Abstract
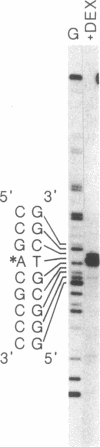
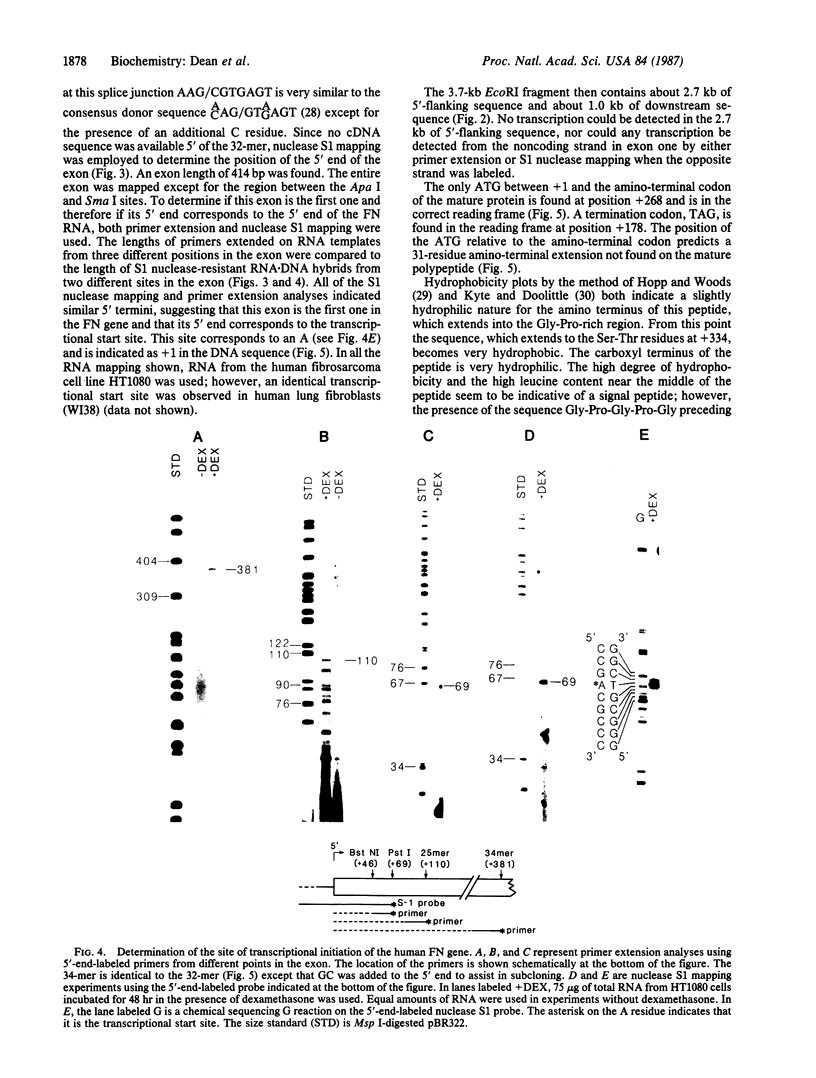
Human fibronectin (FN) genomic clones were isolated by screening a human genomic library with a 75-base oligonucleotide. The sequence of the oligonucleotide corresponds to a region near the 5' end of the human FN cDNA clone pFH6 that contains the amino-terminal coding sequences but does not extend to the 5' end of the mRNA [Kornblihtt, A. R., Umezawa, K., Vibe-Pedersen, K. & Baralle, F. E. (1985) EMBO J. 4, 1755-1759]. The 5' end of the FN gene is found on a 3.7-kilobase-pair EcoRI fragment that contains about 2.7 kilobase pairs of flanking sequence. The first exon is 414 base pairs long, with a 5' untranslated region of 267 base pairs. As deduced on the basis of the position of the initiation codon, FN is synthesized with a 31-residue amino acid extension on the amino terminus that is not present in the mature polypeptide. This amino-terminal extension appears to contain both a signal peptide and a propeptide. The first 200 base pairs of 5'-flanking sequence is very G + C rich. Upstream of this the sequence becomes relatively A + T rich. The sequence ATATAA is found at -25 and the sequence CAAT is present at -150. The sequence GGGGCGGGGC at -102 exhibits homology to the binding site for the transcription factor SP1, and the sequence TGACGTCA at -173 exhibits homology to 5'-flanking sequences important for induction by cAMP.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann H., Eldredge D. Dexamethasone increases the synthesis and secretion of a partially active fibronectin in rat hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):29–40. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. RNA splicing: three themes with variations. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90527-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., de Wet W., Bernard M., Ramirez F. Fine structural analysis of the human pro-alpha 1 (I) collagen gene. Promoter structure, AluI repeats, and polymorphic transcripts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2315–2320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. B., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Sequence rearrangement and duplication of double stranded fibronectin cDNA probably occurring during cDNA synthesis by AMV reverse transcriptase and Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):3055–3064. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. B., Sobel M. E., Yamada K. M., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Effects of transformation on fibronectin gene expression using cloned fibronectin cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):520–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furcht L. T., Mosher D. F., Wendelschafer-Crabb G., Woodbridge P. A., Foidart J. M. Dexamethasone-induced accumulation of a fibronectin and collagen extracellular matrix in transformed human cells. Nature. 1979 Feb 1;277(5695):393–395. doi: 10.1038/277393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Yamada K. M., Kornblihtt A. Human fibronectin is synthesized as a pre-propolypeptide. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano H., Yamada Y., Sullivan M., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I., Yamada K. M. Isolation of genomic DNA clones spanning the entire fibronectin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Yamada K. M. Fibronectins: multifunctional modular glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):369–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll B. J., Zarucki-Schulz T., Dean D. C., O'Malley B. W. Definition of the ovalbumin gene promoter by transfer of an ovalglobin fusion gene into cultured cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6733–6754. