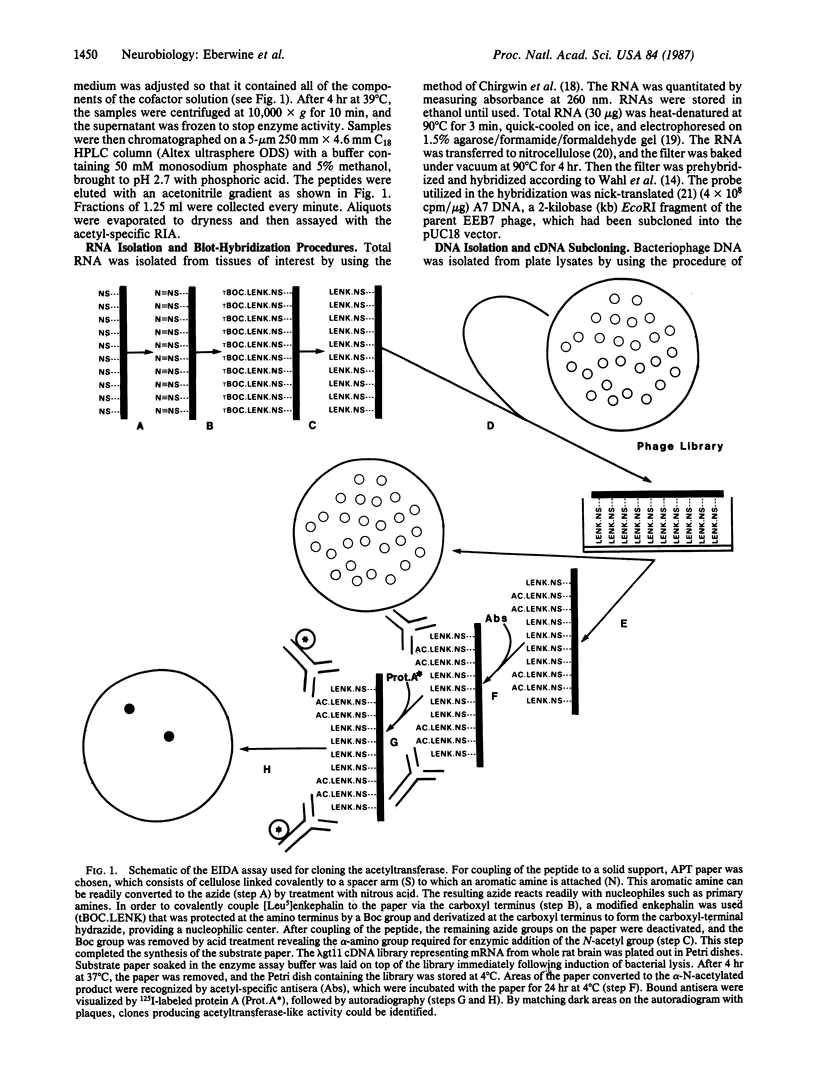
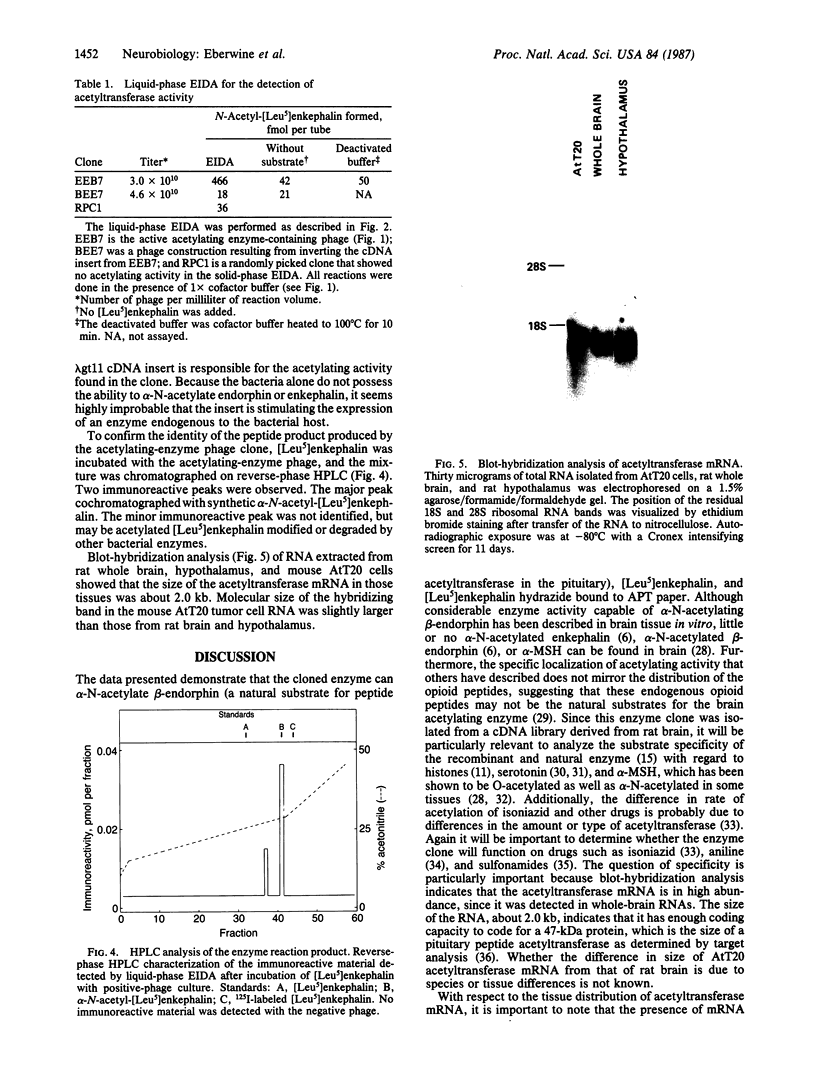
Abstract
The biological activity of many proteins and peptides can be profoundly affected by enzyme-catalyzed covalent modifications such as acetylation, sulfation, glycosylation, or amidation. This article describes the cloning of such an enzyme, a peptide acetyltransferase from rat brain that catalyzes the amino-terminal acetylation of endorphins and perhaps other substrates in vivo. Blot-hybridization analysis suggests that the mRNA encoding the acetyltransferase is approximately 2.0 kilobases, is present in whole rat brain and rat hypothalamus, and is slightly larger in mouse AtT20 tumor cells. The acetyltransferase was cloned by using a strategy whereby a cDNA expression library was screened with a solid-phase enzyme-activity assay; this technique combines the use of the substrate coupled to a solid support and subsequent recognition of the product by using a specific antiserum. We have called this method the enzyme immunodetection assay (EIDA). The EIDA should prove useful in the isolation of other clones for proteins that possess enzymatic activity upon expression in bacterial hosts.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akil H., Young E., Watson S. J., Coy D. H. Opiate binding properties of naturally occurring N- and C-terminus modified beta-endorphins. Peptides. 1981 Fall;2(3):289–292. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(81)80121-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ameer B., Greenblatt D. J. Acetaminophen. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Aug;87(2):202–209. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-2-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brainard G. C., Richardson B. A., King T. S., Matthews S. A., Reiter R. J. The suppression of pineal melatonin content and N-acetyltransferase activity by different light irradiances in the Syrian hamster: a dose-response relationship. Endocrinology. 1983 Jul;113(1):293–296. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-1-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deakin J. F., Doströvsky J. O., Smyth D. G. Influence of N-terminal acetylation and C-terminal proteolysis on the analgesic activity of beta-endorphin. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj1890501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. A., MANLEY K. A., McKUSICK V. A. Genetic control of isoniazid metabolism in man. Br Med J. 1960 Aug 13;2(5197):485–491. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5197.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. J., Erdelyi E., Weber E., Barchas J. D. Identification of pro-opiomelanocortin-derived peptides in the human adrenal medulla. Science. 1983 Sep 2;221(4614):957–960. doi: 10.1126/science.6308766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. J., Lorenz R., Weber E., Barchas J. D. Variants of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone in rat brain and pituitary evidence that acetylated alpha-MSH exists only in the intermediate lobe of pituitary. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 15;106(3):910–919. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91797-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTTMANN S., BOISSONNAS R. A. Influence of the structure of the n-terminal extremity of alpha-MSH on the melanophore stimulating activity of this hormone. Experientia. 1961 Jun 15;17:265–267. doi: 10.1007/BF02161433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glembotski C. C. Characterization of the peptide acetyltransferase activity in bovine and rat intermediate pituitaries responsible for the acetylation of beta-endorphin and alpha-melanotropin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10501–10509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger M., Tesser G. I., De Jong W. W., Bloemendal H. Model studies of enzymatic NH2-terminal acetylation of porteins with des-Nalpha1-acetyl-alpha-melanotropin as a substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J. I., LERNER A. B. Amino-acid sequence of the alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone. Nature. 