Abstract
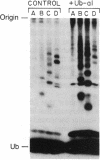
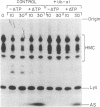
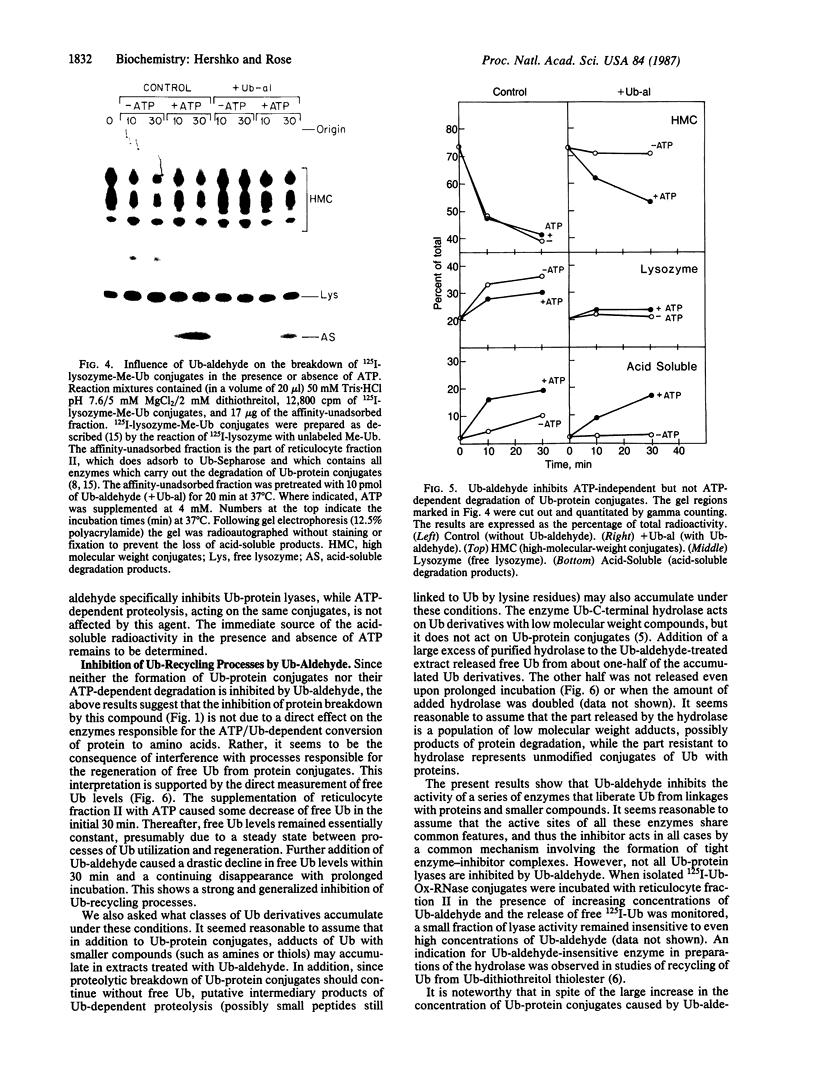
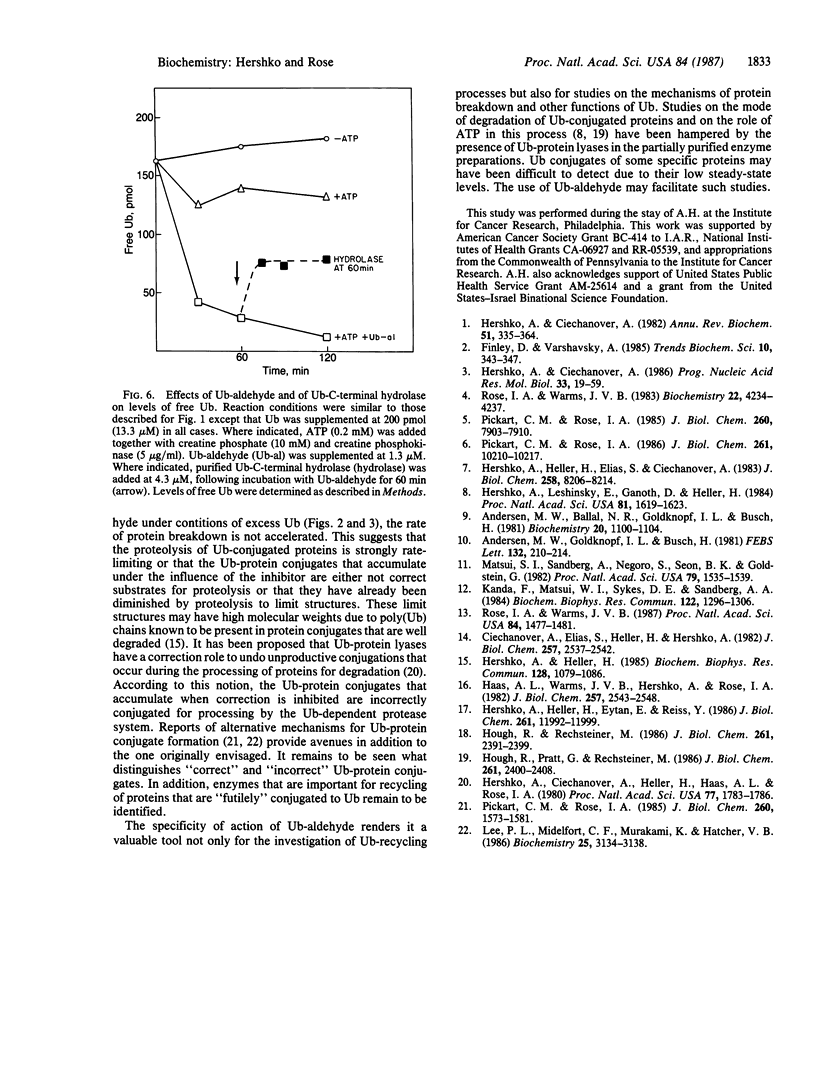
The generation and characterization of ubiquitin (Ub)-aldehyde, a potent inhibitor of Ub-C-terminal hydrolase, has previously been reported. We now examine the action of this compound on the Ub-mediated proteolytic pathway using the system derived from rabbit reticulocytes. Addition of Ub-aldehyde was found to strongly inhibit breakdown of added 125I-labeled lysozyme, but inhibition was overcome by increasing concentrations of Ub. The following evidence shows the effect of Ub-aldehyde on protein breakdown to be indirectly caused by its interference with the recycling of Ub, leading to exhaustion of the supply of free Ub: Ub-aldehyde markedly increased the accumulation of Ub-protein conjugates coincident with a much decreased rate of conjugate breakdown. release of Ub from isolated Ub-protein conjugates in the absence of ATP (and therefore not coupled to protein degradation) is markedly inhibited by Ub-aldehyde. On the other hand, the ATP-dependent degradation of the protein moiety of Ub conjugates, which is an integral part of the proteolytic process, is not inhibited by this agent. Direct measurement of levels of free Ub showed a rapid disappearance caused by the inhibitor. The Ub is found to be distributed in derivatives of a wide range of molecular weight classes. It thus seems that Ub-aldehyde, previously demonstrated to inhibit the hydrolysis of Ub conjugates of small molecules, also inhibits the activity of a series of enzymes that regenerate free Ub from adducts with proteins and intermediates in protein breakdown.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen M. W., Ballal N. R., Goldknopf I. L., Busch H. Protein A24 lyase activity in nucleoli of thioacetamide-treated rat liver releases histone 2A and ubiquitin from conjugated protein A24. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1100–1104. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen M. W., Goldknopf I. L., Busch H. Protein A24 lyase is an isopeptidase. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):210–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Elias S., Heller H., Hershko A. "Covalent affinity" purification of ubiquitin-activating enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2537–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A. L., Warms J. V., Hershko A., Rose I. A. Ubiquitin-activating enzyme. Mechanism and role in protein-ubiquitin conjugation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2543–2548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A., Heller H., Haas A. L., Rose I. A. Proposed role of ATP in protein breakdown: conjugation of protein with multiple chains of the polypeptide of ATP-dependent proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1783–1786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. Mechanisms of intracellular protein breakdown. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:335–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin pathway for the degradation of intracellular proteins. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1986;33:19-56, 301. