Abstract
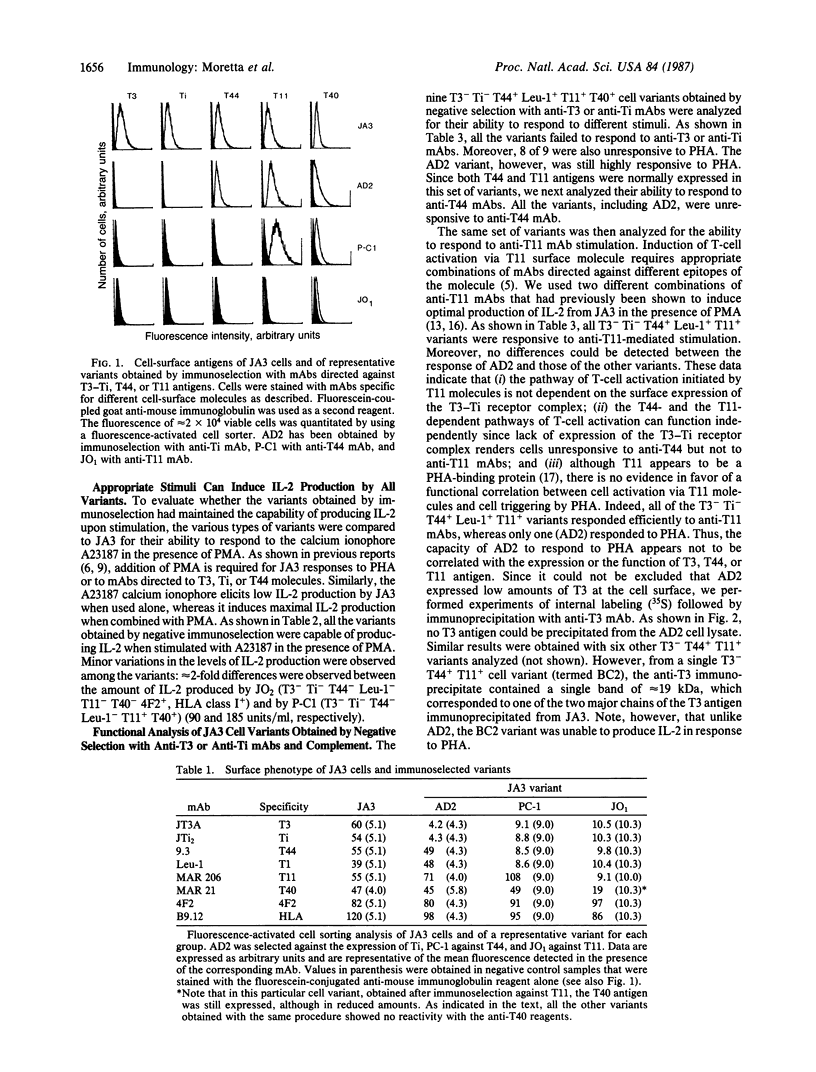
A clone of the interleukin 2-producing Jurkat leukemia cell line termed JA3 (surface phenotype, T3+, Ti+, T44+, T11+, T40+) has been used to induce and select cell variants lacking surface molecules involved in T-cell activation. Following 200 rad of gamma-radiation (1 rad = 0.01 Gy), cells were treated with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed to T3, Ti, T44, or T11 antigen and complement. After growth of the residual cells in culture, "negative" cells were cloned under limiting conditions. Depending on the specificity of the mAb used for the immunoselection, three groups of variants were obtained. (i) The use of mAbs directed to T3 or Ti resulted in cell variants that expressed the T3 Ti- T44+ Leu1+ T11+ T40+ 4F2+ HLA class I+ surface phenotype. (ii) Immunoselection with anti-T44 mAb resulted in 2 variants that shared the T3- Ti- T44- Leu1- T11+ T40+ 4F2+ HLA class I+ phenotype. (iii) Cell treatment with anti-T11 mAb resulted in 15 variants characterized by the lack of T11 antigen expression and of all the other T-cell-specific surface antigens. Therefore, it appears that the different sets of JA3 cell variants, like T cells at discrete stages of intrathymic differentiation, may follow a coordinated expression of surface differentiation antigens. Analysis of the functional responsiveness of the three distinct groups of JA3 cell variants to different stimuli showed that all produced interleukin 2 in response to A23187 calcium ionophore plus phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. The first group of variants (T3- Ti-) did not respond to stimulation with anti-T3, anti-Ti, or anti-T44 mAbs. Eight of 9 did not respond to phytohemagglutinin either; however, all responded to appropriate stimulatory combinations of anti-T11 mAbs (and to calcium ionophore). The second group of variants (T3-, Ti-, T44-, T11+), similar to the first group, did not respond to anti-T3, anti-Ti, anti-T44 mAbs, and phytohemagglutinin, but they were fully responsive to anti-T11 mAb. The last group of variants (lacking all the T-cell-specific surface antigens) only responded to calcium ionophore A23187.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accolla R. S., Scarpellino L., Carra G., Guardiola J. Trans-acting element(s) operating across species barriers positively regulate expression of major histocompatibility complex class II genes. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1117–1133. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilson O. P., Boylston A. W., Crumpton M. J. Phaseolus vulgaris phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) binds to the human T lymphocyte antigen receptor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3239–3245. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. A., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Bensussan A., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Activation of human thymocytes via the 50KD T11 sheep erythrocyte binding protein induces the expression of interleukin 2 receptors on both T3+ and T3- populations. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):330–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Fu S. M., Hansen J. A. Human T cell activation. II. A new activation pathway used by a major T cell population via a disulfide-bonded dimer of a 44 kilodalton polypeptide (9.3 antigen). J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1513–1524. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobach D. F., Hensley L. L., Ho W., Haynes B. F. Human T cell antigen expression during the early stages of fetal thymic maturation. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1752–1759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen B., Rebai N., Liabeuf A., Mawas C. Human cytotoxic T cell structures associated with expression of cytolysis. I. Analysis at the clonal cell level of the cytolysis-inhibiting effect of 7 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Sep;12(9):739–747. