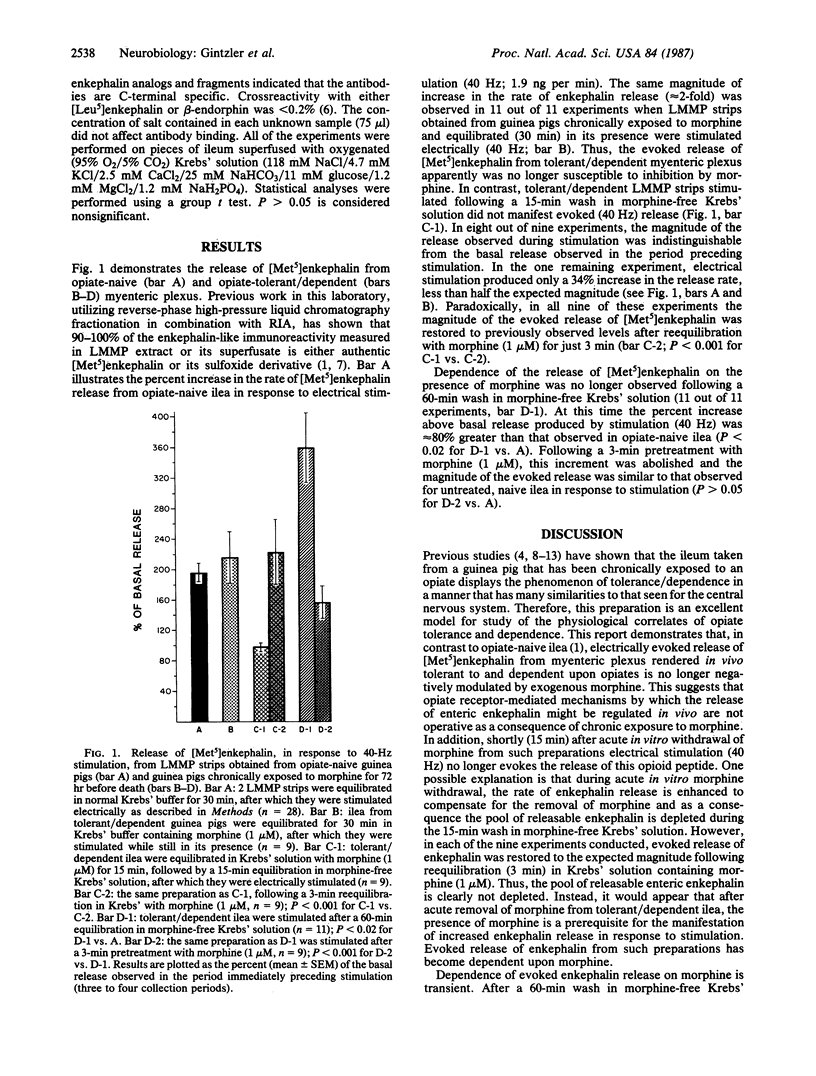
Abstract
Experiments were performed in order to determine whether the state of tolerance to and dependence upon opiates is associated with changes in one or more of the characteristics of the electrically induced release of methionine enkephalin from enteric ganglia. Acute morphine pretreatment substantially reduces the magnitude of the evoked release of this peptide from opiate-naive ilea. However, the rate of the evoked release of enkephalin from morphine-pretreated, tolerant/dependent preparations is indistinguishable from that observed for untreated, naive ilea. Paradoxically, 15 min after acute in vitro withdrawal of morphine form such preparations, the presence of morphine appears to be prerequisite for the manifestation of electrically evoked release of methionine enkephalin. The evoked release of this peptide from ilea 60 min after withdrawal is no longer dependent upon morphine. Moreover, the magnitude of the increase in the rate of enkephalin release from these preparations is almost double that observed for opiate-naive ilea. These data indicate that the manifestation of opiate tolerance/dependence for the release of methionine enkephalin from enteric ganglia comprises several adaptive processes, the consequences of which can be observed at different stages of withdrawal.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBACHE N. Separation of the longitudinal muscle of the rabbit's ileum as a broad sheet. J Physiol. 1954 Aug 27;125(2):53–5P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron S. A., Jaffe B. M., Gintzler A. R. Release of substance P from the enteric nervous system: direct quantitation and characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Nov;227(2):365–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Smith T. W. Peristalsis abolishes the release of methionine-enkephalin from guinea-pig ileum in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 26;70(3):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gintzler A. R. Serotonin participation in gut withdrawal from opiates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Oct;211(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gintzler A. R. Substance P involvement in the expression of gut dependence on opiates. Brain Res. 1980 Jan 20;182(1):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90850-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass J., Chan W. C., Gintzler A. R. Direct analysis of the release of methionine-enkephalin from guinea pig myenteric plexus: modulation by endogenous opioids and exogenous morphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Dec;239(3):742–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass J., Clouet D., Gintzler A. R. Short-term nerve stimulation increases enkephalin production and content in the guinea pig myenteric plexus. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 30;372(1):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91475-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Schulz R. Morphine-tolerant longitudinal muscle strip from guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Aug;48(4):655–666. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08254.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTILA M. The effects of morphine and nalorphine on the small intestine of normal and morphine-tolerant rat and guinea-pig. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1962;19:47–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1962.tb00338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. T., Corbett A. D., Kosterlitz H. W. Increase in potencies of opioid peptides after peptidase inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Karras P. J. Opiate tolerance and dependence induced in vitro in single myenteric neurones. Nature. 1978 Mar 2;272(5648):73–75. doi: 10.1038/272073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Herz A. Aspects of opiate dependence in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 15;19(8):1117–1127. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. Dual regulation of adenylate cyclase accounts for narcotic dependence and tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



