Abstract
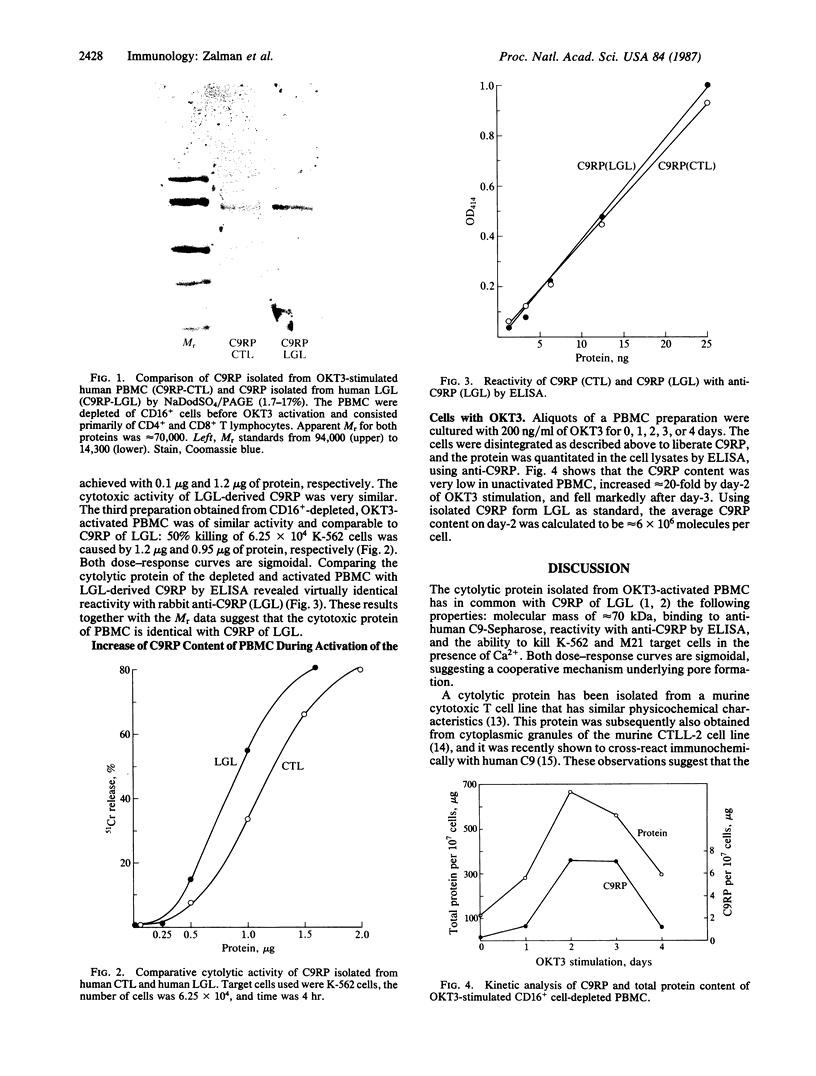
A 70-kDa channel-forming protein has recently been isolated from human large granular lymphocytes maintained in interleukin-2-dependent culture. The protein was shown to be immunochemically related to the ninth component of complement (C9) and was therefore designated C9-related protein (C9RP). Using the procedure that was developed for the isolation of C9RP from large granular lymphocytes--i.e., affinity chromatography employing anti-human C9 linked to Sepharose, a cytolytic protein has now been isolated from OKT3-activated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nineteen to 40 micrograms of active protein was obtained from 1 X 10(9) human peripheral blood mononuclear cells after the cells were cultured for 3 days with OKT3 (monoclonal antibody to cell surface antigen T3). During this period, a marked increment occurred in the amount of the cytotoxic protein contained per cell, indicating that OKT3 induced de novo synthesis of the protein. By NaDodSO4/PAGE the molecular mass was determined to be 70 kDa. By ELISA the isolated protein and C9RP of large granular lymphocytes reacted to the same extent with anti-C9RP. Using K-562 or M21 human melanoma cells as targets, the cytotoxic activity of the isolated protein, in the presence of 5 mM Ca2+, was comparable to that of C9RP. The same cytolytic protein was isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells that were depleted of CD16+ cells prior to OKT3 activation and that consisted primarily of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes. These results suggest that the cytolytic protein of OKT3-activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes is identical with C9RP of interleukin-2-stimulated large granular lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Domzig W., Stadler B. M., Herberman R. B. Interleukin 2 dependence of human natural killer (NK) cell activity. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1970–1973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Yue C. C., Yang J., Rosenberg S. A. Cytolytic and biochemical properties of cytoplasmic granules of murine lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2611–2617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Reynolds C. W., Ortaldo J. R. Mechanism of cytotoxicity by natural killer (NK) cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:651–680. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung G., Honsik C. J., Reisfeld R. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Activation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by anti-T3: killing of tumor target cells coated with anti-target-anti-T3 conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4479–4483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Phillips J. H., Warner N. L., Babcock G. F. Subpopulations of human natural killer cells defined by expression of the Leu-7 (HNK-1) and Leu-11 (NK-15) antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1789–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. A., Kranz D. M., Kurnick J. T., Boyle L. A., Levy R., Eisen H. N. Heteroantibody duplexes target cells for lysis by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8648–8652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger B., Weiss A., Weyand C., Goronzy J., Stobo J. D. T cell activation: differences in the signals required for IL 2 production by nonactivated and activated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3669–3673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. Isolation of a lytic, pore-forming protein (perforin) from cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9069–9072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez P., Hoffman R. W., Shaw S., Bluestone J. A., Segal D. M. Specific targeting of cytotoxic T cells by anti-T3 linked to anti-target cell antibody. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):354–356. doi: 10.1038/316354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and biochemical and functional characterization of perforin 1 from cytolytic T-cell granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8629–8633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab R., Crow M. K., Russo C., Weksler M. E. Requirements for T cell activation by OKT3 monoclonal antibody: role of modulation of T3 molecules and interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1714–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Podack E. R. Formation of transmembrane tubules by spontaneous polymerization of the hydrophilic complement protein C9. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):534–538. doi: 10.1038/298534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Landgraf B., Bentin J., Valentine M., Lotz M., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Activation of resting T lymphocytes by anti-CD3 (T3) antibodies in the absence of monocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1719–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A., Podack E. R. The ninth component of complement and the pore-forming protein (perforin 1) from cytotoxic T cells: structural, immunological, and functional similarities. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):184–190. doi: 10.1126/science.2425429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Podack E. R., Cohn Z. A. Properties of a purified pore-forming protein (perforin 1) isolated from H-2-restricted cytotoxic T cell granules. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):144–155. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Brothers M. A., Chiu F. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mechanism of cytotoxicity of human large granular lymphocytes: relationship of the cytotoxic lymphocyte protein to the ninth component (C9) of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5262–5266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Brothers M. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A C9 related channel forming protein in the cytoplasmic granules of human large granular lymphocytes. Biosci Rep. 1985 Dec;5(12):1093–1100. doi: 10.1007/BF01119631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]