Abstract
Transcription of PHO5 is strongly regulated in response to the level of inorganic phosphate (Pi) present in the growth medium. We have identified elements required for PHO5 expression by analyzing small deletions in the PHO5 promoter on chromosome II. The results reveal three functionally different components of the PHO5 promoter: regulatory regions, a "TATA" element, and specific mRNA initiation sites. The regulatory regions contain related 19-base-pair (bp) dyad sequences acting as phosphate-controlled upstream activation sites (UASpS). These UASpS mediate the transcriptional activation of PHO5 observed in low Pi conditions. The unlinked but coordinately regulated PHO11 promoter contains a single copy of an almost identical dyad sequence, suggesting that there is a common regulatory UASp for both genes. A TATA element is absolutely required for detectable PHO5 transcription. Specific purine-pyrimidine motifs (RRYRR) (R = purine and Y = pyrimidine) serve as PHO5 mRNA initiation sites, but only if they lie 55-110 bp downstream of a functional TATA element. Such an "initiation window" is not found in higher eukaryotes and implies mechanistic differences in the transcription machineries between yeast and higher eukaryotes.
Full text
PDF


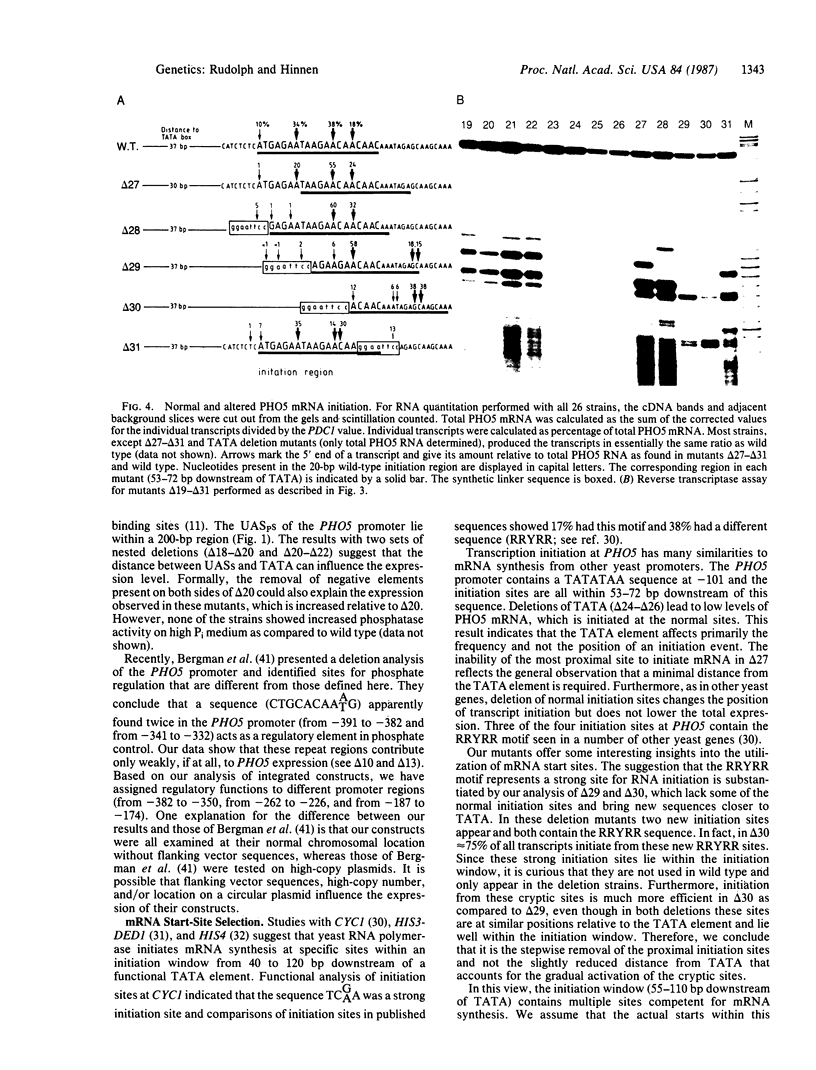

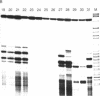
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen N., Thill G. P., Kramer R. A. RNA and homology mapping of two DNA fragments with repressible acid phosphatase genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):562–569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa W., Meyhack B., Rudolph H., Schweingruber A. M., Hinnen A. Structural analysis of the two tandemly repeated acid phosphatase genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7721–7739. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., McClinton D. C., Madden S. L., Preis L. H. Molecular analysis of the DNA sequences involved in the transcriptional regulation of the phosphate-repressible acid phosphatase gene (PHO5) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6070–6074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Yeast mRNA initiation sites are determined primarily by specific sequences, not by the distance from the TATA element. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3273–3280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Daves R. S., Lucchini G., Fink G. R. A short nucleotide sequence required for regulation of HIS4 by the general control system of yeast. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90499-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Hoar E. Upstream activation sites of the CYC1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are active when inverted but not when placed downstream of the "TATA box". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7860–7864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters: positive and negative elements. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Fink G. R. Repeated DNA sequences upstream from HIS1 also occur at several other co-regulated genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5238–5247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Lucchini G., Fink G. R. A synthetic HIS4 regulatory element confers general amino acid control on the cytochrome c gene (CYC1) of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Holland M. J. The primary structure of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9839–9845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Tamai Y., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of PHO8 expression by PHO regulatory genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):248–252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. A., Andersen N. Isolation of yeast genes with mRNA levels controlled by phosphate concentration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6541–6545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire J. M., Willcocks T., Halvorson H. O., Bostian K. A. Regulation of repressible acid phosphatase gene transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2131–2141. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyhack B., Bajwa W., Rudolph H., Hinnen A. Two yeast acid phosphatase structural genes are the result of a tandem duplication and show different degrees of homology in their promoter and coding sequences. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):675–680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Lumelsky N., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. Detection of single base substitutions in total genomic DNA. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):495–498. doi: 10.1038/313495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagawa F., Fink G. R. The relationship between the "TATA" sequence and transcription initiation sites at the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. Molecular analysis of a cell lineage. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):670–676. doi: 10.1038/302670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Restriction and modification enzymes and their recognition sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13 (Suppl):r165–r200. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.suppl.r165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. T., Lemire J. M., Bostian K. A. Acid phosphatase polypeptides in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are encoded by a differentially regulated multigene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H., Koenig-Rauseo I., Hinnen A. One-step gene replacement in yeast by cotransformation. Gene. 1985;36(1-2):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Ciriacy M., Zimmermann F. K. The synthesis of yeast pyruvate decarboxylase is regulated by large variations in the messenger RNA level. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;192(1-2):247–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00327674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Genetic properties and chromatin structure of the yeast gal regulatory element: an enhancer-like sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7865–7869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thill G. P., Kramer R. A., Turner K. J., Bostian K. A. Comparative analysis of the 5'-end regions of two repressible acid phosphatase genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):570–579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Hanley S., West R., Jr, Ptashne M. Use of lacZ fusions to delimit regulatory elements of the inducible divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1985–1998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]