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Umezawa K., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Primary structure of human fibronectin: differential splicing may generate at least 10 polypeptides from a single gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1755–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Human fibronectin: cell specific alternative mRNA splicing generates polypeptide chains differing in the number of internal repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5853–5868. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Human fibronectin: molecular cloning evidence for two mRNA species differing by an internal segment coding for a structural domain. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):221–226. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human and bovine fibronectins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien Y. H., Wong M. J., Golbus M. S., Stern R. Hydrocortisone stimulates fibronectin synthesis in cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Jul;120(1):103–107. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041200114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau N., Goyette R., Valet J. P., Deschenes J. The effect of dexamethasone on formation of a fibronectin extracellular matrix by rat hepatocytes in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Feb;125(2):497–502. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldberg A., Linney E., Ruoslahti E. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone coding for the cell attachment domain in human fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10193–10196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver N., Newby R. F., Furcht L. T., Bourgeois S. Regulation of fibronectin biosynthesis by glucocorticoids in human fibrosarcoma cells and normal fibroblasts. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90357-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Identification and isolation of a 140 kd cell surface glycoprotein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E., Hayman E. G. Fibronectin: current concepts of its structure and functions. Coll Relat Res. 1981;1(1):95–128. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(80)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Wynshaw-Boris A., Short H. P., Hanson R. W. Characterization of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) promoter-regulatory region. II. Identification of cAMP and glucocorticoid regulatory domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9721–9726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Kemmler W., Tager H. S., Peterson J. D. Proteolytic processing in the biosynthesis of insulin and other proteins. Fed Proc. 1974 Oct;33(10):2105–2115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Schwarzbauer J. E., Hynes R. O. A single rat fibronectin gene generates three different mRNAs by alternative splicing of a complex exon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi J. S., Hirano H., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Transcriptional control of the fibronectin gene in chick embryo fibroblasts transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5787–5793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vibe-Pedersen K., Kornblihtt A. R., Baralle F. E. Expression of a human alpha-globin/fibronectin gene hybrid generates two mRNAs by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2511–2516. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Cell surface interactions with extracellular materials. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:761–799. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pastan I. Quantitation of a transformation-sensitive, adhesive cell surface glycoprotein. Decrease of several untransformed permanent cell lines. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):649–654. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]