinical significance, and prognostic value of circulating cardiac troponin I and T elevation in hemodynamically stable patients with suspected myocardial contusion after blunt chest trauma. J Trauma 48: 924–931, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Bhattacharya SK, Goodwin TG, Crawford AJ. Submicro determination of copper and zinc in needle biopsy-sized cardiac and skeletal muscles by atomic absorption spectroscopy using stoichiometric air-acetylene flame. Anal Lett 17: 1567–1591, 1984 [Google Scholar]
- 12. Bhattacharya SK, Johnson PL, Thakar JH. Reversal of impaired oxidative phosphorylation and calcium overloading in the skeletal muscle mitochondria of CHF-146 dystrophic hamsters. Mol Chem Neuropathol 34: 53–77, 1998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Brooks WW, Conrad CH. Isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury and diastolic dysfunction in mice: structural and functional correlates. Comp Med 59: 339–343, 2009 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Buchalter MB, Rademakers FE, Weiss JL, Rogers WJ, Weisfeldt ML, Shapiro EP. Rotational deformation of the canine left ventricle measured by magnetic resonance tagging: effects of catecholamines, ischaemia, and pacing. Cardiovasc Res 28: 629–635, 1994 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Burchard KW, Simms HH, Robinson A, DiAmico R, Gann DS. Hypocalcemia during sepsis. Relationship to resuscitation and hemodynamics. Arch Surg 127: 265–272, 1992 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Burniston JG, Ellison GM, Clark WA, Goldspink DF, Tan LB. Relative toxicity of cardiotonic agents: some induce more cardiac and skeletal myocyte apoptosis and necrosis in vivo than others. Cardiovasc Toxicol 5: 355–364, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Cander B, Dundar ZD, Gul M, Girisgin S. Prognostic value of serum zinc levels in critically ill patients. J Crit Care. In press. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Carlstedt F, Lind L, Joachimsson PO, Rastad J, Wide L, Ljunghall S. Circulating ionized calcium and parathyroid hormone levels following coronary artery by-pass surgery. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 59: 47–53, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Carlstedt F, Lind L, Rastad J, Stjernstrom H, Wide L, Ljunghall S. Parathyroid hormone and ionized calcium levels are related to the severity of illness and survival in critically ill patients. Eur J Clin Invest 28: 898–903, 1998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Carlstedt F, Lind L, Wide L, Lindahl B, Hänni A, Rastad J, Ljunghall S. Serum levels of parathyroid hormone are related to the mortality and severity of illness in patients in the emergency department. Eur J Clin Invest 27: 977–981, 1997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Chanoit G, Lee S, Xi J, Zhu M, McIntosh RA, Mueller RA, Norfleet EA, Xu Z. Exogenous zinc protects cardiac cells from reperfusion injury by targeting mitochondrial permeability transition pore through inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295: H1227–H1233, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Cherry RA, Bradburn E, Carney DE, Shaffer ML, Gabbay RA, Cooney RN. Do early ionized calcium levels really matter in trauma patients? J Trauma 61: 774–779, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Chhokar VS, Sun Y, Bhattacharya SK, Ahokas RA, Myers LK, Xing Z, Smith RA, Gerling IC, Weber KT. Hyperparathyroidism and the calcium paradox of aldosteronism. Circulation 111: 871–878, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Choi YC, Hwang SY. The value of initial ionized calcium as a predictor of mortality and triage tool in adult trauma patients. J Korean Med Sci 23: 700–705, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Chvapil M, Owen JA. Effect of zinc on acute and chronic isoproterenol induced heart injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol 9: 151–159, 1977 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Cvijanovich NZ, King JC, Flori HR, Gildengorin G, Wong HR. Zinc homeostasis in pediatric critical illness. Pediatr Crit Care Med 10: 29–34, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. de Souza RF, De Giovani WF. Synthesis, spectral and electrochemical properties of A1(III) and Zn(II) complexes with flavonoids. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 61: 1985–1990, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Deleu D, Kettern MA, Hanssens Y, Kumar S, Salim K, Miyares F. Neurogenic stunned myocardium following hemorrhagic cerebral contusion. Saudi Med J 28: 283–285, 2007 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Dickerson RN, Henry NY, Miller PL, Minard G, Brown RO. Low serum total calcium concentration as a marker of low serum ionized calcium concentration in critically ill patients receiving specialized nutrition support. Nutr Clin Pract 22: 323–328, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Fleckenstein A. [Metabolic problems in myocardium insufficiency]. