Abstract
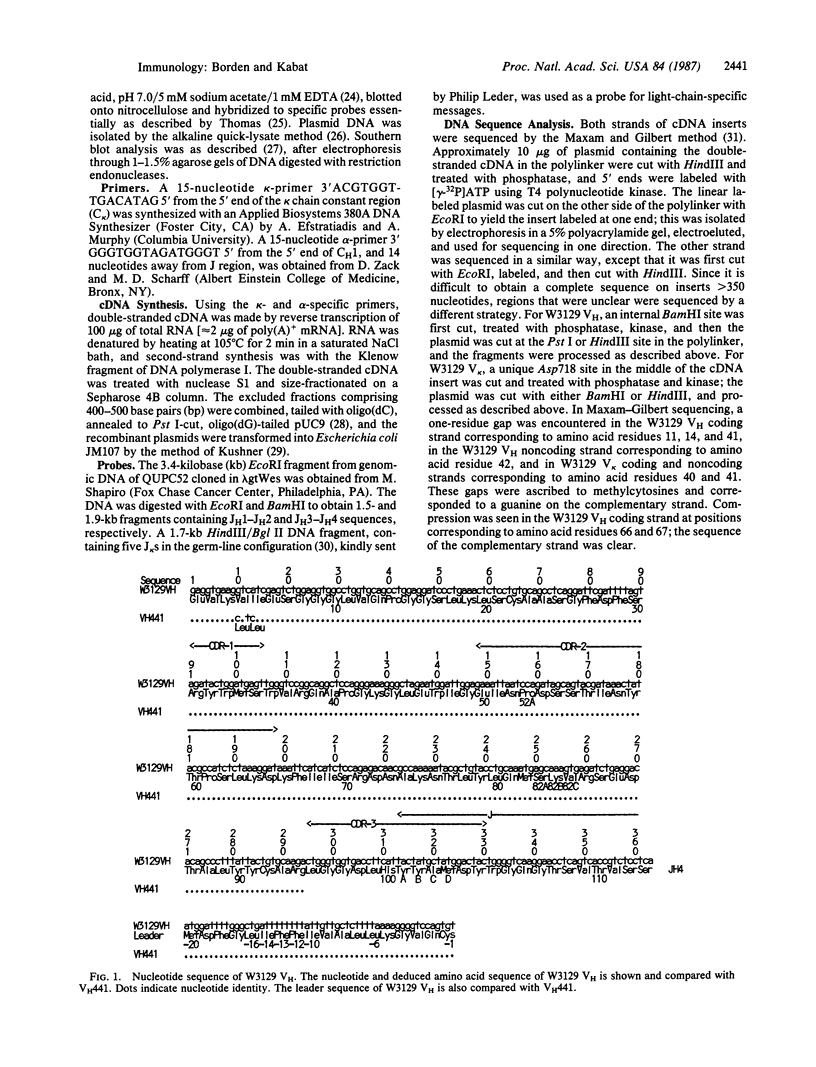
The complete nucleotide sequences of the cDNAs encoding the heavy- and light-chain variable regions (VH and VL) of myeloma protein W3129, an anti-alpha(1----6)-dextran with a unique combining site, have been determined. The VH region is encoded by a germ-line gene highly homologous to VH441, which also appears to be used in some anti-galactans and anti-levans. W3129 VH uses a diversity region that is not found in any of the galactan- or levan-specific antibodies and whose germ-line counterpart is unknown. The W3129 light chain differs from complete light-chain sequences thus far reported but is identical in the first 23 amino acids with NZB IgA myeloma PC118.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Baltimore D. Joining of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene segments: implications from a chromosome with evidence of three D-JH fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4118–4122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenburger W., Steinmetz M., Zachau H. G. Functional and non-functional joining in immunoglobulin light chain genes of a mouse myeloma. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):603–607. doi: 10.1038/287603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barstad P., Farnsworth V., Weigert M., Cohn M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin heavy chains are coded by multiple germ line variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4096–4100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett L. G., Glaudemans C. P. The affinity of a linear, alpha-D-(1 leads to 6)-linked D-glucopyranan (dextran) for homogeneous immunoglobulin A W3129. Carbohydr Res. 1979 Jul;72:315–319. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83958-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Gough N. M., Adams J. M. Plasmacytomas with more than one immunoglobulin kappa mRNA: implications for allelic exclusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5812–5816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boersch-Supan M. E., Agarwal S., White-Scharf M. E., Imanishi-Kari T. Heavy chain variable region. Multiple gene segments encode anti-4-(hydroxy-3-nitro-phenyl)acetyl idiotypic antibodies. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1272–1292. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur P. H., Riblet R. The immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (Igh-V) locus in the mouse. I. One hundred Igh-V genes comprise seven families of homologous genes. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):922–930. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J., Kabat E. A., Dorner M. M., Liao J. Binding properties of immunoglobulin combining sites specific for terminal or nonterminal antigenic determinants in dextran. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):435–459. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J., Kabat E. A., Liao J., Potter M. Immunochemical studies on mouse myeloma proteins reactive with dextrans or with fructosans and on human antilevans. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):159–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Hoostelaere L., Potter M. Genetics of the alpha 1,6-dextran response: expression of the QUPC52 idiotype in different inbred and congenic strains of mice. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):492–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez C., Lieberman R., Möller G. The immune response to the alpha 1-6 epitope of dextran is determined by a gene linked to the IgCH locus. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(1):77–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaudemans C. P. Immunodominance of terminal sugars revisited. Mol Immunol. 1986 Aug;23(8):917–918. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gridley T., Margolies M. N., Gefter M. L. The association of various D elements with a single-immunoglobulin VH gene segment: influence on the expression of a major cross-reactive idiotype. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1236–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivars F., Holmberg D., Coutinho A. The immune response to bacterial dextrans. I. Genetic control of responsiveness. Scand J Immunol. 1983 May;17(5):419–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juszczak E., Near R. I., Gefter M. L., Margolies M. N. Complete heavy and light chain variable region sequence of anti-arsonate monoclonal antibodies from BALB/c and A/J mice sharing the 36-60 idiotype are highly homologous. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2603–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KABAT E. A. Heterogeneity in extent of the combining regions of human antidextran. J Immunol. 