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Heller H., Elias S., Ciechanover A. Components of ubiquitin-protein ligase system. Resolution, affinity purification, and role in protein breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8206–8214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Heller H., Eytan E., Reiss Y. The protein substrate binding site of the ubiquitin-protein ligase system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11992–11999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Heller H. Occurrence of a polyubiquitin structure in ubiquitin-protein conjugates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 16;128(3):1079–1086. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Leshinsky E., Ganoth D., Heller H. ATP-dependent degradation of ubiquitin-protein conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough R., Pratt G., Rechsteiner M. Ubiquitin-lysozyme conjugates. Identification and characterization of an ATP-dependent protease from rabbit reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2400–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough R., Rechsteiner M. Ubiquitin-lysozyme conjugates. Purification and susceptibility to proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2391–2399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda F., Matsui S., Sykes D. E., Sandberg A. A. Affinity of chromatin constituents for isopeptidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1296–1306. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91233-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. L., Midelfort C. F., Murakami K., Hatcher V. B. Multiple forms of ubiquitin-protein ligase. Binding of activated ubiquitin to protein substrates. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3134–3138. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S., Sandberg A. A., Negoro S., Seon B. K., Goldstein G. Isopeptidase: a novel eukaryotic enzyme that cleaves isopeptide bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1535–1539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Rose I. A. Functional heterogeneity of ubiquitin carrier proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1573–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Rose I. A. Mechanism of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase. Borohydride and hydroxylamine inactivate in the presence of ubiquitin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10210–10217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Rose I. A. Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase acts on ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal amides. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7903–7910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose I. A., Warms J. V. A specific endpoint assay for ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1477–1481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose I. A., Warms J. V. An enzyme with ubiquitin carboxy-terminal esterase activity from reticulocytes. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 30;22(18):4234–4237. doi: 10.1021/bi00287a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]