Abstract
Identification and characterization of the cDNA encoding rat neuropeptide Y revealed the nucleotide sequence coding for a 98-amino acid precursor. The deduced amino acid sequence for rat neuropeptide Y is identical to the human peptide and is highly homologous to avian pancreatic polypeptide. The tertiary structure of avian pancreatic polypeptide has been previously derived from crystallographic data by Blundell and coworkers. The homology between neuropeptide Y and avian pancreatic polypeptide preserves all of the residues essential for the maintenance of the tertiary structure. Thus, it has been possible to compute a three-dimensional model of the mammalian neuropeptide, neuropeptide Y, based on the known structure of the avian homologue. This model suggest that neuropeptide preserves a compact tertiary structure characterized by extensive hydrophobic interactions between an N-terminal polyproline-II-like helix and a C-terminal alpha-helix. The model has been used to identify amino acids residing in key positions within this structure and, thereby, to direct future analysis of neuropeptide Y structure-function relationships.
Full text
PDF
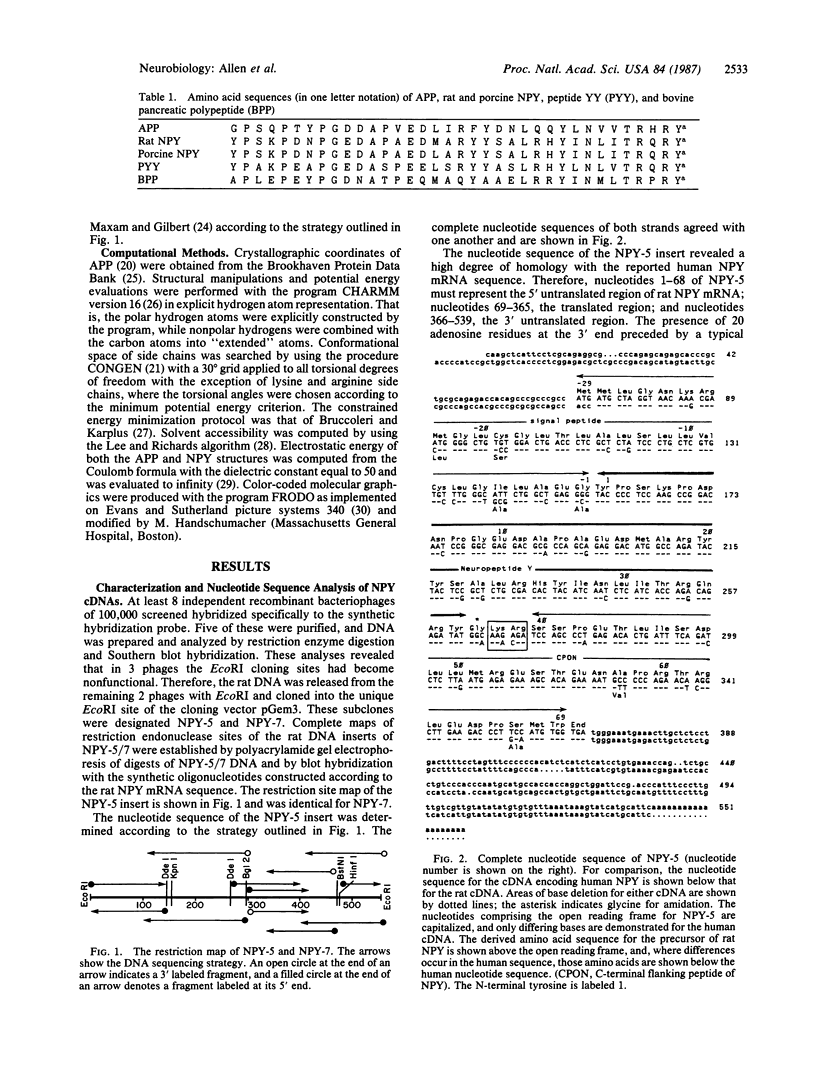
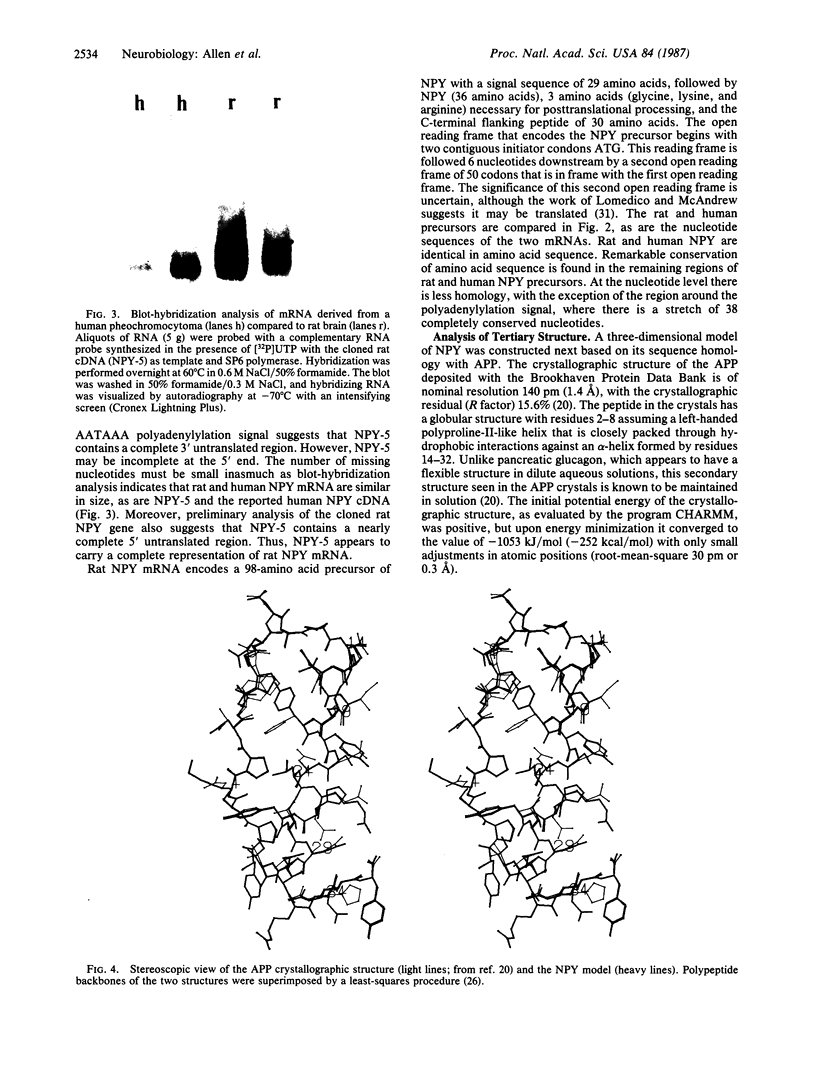


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. M., Bircham P. M., Edwards A. V., Tatemoto K., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) reduces myocardial perfusion and inhibits the force of contraction of the isolated perfused rabbit heart. Regul Pept. 1983 Jul;6(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Ferrier I. N., Roberts G. W., Cross A. J., Adrian T. E., Crow T. J., Bloom S. R. Elevation of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in substantia innominata in Alzheimer's type dementia. J Neurol Sci. 1984 Jun;64(3):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(84)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Polak J. M., Rodrigo J., Darcy K., Bloom S. R. Localisation of neuropeptide Y in nerves of the rat cardiovascular system and the effect of 6-hydroxydopamine. Cardiovasc Res. 1985 Sep;19(9):570–577. doi: 10.1093/cvr/19.9.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Raine A. E., Ledingham J. G., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide Y: a novel renal peptide with vasoconstrictor and natriuretic activity. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Apr;68(4):373–377. doi: 10.1042/cs0680373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen Y. S., Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Tatemoto K., Crow T. J., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):877–879. doi: 10.1126/science.6136091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruccoleri R. E., Karplus M. Prediction of the folding of short polypeptide segments by uniform conformational sampling. Biopolymers. 1987 Jan;26(1):137–168. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chronwall B. M., DiMaggio D. A., Massari V. J., Pickel V. M., Ruggiero D. A., O'Donohue T. L. The anatomy of neuropeptide-Y-containing neurons in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1985 Aug;15(4):1159–1181. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. T., Kalra P. S., Crowley W. R., Kalra S. P. Neuropeptide Y and human pancreatic polypeptide stimulate feeding behavior in rats. Endocrinology. 1984 Jul;115(1):427–429. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-1-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbaere L. T., Brayer G. D., James M. N. Comparison of the predicted model of alpha-lytic protease with the x-ray structure. Nature. 