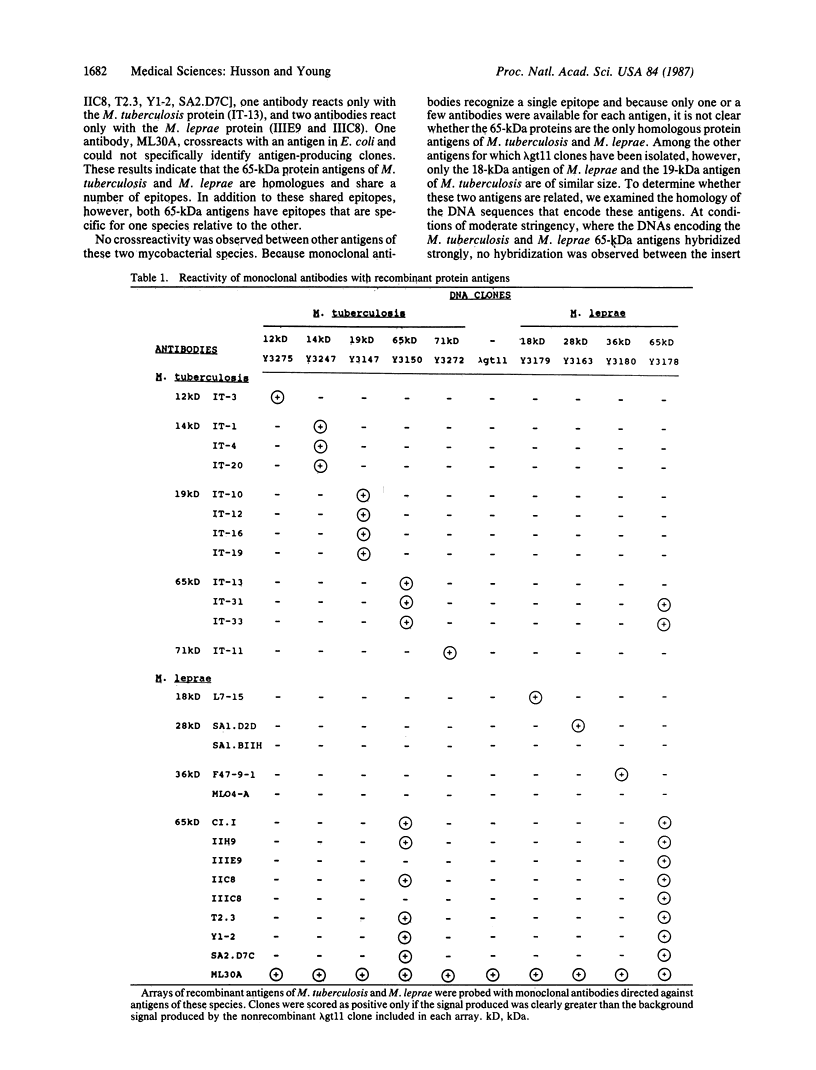
Abstract
Mycobacterium tuberculosis genes encoding immunologically relevant proteins were isolated by systematically screening a lambda gt11 recombinant DNA expression library with a collection of murine monoclonal antibodies directed against protein antigens of this pathogen. These antibodies, previously characterized by a World Health Organization workshop on monoclonal antibodies against mycobacteria, were used to isolate DNA sequences encoding five major protein antigens of this pathogen. To evaluate the extent of crossreactivity between these M. tuberculosis antigens and antigens of Mycobacterium leprae, recombinant antigens were probed with monoclonal antibodies directed against the protein antigens of these bacilli. One of the antigens, a 65-kDa protein, has determinants common to M. tuberculosis and M. leprae. We find not only that this antigen is recognized by mouse monoclonal antibodies but that it is the major protein recognized by anti-M. tuberculosis rabbit sera. The 65-kDa proteins of M. tuberculosis and M. leprae appear to play a role in the humoral and cell-mediated immune response to these pathogens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen A. B., Yuan Z. L., Hasløv K., Vergmann B., Bennedsen J. Interspecies reactivity of five monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis as examined by immunoblotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):446–451. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.446-451.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Godal T. Selective primary health care: strategies for control of disease in the developing world. V. Leprosy. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):765–780. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton W. J., Hellqvist L., Basten A., Raison R. L. Mycobacterium leprae antigens involved in human immune responses. I. Identification of four antigens by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4171–4177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates A. R., Hewitt J., Allen B. W., Ivanyi J., Mitchison D. A. Antigenic diversity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis detected by means of monoclonal antibodies. Lancet. 1981 Jul 25;2(8239):167–169. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmrich F., Thole J., van Embden J., Kaufmann S. H. A recombinant 64 kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin specifically stimulates human T4 clones reactive to mycobacterial antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):1024–1029. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine P. Leprosy and tuberculosis--an epidemiological comparison. Tubercle. 1984 Jun;65(2):137–153. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(84)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis T. P., Buchanan T. M. Production and partial characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):172–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.172-178.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi J., Sinha S., Aston R., Cussell D., Keen M., Sengupta U. Definition of species specific and cross-reactive antigenic determinants of Mycobacterium leprae using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jun;52(3):528–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolk A. H., Ho M. L., Klatser P. R., Eggelte T. A., Kuijper S., de Jonge S., van Leeuwen J. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis (BCG) and M. leprae. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Dec;58(3):511–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luelmo F. BCG vaccination. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Mar;125(3 Pt 2):70–72. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.3P2.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden P., Kelleher P. J., Freed J. H., Nielsen L. D., Brennan P. J., McPheron L., McClatchy J. K. Immunological evaluation of a component isolated from Mycobacterium bovis BCG with a monoclonal antibody to M. bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):519–525. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.519-525.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Gill H. K., Nerland A., Britton W. J., Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Young R. A., Godal T. Human T-cell clones recognize a major M. leprae protein antigen expressed in E. coli. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):63–66. doi: 10.1038/319063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitchenik A. E., Cole C., Russell B. W., Fischl M. A., Spira T. J., Snider D. E., Jr Tuberculosis, atypical mycobacteriosis, and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome among Haitian and non-Haitian patients in south Florida. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Nov;101(5):641–645. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-5-641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Results of a World Health Organization-sponsored workshop on monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):603–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.603-605.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Results of a World Health Organization-sponsored workshop to characterize antigens recognized by mycobacterium-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):718–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.718-720.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar P., Agis F., Wallach D., Flageul B., Cottenot F., Augier J., Bach M. A. M. leprae and PPD-triggered T cell lines in tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4255–4263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., Dauwerse H. G., Das P. K., Groothuis D. G., Schouls L. M., van Embden J. D. Cloning of Mycobacterium bovis BCG DNA and expression of antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):800–806. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.800-806.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Swenson J. M., Silcox V. A., Good R. C., Tschen J. A., Stone M. S. Spectrum of disease due to rapidly growing mycobacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):657–679. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Fohn M. J., Khanolkar S. R., Buchanan T. M. Monoclonal antibodies to a 28,000 mol. wt protein antigen of Mycobacterium leprae. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jun;60(3):546–552. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Bloom B. R., Grosskinsky C. M., Ivanyi J., Thomas D., Davis R. W. Dissection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using recombinant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Mehra V., Sweetser D., Buchanan T., Clark-Curtiss J., Davis R. W., Bloom B. R. Genes for the major protein antigens of the leprosy parasite Mycobacterium leprae. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):450–452. doi: 10.1038/316450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]