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol 51: 15–30, 1967 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Fleckenstein A, Kanke J, Döring HJ, Leder O. Key role of Ca in the production of noncoronarogenic myocardial necroses. Recent Adv Stud Card Struct Metab 6: 21–32, 1975 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Gandhi MS, Deshmukh PA, Kamalov G, Zhao T, Zhao W, Whaley JT, Tichy JR, Bhattacharya SK, Ahokas RA, Sun Y, Gerling IC, Weber KT. Causes and consequences of zinc dyshomeostasis in rats with chronic aldosteronism. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 52: 245–252, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Gastwirth VG, Yang HS, Steidley DE, Scott RL, Chandrasekaran K. Dobutamine stress-induced cardiomyopathy in an orthotopic heart transplant patient. J Heart Lung Transplant 28: 968–970, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Gengo PJ, Sabbah HN, Steffen RP, Sharpe JK, Kono T, Stein PD, Goldstein S. Myocardial beta adrenoceptor and voltage sensitive calcium channel changes in a canine model of chronic heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 24: 1361–1369, 1992 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Gissel H. The role of Ca2+ in muscle cell damage. Ann NY Acad Sci 1066: 166–180, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Goldspink DF, Burniston JG, Ellison GM, Clark WA, Tan LB. Catecholamine-induced apoptosis and necrosis in cardiac and skeletal myocytes of the rat in vivo: the same or separate death pathways? Exp Physiol 89: 407–416, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Haase H, Hebel S, Engelhardt G, Rink L. Flow cytometric measurement of labile zinc in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Anal Biochem 352: 222–230, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Hästbacka J, Pettilä V. Prevalence and predictive value of ionized hypocalcemia among critically ill patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 47: 1264–1269, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Illi A, Sundberg S, Ojala-Karlsson P, Korhonen P, Scheinin M, Gordin A. The effect of entacapone on the disposition and hemodynamic effects of intravenous isoproterenol and epinephrine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 58: 221–227, 1995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Judd JT, Wexler BC. Myocardial connective tissue metabolism in response to injury. Histological and chemical studies of mucopolysaccharide and collagen in rat hearts after isoproterenol-induced infarction. Circ Res 25: 201–214, 1969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kamalov G, Ahokas RA, Zhao W, Johnson PL, Shahbaz AU, Bhattacharya SK, Sun Y, Gerling IC, Weber KT. Temporal responses to intrinsically coupled calcium and zinc dyshomeostasis in cardiac myocytes and mitochondria during aldosteronism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298: H385–H394, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Kamalov G, Ahokas RA, Zhao W, Zhao T, Shahbaz AU, Johnson PL, Bhattacharya SK, Sun Y, Gerling IC, Weber KT. Uncoupling the coupled calcium and zinc dyshomeostasis in cardiac myocytes and mitochondria seen in aldosteronism. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 55: 248–254, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Kamalov G, Deshmukh PA, Baburyan NY, Gandhi MS, Johnson PL, Ahokas RA, Bhattacharya SK, Sun Y, Gerling IC, Weber KT. Coupled calcium and zinc dyshomeostasis and oxidative stress in cardiac myocytes and mitochondria of rats with chronic aldosteronism. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 53: 414–423, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Kondoh M, Tsukada M, Kuronaga M, Higashimoto M, Takiguchi M, Himeno S, Watanabe Y, Sato M. Induction of hepatic metallothionein synthesis by endoplasmic reticulum stress in mice. Toxicol Lett 148: 133–139, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Lathers CM, Levin RM, Spivey WH. Regional distribution of myocardial β-adrenoceptors in the cat. Eur J Pharmacol 130: 111–117, 1986 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Lee S, Chanoit G, McIntosh R, Zvara DA, Xu Z. Molecular mechanism underlying Akt activation in zinc-induced cardioprotection. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297: H569–H575, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Margey R, Diamond P, McCann H, Sugrue D. Dobutamine stress echo-induced apical ballooning (Takotsubo) syndrome. Eur J Echocardiogr 10: 395–399, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Mathew BM, Kumar S, Ahmad MS, Seth TD, Hasan MZ, Jamil SA. A temporal profile of myocardial zinc changes after isoproterenol induced cardiac necrosis. Jpn Circ J 42: 353–357, 1978 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. McIntosh R, Lee S, Ghio AJ, Xi J, Zhu M, Shen X, Chanoit G, Zvara DA, Xu Z. The critical role of intracellular zinc in adenosine A2 receptor activation induced cardioprotection against reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol 49: 41–47, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Mohanty JG, Jaffe JS, Schulman ES, Raible DG. A highly sensitive fluorescent micro-assay of H2O2 release from activated human leukocytes using a dihydroxyphenoxazine derivative. J Immunol Methods 202: 133–141, 1997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Myslivecek J, Nováková M, Palkovits M, Krizanová O, Kvetnanský R. Distribution of mRNA and binding sites of adrenoceptors and muscarinic receptors in the rat heart. Life Sci 79: 112–120, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Ng Y, Goldspink DF, Burniston JG, Clark WA, Colyer J, Tan LB. Characterisation of isoprenaline myotoxicity on slow-twitch skeletal versus cardiac muscle. Int J Cardiol 86: 299–309, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Nykamp D, Titak JA. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, or broken-heart syndrome. Ann Pharmacother 44: 590–593, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Rajan GP, Zellweger R. Cardiac troponin I as a predictor of arrhythmia and ventricular dysfunction in trauma patients with myocardial contusion. J Trauma 57: 801–808, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Rona G, Chappel CI, Balazs T, Gaudry R. An infarct-like myocardial lesion and other toxic manifestations produced by isoproterenol in the rat. AMA Arch Pathol 67: 443–455, 1959 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Rushmer RF, Thal N. The mechanics of ventricular contraction; a cinefluorographic study. Circulation 4: 219–228, 1951 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Sedmera D, Reckova M, Bigelow MR, Dealmeida A, Stanley CP, Mikawa T, Gourdie RG, Thompson RP. Developmental transitions in electrical activation patterns in chick embryonic heart. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 280: 1001–1009, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Selektor Y, Parker RB, Sun Y, Zhao W, Bhattacharya SK, Weber KT. Tissue 65Zinc translocation in a rat model of chronic aldosteronism. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 51: 359–364, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Smogorzewski M, Zayed M, Zhang YB, Roe J, Massry SG. Parathyroid hormone increases cytosolic calcium concentration in adult rat cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 264: H1998–H2006, 1993 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Song Y, Wang J, Li XK, Cai L. Zinc and the diabetic heart. Biometals 18: 325–332, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Sun Y, Zhang J, Lu L, Chen SS, Quinn MT, Weber KT. Aldosterone-induced inflammation in the rat heart. Role of oxidative stress. Am J Pathol 161: 1773–1781, 2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Thomas M, Vidal A, Bhattacharya SK, Ahokas RA, Sun Y, Gerling IC, Weber KT. Zinc dyshomeostasis in rats with aldosteronism. Response to spironolactone. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293: H2361–H2366, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Upsher ME, Weiss HR. Heterogeneous distribution of beta adrenoceptors in the dog left ventricle. J Mol Cell Cardiol 18: 657–660, 1986 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Vidal A, Sun Y, Bhattacharya SK, Ahokas RA, Gerling IC, Weber KT. Calcium paradox of aldosteronism and the role of the parathyroid glands. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290: H286–H294, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Wang BH, Yu XJ, Wang D, Qi XM, Wang HP, Yang TT, Xu XH. Alterations of trace elements (Zn, Se, Cu, Fe) and related metalloenzymes in rabbit blood after severe trauma. J Trace Elem Med Biol 21: 102–107, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Zhou Z, Wang L, Song Z, Saari JT, McClain CJ, Kang YJ. Zinc supplementation prevents alcoholic liver injury in mice through attenuation of oxidative stress. Am J Pathol 166: 1681–1690, 2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Zielen P, Klisiewicz A, Januszewicz A, Prejbisz A, Kabat M, Peczkowska M, Stepinska J, Hoffman P. Pheochromocytoma-related ‘classic’ takotsubo cardiomyopathy. J Hum Hypertens 24: 363–366, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]