1956 Dec;77(6):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KABAT E. A. The upper limit for the size of the human antidextran combining site. J Immunol. 1960 Jan;84:82–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaartinen M., Griffiths G. M., Hamlyn P. H., Markham A. F., Karjalainen K., Pelkonen J. L., Mäkelä O., Milstein C. Anti-oxazolone hybridomas and the structure of the oxazolone idiotype. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):937–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Wiedemann L. M., Pittet A. C., Strauss S., Nelson K. J., Davis J., Van Ness B., Perry R. P. Nonproductive kappa immunoglobulin genes: recombinational abnormalities and other lesions affecting transcription, RNA processing, turnover, and translation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1660–1675. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa Y., Tonegawa S. Organization, structure, and assembly of immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity DNA segments. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):201–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies of conjugates of isomaltosyl oligosaccharides to lipid: production and characterization of mouse hybridoma antibodies specific for stearyl-isomaltosyl oligosaccharides. Mol Immunol. 1985 Sep;22(9):1021–1037. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh E., Black B., Riblet R., Weigert M., Hood J. M., Hood L. Myeloma proteins from NZB and BALB/c mice: structural and functional differences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1395–1399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGE R. G., KABAT E. A. IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON DEXTRANS. III. THE SPECIFICITIES OF RABBIT ANTIDEXTRANS. FURTHER FINDINGS ON ANTIDEXTRANS WITH 1,2- AND 1,6-SPECIFICITIES. J Immunol. 1963 Nov;91:633–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The nucleotide sequence of a 5.5-kilobase DNA segment containing the mouse kappa immunoglobulin J and C region genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman B. A., Kabat E. A. An immunochemical study of the combining site specificities of C57BL/6J monoclonal antibodies to alpha (1----6)-linked dextran B512. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1220–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollo R., Auffray C., Sikorav J. L., Rougeon F. Mouse heavy chain variable regions: nucleotide sequence of a germ-line VH gene segment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4099–4109. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Klotz J. L., Bond M. W., Nahm M., Davie J. M., Hood L. Multiple VH gene segments encode murine antistreptococcal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):179–192. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Newell J. B., Rudikoff S., Haber E. Classification of mouse VK groups based on the partial amino acid sequence to the first invariant tryptophan: impact of 14 new sequences from IgG myeloma proteins. Mol Immunol. 1982 Dec;19(12):1619–1630. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. N., Rudikoff S., Krutzsch H., Potter M. Structural evidence for independent joining region gene in immunoglobulin heavy chains from anti-galactan myeloma proteins and its potential role in generating diversity in complementarity-determining regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2890–2894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon J., Kabat E. A., Morrison S. L. Immunochemical characterization of binding sites of hybridoma antibodies specific for alpha (1 leads to 6) linked dextran. Mol Immunol. 1982 Mar;19(3):375–388. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikder S. K., Akolkar P. N., Kaladas P. M., Morrison S. L., Kabat E. A. Sequences of variable regions of hybridoma antibodies to alpha (1----6) dextran in BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4215–4221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnelle C., Rocca-Serra J., Moulin A., Moinier D., Fougereau M. V kappa gene family in (Glu60 Ala30 Tyr10)n (GAT)-specific antibodies that express CGAT (or pGAT) public idiotypic specificities. Protein and mRNA sequencing of eight monoclonal V kappa chains. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1415–1427. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M., Raschke W. C., Carson D., Cohn M. Immunochemical analysis of the idiotypes of mouse myeloma proteins with specificity for levan or dextran. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):137–147. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies of conjugates of isomaltosyl oligosaccharides to lipid: specificities and reactivities of the antibodies formed in rabbits to stearyl-isomaltosyl oligosaccharides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):262–276. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