1957 Jun 29;179(4574):1346–1347. doi: 10.1038/1791346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:333–342. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Inoue A., Kita T., Nakamura M., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Numa S. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA for bovine corticotropin-beta-lipotropin precursor. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):423–427. doi: 10.1038/278423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donohue T. L., Chappell M. C. Distribution of an enzyme which acetylates alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone in rat brain and pituitary gland and effects of arcuate nucleus lesions. Peptides. 1982 Jan-Feb;3(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(82)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E., Nicolaisen A. K., Ong E. S., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone exerts rapid nuclear effects to increase production of the primary prolactin mRNA transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6662–6666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman D., Chawla R. K., Hollins B. M. N,O-Diacetylserine1 alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone, a naturally occurring melanotropic peptide. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10102–10108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Wangh L. J., Allfrey V. G. Processing of newly synthesized histone molecules. Science. 1975 Oct 10;190(4210):117–128. doi: 10.1126/science.1166303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Diazotizable arylamine cellulose papers for the coupling and hybridization of nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1799–1810. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Diazotizable arylamine cellulose papers for the coupling and hybridization of nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1799–1810. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seizinger B. R., Höllt V. In vitro biosynthesis and N-acetylation of beta-endorphin in pars intermedia of the rat pituitary. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 30;96(2):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Structure of chromatin containing extensively acetylated H3 and H4. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. G., Massey D. E., Zakarian S., Finnie M. D. Endorphins are stored in biologically active and inactive forms: isolation of alpha-N-acetyl peptides. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):252–254. doi: 10.1038/279252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Barchas J. D. Acetylated and nonacetylated forms of beta-endorphin in rat brain and pituitary. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 15;103(3):982–989. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90906-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Chang J. K., Barchas J. D. Antibodies specific for alpha-N-acetyl-beta-endorphins: radioimmunoassays and detection of acetylated beta-endorphins in pituitary extracts. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):436–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodford T. A., Dixon J. E. The Nalpha-acetylation of corticotropin and fragments of corticotropin by a rat pituitary Nalpha-acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4993–4999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakarian S., Smyth D. Distribution of active and inactive forms of endorphins in rat pituitary and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5972–5976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]