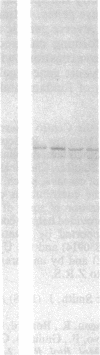
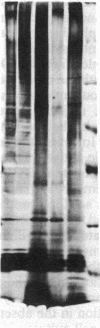
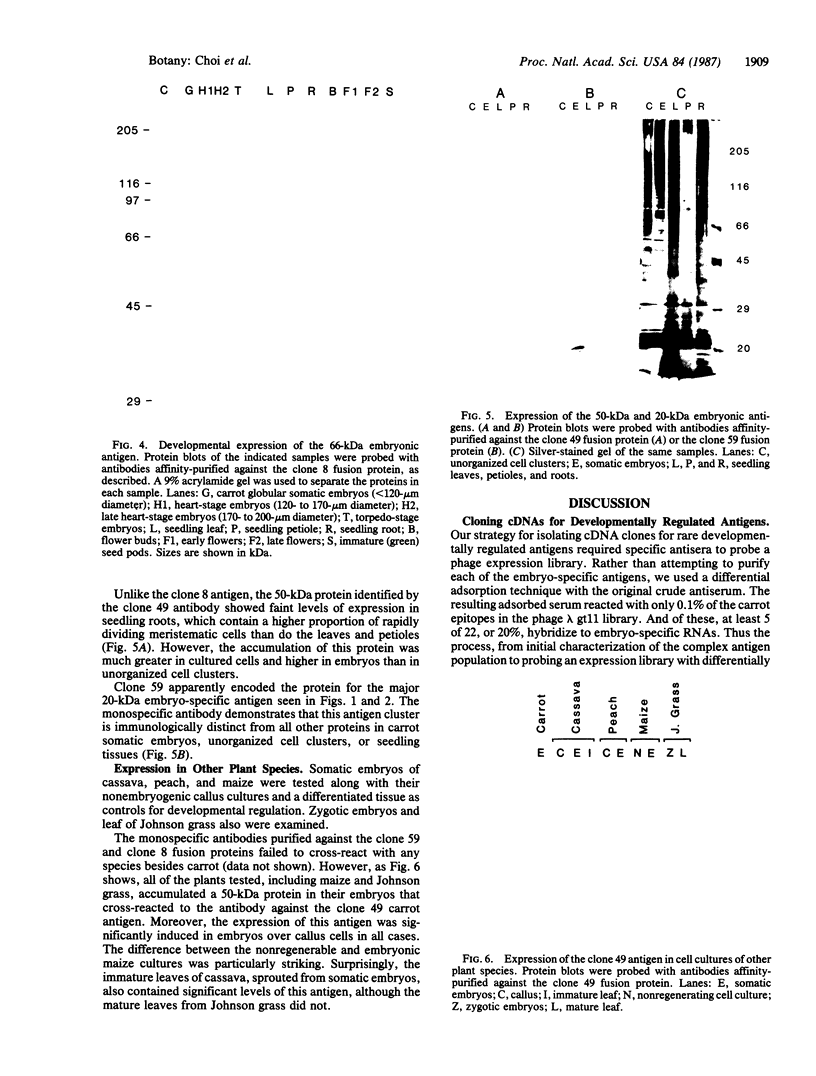
Abstract
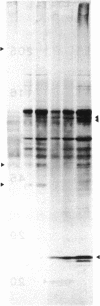
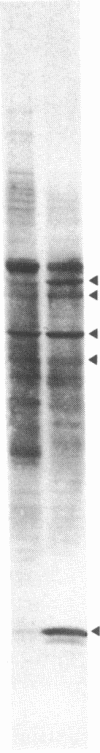
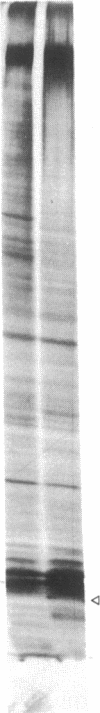
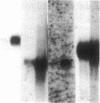
Genes specifically induced during somatic embryogenesis may play key roles in plant embryo development. An antiserum against an extract of carrot somatic embryos revealed a few rare antigens induced at the onset of embryogenesis. Through differential immunoadsorption techniques, we purified antibodies against the embryo-specific antigens and probed a phage λ gt11 library of cDNA from carrot somatic embryos. This paper describes three distinct cDNA clones that hybridize to embryo-specific RNAs. Monospecific antibodies, purified by affinity to the recombinant phage fusion proteins, confirm that the cloned cDNAs encode unique embryo-specific peptide antigens. One 50-kDa protein correlates with embryogenic ability in cultures of other plant species, including cereals.
Keywords: somatic embryogenesis, differential immunoadsorption, expression vectors
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dworkin M. B., Dawid I. B. Use of a cloned library for the study of abundant poly(A)+RNA during Xenopus laevis development. Dev Biol. 1980 May;76(2):449–464. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker J. R., Davis R. W. Inhibition of gene expression in plant cells by expression of antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5372–5376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Hoschek G., Ditta G. S., Breidenbach R. W. Developmental regulation of cloned superabundant embryo mRNAs in soybean. Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 30;83(2):218–231. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90468-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock K., Tsang V. C. India ink staining of proteins on nitrocellulose paper. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R. Identification of concanavalin A-binding proteins after sodium dodecyl sulfate--gel electrophoresis and protein blotting. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jun;123(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung Z. R., Okimoto R. Coordinate gene expression during somatic embryogenesis in carrots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2661–2665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung Z. R., Okimoto R. Embryonic proteins in somatic embryos of carrot. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung Z. R. Turbidimetric measurement of plant cell culture growth. Plant Physiol. 1976 Mar;57(3):460–462. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.3.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Hollenberg S. M., Ong E. S., Harmon J. M., Brower S. T., Cidlowski J., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Identification of human glucocorticoid receptor complementary DNA clones by epitope selection. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):740–742. doi: 10.1126/science.2581314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]