Abstract
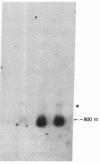
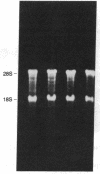
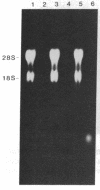
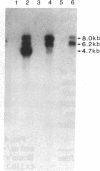
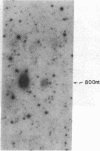
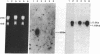
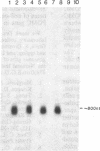
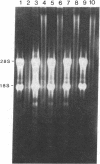
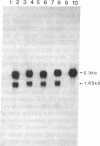
Proopiomelanocortin (POMC), a major pituitary product, is also present in the adult mouse testis. We have shown previously that POMC mRNAs are most abundant in a subpopulation of Leydig cells associated with tubules in specific stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium. In the present study, we examined the expression of the gene encoding POMC during testicular development and in other tissues of the male reproductive system. We also analyzed the effects of cellular interactions on POMC gene expression in the testis. Blot-hybridization analysis revealed that POMC transcripts of approximately equal to 800 nucleotides were present in enriched populations of meiotic prophase spermatocytes and in caput epididymis but were absent in cauda epididymis and vas deferens. POMC transcripts were present in fetal testis (day 17 of gestation to newborn), could not be detected in prepuberal testis (days 7-8 postpartum), but reappeared in the adult testis. No difference in the size or abundance of POMC transcripts was seen in testes from mouse mutant strains in which spermatogenesis is arrested in early spermiogenesis. In contrast, POMC transcripts were virtually undetectable in testes that are devoid of germ cells. These results emphasize the importance of interactions between germ cells and interstitial cells and the regulation of the POMC gene in the mammalian testis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardin C. W., Shaha C., Mather J., Salomon Y., Margioris A. N., Liotta A. S., Gerendai I., Chen C. L., Krieger D. T. Identification and possible function of pro-opiomelanocortin-derived peptides in the testis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;438:346–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb38296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R., Cavicchia J. C., Millette C. F., O'Brien D. A., Bhatnagar Y. M., Dym M. Spermatogenic cells of the prepuberal mouse. Isolation and morphological characterization. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):68–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. I., Gall A. M., Southard J. L., Sidman R. L. Abnormal spermiogenesis in quaking, a myelin-deficient mutant mouse. Biol Reprod. 1971 Aug;5(1):30–58. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/5.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Chang C. C., Krieger D. T., Bardin C. W. Expression and regulation of proopiomelanocortin-like gene in the ovary and placenta: comparison with the testis. Endocrinology. 1986 Jun;118(6):2382–2389. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-6-2382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Mather J. P., Morris P. L., Bardin C. W. Expression of pro-opiomelanocortin-like gene in the testis and epididymis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5672–5675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng M. C., Clements J. A., Smith A. I., Lolait S. J., Funder J. W. N-acetyl endorphin in rat spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):832–835. doi: 10.1172/JCI111779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubb C., Nolan C. Genetic control of steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis in inbred mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;438:519–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb38322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerendai I., Shaha C., Thau R., Bardin C. W. Do testicular opiates regulate Leydig cell function? Endocrinology. 1984 Oct;115(4):1645–1647. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-4-1645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gizang-Ginsberg E., Wolgemuth D. J. Localization of mRNAs in mouse testes by in situ hybridization: distribution of alpha-tubulin and developmental stage specificity of pro-opiomelanocortin transcripts. Dev Biol. 1985 Oct;111(2):293–305. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90484-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handel M. A., Eppig J. J. Sertoli cell differentiation in the testes of mice genetically deficient in germ cells. Biol Reprod. 1979 Jun;20(5):1031–1038. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod20.5.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Millette C. F. Expression of proenkephalin messenger RNA by mouse spermatogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5015–5018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margioris A. N., Liotta A. S., Vaudry H., Bardin C. W., Krieger D. T. Characterization of immunoreactive proopiomelanocortin-related peptides in rat testes. Endocrinology. 1983 Aug;113(2):663–671. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-2-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Bruce W. R., Clermont Y. Cellular composition of fractions of mouse testis cells following velocity sedimentation separation. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Apr;79(1):213–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEBEL B. R., AMAROSE A. P., HACKET E. M. Calendar of gametogenic development in the prepuberal male mouse. Science. 1961 Sep 22;134(3482):832–833. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3482.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OAKBERG E. F. A description of spermiogenesis in the mouse and its use in analysis of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium and germ cell renewal. Am J Anat. 1956 Nov;99(3):391–413. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000990303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintar J. E., Schachter B. S., Herman A. B., Durgerian S., Krieger D. T. Characterization and localization of proopiomelanocortin messenger RNA in the adult rat testis. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):632–634. doi: 10.1126/science.6740329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Wolgemuth D. J. Haploid expression of a unique c-abl transcript in the mouse male germ line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1791–1794. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo J., De Rosas J. C. Differentiation of the Leydig cell of the mouse testis during the fetal period--an ultrastructural study. Am J Anat. 1971 Apr;130(4):461–480. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001300407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo J. Fine structure of the Leydig cell during postnatal differentiation of the mouse testis. Anat Rec. 1971 Jul;170(3):343–355. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091700310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaha C., Liotta A. S., Krieger D. T., Bardin C. W. The ontogeny of immunoreactive beta-endorphin in fetal, neonatal, and pubertal testes from mouse and hamster. Endocrinology. 1984 May;114(5):1584–1591. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-5-1584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu-Dong T., Phillips D. M., Halmi N., Krieger D., Bardin C. W. Beta-endorphin is present in the male reproductive tract of five species. Biol Reprod. 1982 Oct;27(3):755–764. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod27.3.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M., Herbert E. Complete amino acid sequence of mouse pro-opiomelanocortin derived from the nucleotide sequence of pro-opiomelanocortin cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Ledley F., Goff S., Lee R., Groner Y., Baltimore D. The mouse c-abl locus: molecular cloning and characterization. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters S. H., Distel R. J., Hecht N. B. Mouse testes contain two size classes of actin mRNA that are differentially expressed during spermatogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1649–1654. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock R., Sweet R., Weiss M., Cedar H., Axel R. Intragenic DNA spacers interrupt the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Engelmyer E., Duggal R. N., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Mutter G. L., Ponzetto C., Viviano C., Zakeri Z. F. Isolation of a mouse cDNA coding for a developmentally regulated, testis-specific transcript containing homeo box homology. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1229–1235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Engelmyer E., Gavin B. J., Ponzetto C. Separation of mouse testis cells on a Celsep (TM) apparatus and their usefulness as a source of high molecular weight DNA or RNA. Gamete Res. 1985;12:1–10. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1120120102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]