Abstract
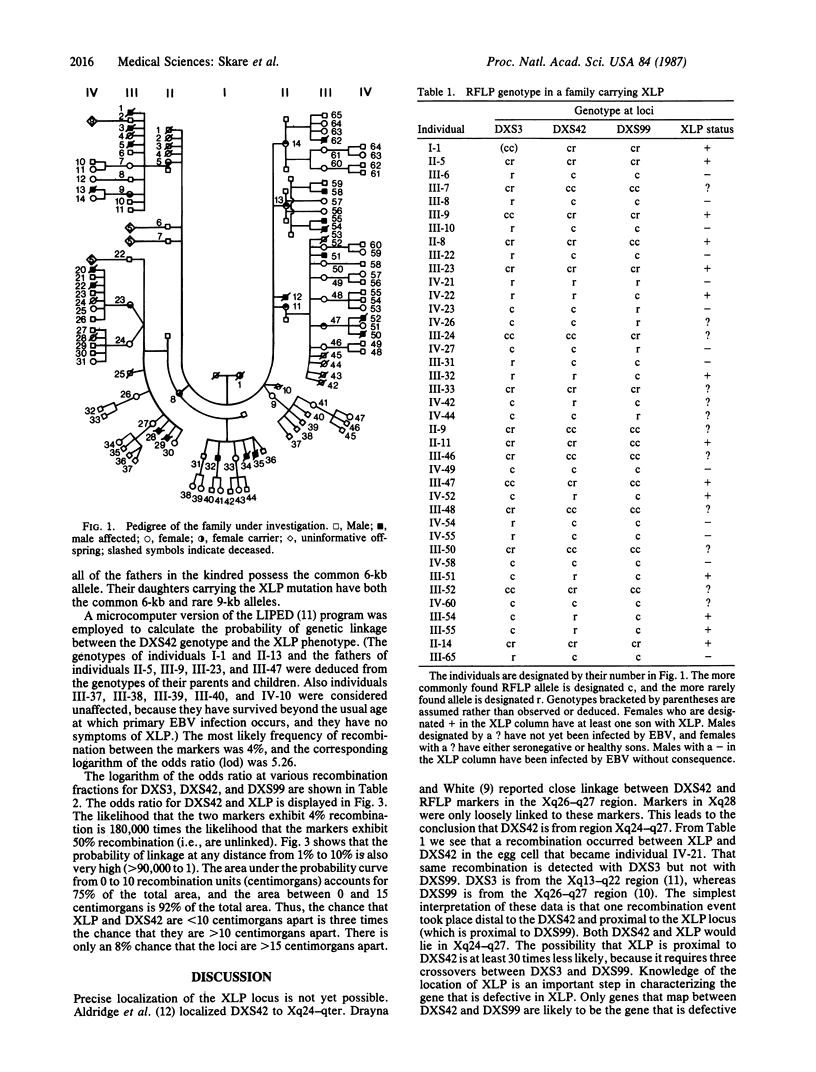
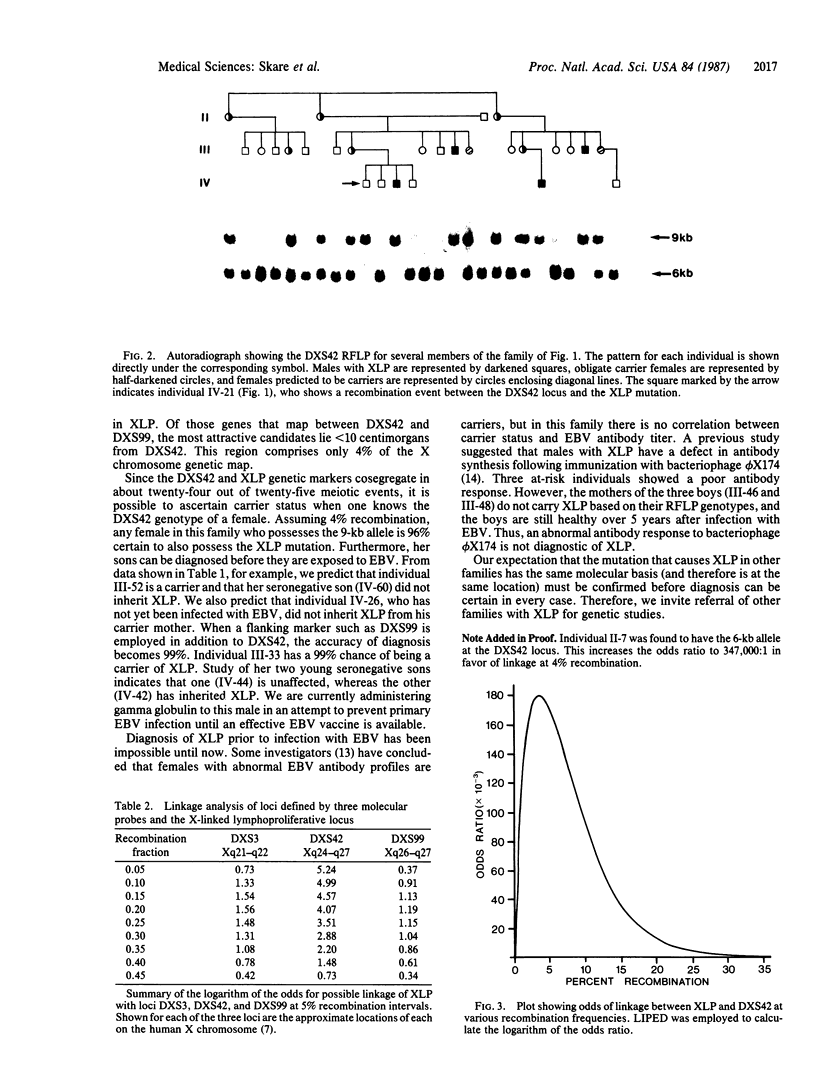
The X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome is triggered by Epstein-Barr virus infection and results in fatal mononucleosis, immunodeficiency, and lymphoproliferative disorders. This study shows that the mutation responsible for X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome is genetically linked to a restriction fragment length polymorphism detected with the DXS42 probe (from Xq24-q27). The most likely recombination frequency between the loci is 4%, and the associated logarithm of the odds is 5.26. Haplotype analysis using flanking restriction fragment length polymorphism markers indicates that the locus for X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome is distal to probe DXS42 but proximal to probe DXS99 (from Xq26-q27). It is now possible to predict which members of a family with X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome are carrier females and to diagnose the syndrome prenatally.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., DeLor C. J., Clausen K. P., Hurtubise P., Henle W., Hewetson J. F. Fatal infectious mononucleosis in a family. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 14;290(7):363–367. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402142900704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L. M., Phillips M. A., Forster-Gibson C. J., Beckett J., Partington M. W., Simpson N. E., Holden J. J., White B. N. Genetic mapping of DNA segments relative to the locus for the fragile-X syndrome at Xq27.3. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):463–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs H. D., Sullivan J. L., Wedgwood R. J., Seeley J. K., Sakamoto K., Purtilo D. T. X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome: abnormal antibody responses to bacteriophage phi X 174. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1983;19(3):321–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provisor A. J., Iacuone J. J., Chilcote R. R., Neiburger R. G., Crussi F. G. Acquired agammaglobulinemia after a life-threatening illness with clinical and laboratory features of infectious mononucleosis in three related male children. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 10;293(2):62–65. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507102930202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Cassel C. K., Yang J. P., Harper R. X-linked recessive progressive combined variable immunodeficiency (Duncan's disease). Lancet. 1975 Apr 26;1(7913):935–940. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., DeFlorio D., Jr, Hutt L. M., Bhawan J., Yang J. P., Otto R., Edwards W. Variable phenotypic expression of an X-linked recessive lymphoproliferative syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 17;297(20):1077–1080. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711172972001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Sakamoto K., Barnabei V., Seeley J., Bechtold T., Rogers G., Yetz J., Harada S. Epstein-Barr virus-induced diseases in boys with the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome (XLP): update on studies of the registry. Am J Med. 1982 Jul;73(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90923-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto K., Seeley J. K., Lindsten T., Sexton J., Yetz J., Ballow M., Purtilo D. T. Abnormal anti-Epstein Barr virus antibodies in carriers of the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome and in females at risk. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):904–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L., Byron K. S., Brewster F. E., Baker S. M., Ochs H. D. X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Natural history of the immunodeficiency. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1765–1778. doi: 10.1172/JCI110932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Skolnick M. H., Pearson P. L., Mandel J. L. Report of the Committee on Human Gene Mapping by Recombinant DNA Techniques. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):360–489. doi: 10.1159/000132180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