1979 May 10;279(5709):165–168. doi: 10.1038/279165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Edvinsson L., Wahlestedt C., Uddman R., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Neuropeptide Y co-exists and co-operates with noradrenaline in perivascular nerve fibers. Regul Pept. 1984 Apr;8(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover I., Haneef I., Pitts J., Wood S., Moss D., Tickle I., Blundell T. Conformational flexibility in a small globular hormone: x-ray analysis of avian pancreatic polypeptide at 0.98-A resolution. Biopolymers. 1983 Jan;22(1):293–304. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert E., Uhler M. Biosynthesis of polyprotein precursors to regulatory peptides. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Ljungdahl A., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M. Peptidergic neurones. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):515–521. doi: 10.1038/284515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter A. B., Montminy M. R., Jamieson E., Goodman R. H. Exons of the human pancreatic polypeptide gene define functional domains of the precursor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13013–13017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., McAndrew S. J. Eukaryotic ribosomes can recognize preproinsulin initiation codons irrespective of their position relative to the 5' end of mRNA. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):221–226. doi: 10.1038/299221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Pancreatic polypeptide family (APP, BPP, NPY and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martel J. C., St-Pierre S., Quirion R. Neuropeptide Y receptors in rat brain: autoradiographic localization. Peptides. 1986 Jan-Feb;7(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Lumpkin M. D., Samson W. K., McCann S. M. Neuropeptide Y affects secretion of luteinizing hormone and growth hormone in ovariectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):561–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minth C. D., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M., Dixon J. E. Cloning, characterization, and DNA sequence of a human cDNA encoding neuropeptide tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4577–4581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Bruccoleri R., Karplus M. An analysis of incorrectly folded protein models. Implications for structure predictions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 25;177(4):787–818. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read R. J., Brayer G. D., Jurásek L., James M. N. Critical evaluation of comparative model building of Streptomyces griseus trypsin. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6570–6575. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rioux F., Bachelard H., Martel J. C., St-Pierre S. The vasoconstrictor effect of neuropeptide Y and related peptides in the guinea pig isolated heart. Peptides. 1986 Jan-Feb;7(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley B. G., Leibowitz S. F. Neuropeptide Y: stimulation of feeding and drinking by injection into the paraventricular nucleus. Life Sci. 1984 Dec 24;35(26):2635–2642. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y--a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):659–660. doi: 10.1038/296659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Isolation and characterization of peptide YY (PYY), a candidate gut hormone that inhibits pancreatic exocrine secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2514–2518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A., Russell S. T., Churg A. K. Macroscopic models for studies of electrostatic interactions in proteins: limitations and applicability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4785–4789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]