Abstract
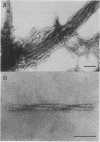
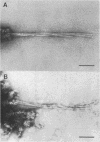
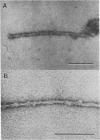
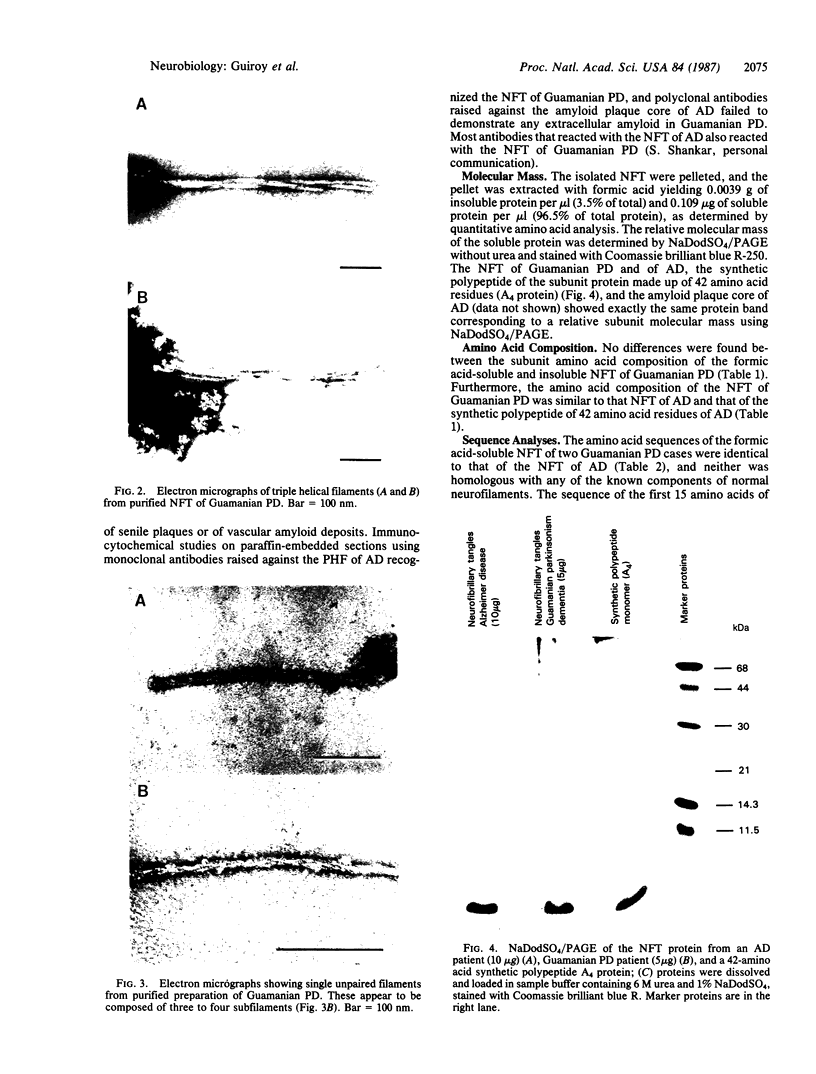
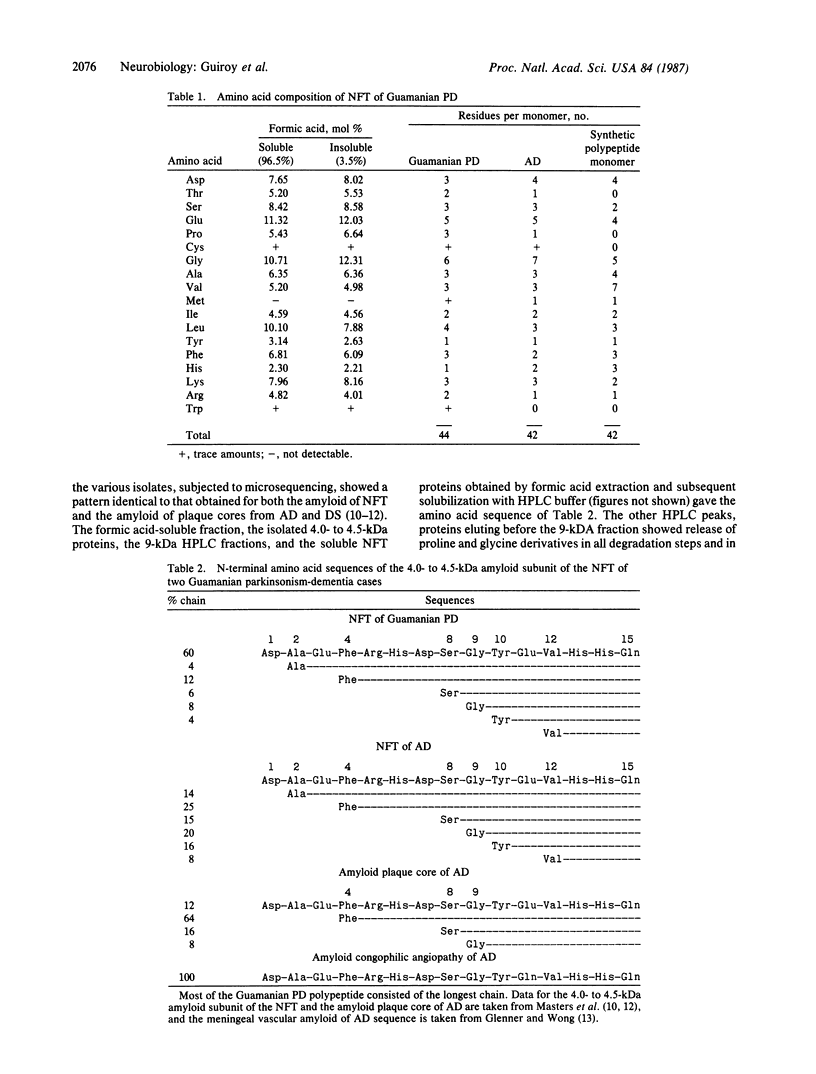
The presence of abundant intraneuronal amyloid in the form of neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) in the brains of Guamanian parkinsonism-dementia patients and the absence of extraneuronal amyloid in the form of vascular amyloid deposits or senile plaques permit the purification of NFT without contamination with extraneuronal amyloid. Thus, we have isolated and determined the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide subunit of the amyloid fibrils of these NFT and describe their ultrastructure. The NFT, which consist of single and paired helical filaments, similar to those of Alzheimer disease, and occasionally triple helical filaments, are composed of multimeric aggregates of a polypeptide of 42 amino acids (A4 protein). The relative molecular mass of the subunit protein, 4.0-4.5 kDa, is the same as the molecular mass of the amyloid of NFT, of the amyloid plaque cores, and of vascular amyloid deposits in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome; the sequence of 15 amino acid residues at the N-terminus of the amyloid fibrils in the NFT of Guamanian parkinsonism-dementia is identical to that of the amyloid of NFT, amyloid plaque cores, and cerebrovascular deposits in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Furthermore, the heterogeneity, or variation in polypeptide length, of the N-terminus of the amyloid of Guamanian parkinsonism-dementia is the same as in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Our observations indicate that the brain amyloids of these diseases have a common subunit protein, which would also indicate a common pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Garruto R. M., Swyt C., Yanagihara R., Fiori C. E., Gajdusek D. C. Intraneuronal co-localization of silicon with calcium and aluminum in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism with dementia of Guam. N Engl J Med. 1986 Sep 11;315(11):711–712. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198609113151115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome: sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1131–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRANO A., KURLAND L. T., KROOTH R. S., LESSELL S. Parkinsonism-dementia complex, an endemic disease on the island of Guam. I. Clinical features. Brain. 1961 Dec;84:642–661. doi: 10.1093/brain/84.4.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRANO A., MALAMUD N., KURLAND L. T. Parkinsonism-dementia complex, an endemic disease on the island of Guam. II. Pathological features. Brain. 1961 Dec;84:662–679. doi: 10.1093/brain/84.4.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara Y., Abraham C., Selkoe D. J. Antibodies to paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease do not recognize normal brain proteins. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):727–730. doi: 10.1038/304727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD M. ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE--AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPICAL STUDY. Brain. 1964 Jun;87:307–320. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R. N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Rohwer R. G., Kascsak R., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection-specific particle from the unconventional slow virus diseases. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):437–440. doi: 10.1126/science.6377496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers-Johnson P., Garruto R. M., Yanagihara R., Chen K. M., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia on Guam: a 30-year evaluation of clinical and neuropathologic trends. Neurology. 1986 Jan;36(1):7–13. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY R. D. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF NEUROFIBRILLARY TANGLES IN ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963 Oct;22:629–642. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196310000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H. M., Narang H. K., Terry R. D. Neurofibrillary tangles of paired helical filaments. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Feb;27(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. W., Quaranta V., Glenner G. G. Neuritic plaques and cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer disease are antigenically related. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8729–8732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]