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Clonotypic structures involved in antigen-specific human T cell function. Relationship to the T3 molecular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):705–719. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milanese C., Richardson N. E., Reinherz E. L. Identification of a T helper cell-derived lymphokine that activates resting T lymphocytes. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1118–1122. doi: 10.1126/science.2935936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A. Frequency and surface phenotype of human T lymphocytes producing interleukin 2. Analysis by limiting dilution and cell cloning. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Feb;15(2):148–155. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Olive D., Poggi A., Pantaleo G., Mawas C., Moretta L. Modulation of surface T11 molecules induced by monoclonal antibodies: analysis of the functional relationship between antigen-dependent and antigen-independent pathways of human T cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Nov;16(11):1427–1432. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Lopez-Botet M., Mingari M. C., Carrel S., Moretta L. Involvement of T11 molecules in antigen receptor-mediated T lymphocyte functions: effect of anti-T11 monoclonal antibody on functional capabilities of alloreactive T cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Aug;15(8):841–844. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Lopez-Botet M., Mingari M. C., Moretta L. Anticlonotypic monoclonal antibodies induce proliferation of clonotype-positive T cells in peripheral blood human T lymphocytes. Evidence for a phenotypic (T4/T8) heterogeneity of the clonotype-positive proliferating cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1393–1398. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Lopez-Botet M., Moretta L. Involvement of T44 molecules in an antigen-independent pathway of T cell activation. Analysis of the correlations to the T cell antigen-receptor complex. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):823–838. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Lopez-Botet M., Moretta L. Selection and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to the idiotype-like structure of an interleukin-2-producing human leukemia T-cell line. Int J Cancer. 1985 Aug 15;36(2):253–259. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flynn K., Krensky A. M., Beverley P. C., Burakoff S. J., Linch D. C. Phytohaemagglutinin activation of T cells through the sheep red blood cell receptor. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):686–687. doi: 10.1038/313686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D., Ragueneau M., Cerdan C., Dubreuil P., Lopez M., Mawas C. Anti-CD2 (sheep red blood cell receptor) monoclonal antibodies and T cell activation. I. Pairs of anti-T11.1 and T11.2 (CD2 subgroups) are strongly mitogenic for T cells in presence of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Sep;16(9):1063–1068. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Acuto O., Fabbi M., Bensussan A., Milanese C., Royer H. D., Meuer S. C., Schlossman S. F. Clonotypic surface structure on human T lymphocytes: functional and biochemical analysis of the antigen receptor complex. Immunol Rev. 1984 Oct;81:95–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb01106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano R. F., Pratt J. C., Schmidt R. E., Ritz J., Reinherz E. L. Activation of cytolytic T lymphocyte and natural killer cell function through the T11 sheep erythrocyte binding protein. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):428–430. doi: 10.1038/317428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Stobo J. D. Requirement for the coexpression of T3 and the T cell antigen receptor on a malignant human T cell line. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1284–1299. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]