Abstract
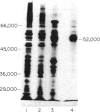
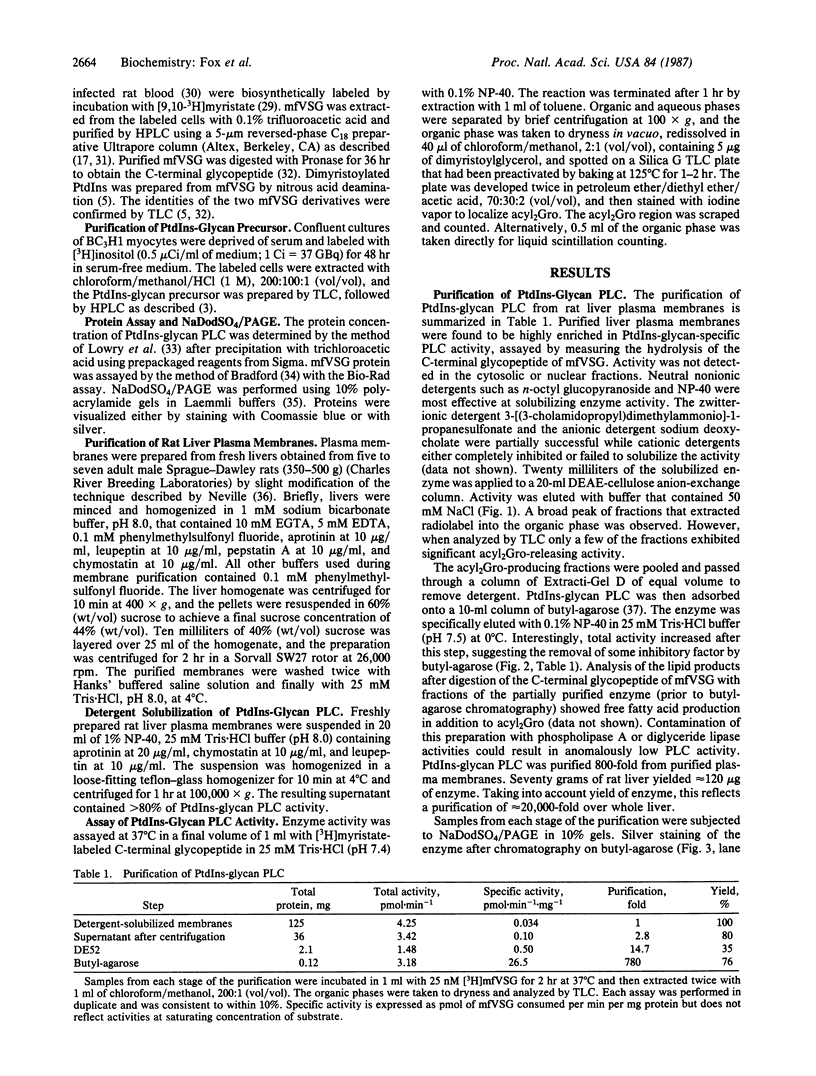
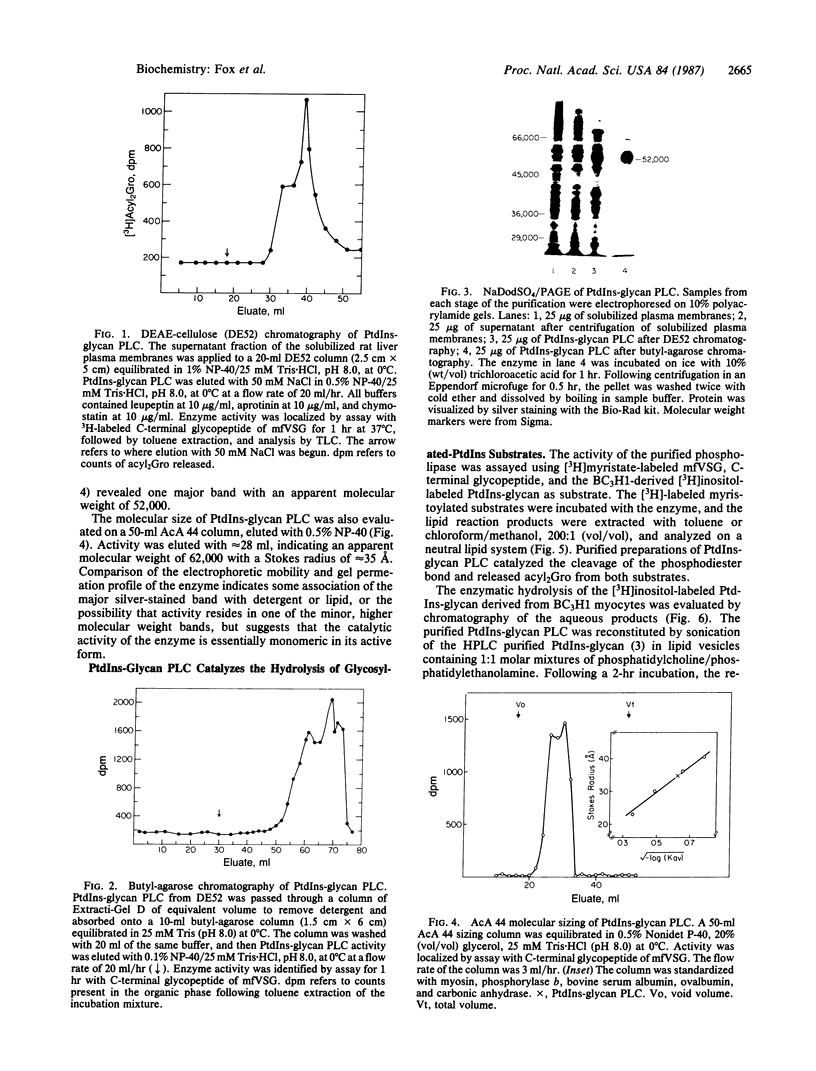
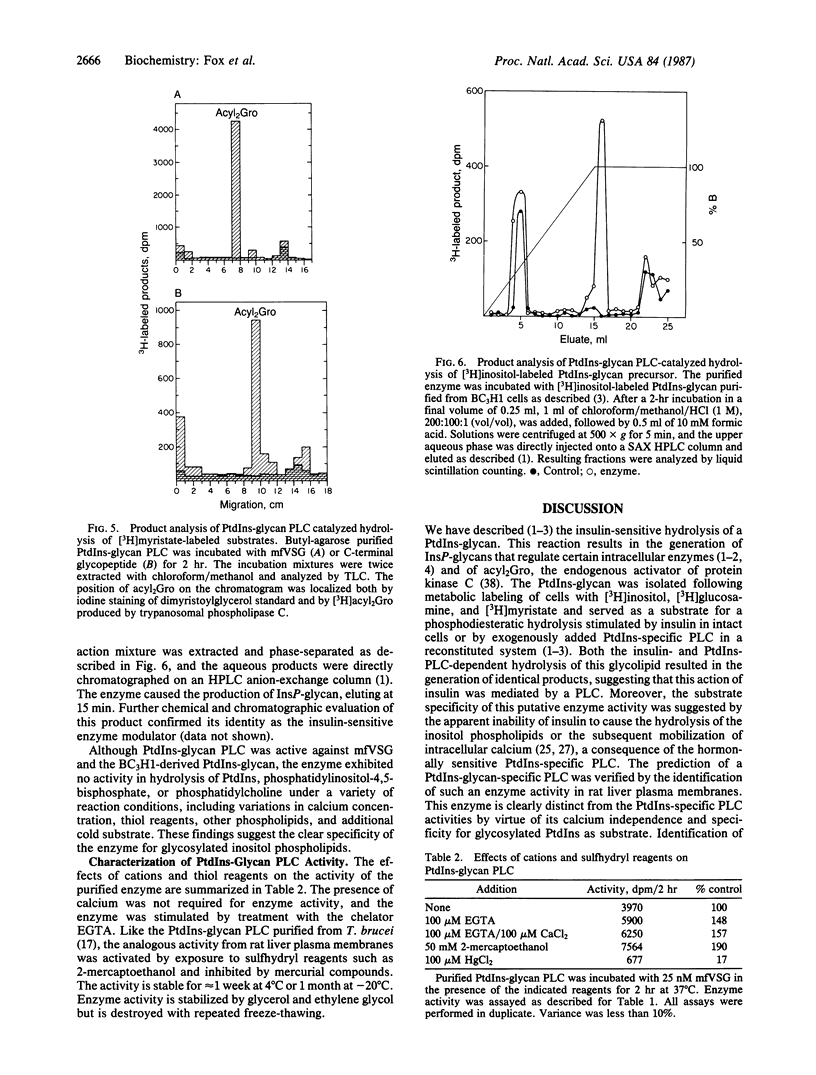
Insulin stimulates the hydrolysis of a phosphatidylinositol-glycan, resulting in the generation of two related inositol phosphate-glycan enzyme modulators and diacylglycerol. A phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase C that catalyzed this reaction was found in the plasma-membrane fraction of rat liver. The enzymatic activity was measured by the release of diacylglycerol from the glycosylated-phosphatidylinositol-membrane-anchored variant surface glycoproteins of African trypanosomes. The enzyme also catalyzed the production of an inositol phosphate-glycan from an insulin-sensitive phosphatidylinositol-glycan precursor. The enzyme was solubilized with neutral nonionic detergent and purified to near homogeneity by anion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-cellulose, followed by hydrophobic chromatography on butyl-agarose. The resulting enzyme preparation was purified approximately 20,000-fold from whole liver and exhibited one major silver-stained band of Mr 52,000 on NaDodSO4/PAGE. Gel permeation chromatography of the purified activity revealed a Stokes radius of 35 A and an apparent molecular weight of 62,000, suggesting that the enzyme was tightly associated with lipid or detergent but existed as a monomer in its active form. The enzyme was specific for glycosylated phosphatidylinositol; no hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, or phosphatidylcholine was observed. The enzyme was calcium independent and thiol activated. These data suggest a role for the phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase C as an effector for some of the metabolic actions of insulin.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow R., Overath P. Purification and characterization of the membrane-form variant surface glycoprotein hydrolase of Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11918–11923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso de Almeida M. L., Turner M. J. The membrane form of variant surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):349–352. doi: 10.1038/302349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. W., Olafson R. W., Pearson T. W. Rapid preparative scale purification of myristylated variant surface glycoproteins from African trypanosomes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Oct;17(1):19–34. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Identification, purification and properties of clone-specific glycoprotein antigens constituting the surface coat of Trypanosoma brucei. Parasitology. 1975 Dec;71(3):393–417. doi: 10.1017/s003118200004717x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Low M. G., Nussenzweig V. Release of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) from the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PIPLC). Selective modification of a complement regulatory protein. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1150–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Torrontegui G., Berthet J. The action of insulin on the incorporation of [32P]phosphate in the phospholipids of rat adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 1;116(3):477–481. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Davis J. S., Barnes D. E., Standaert M. L., Babischkin J. S., Hock R., Rosic N. K., Pollet R. J. The de novo phospholipid effect of insulin is associated with increases in diacylglycerol, but not inositol phosphates or cytosolic Ca2+. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):269–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2310269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Larson R. E., Sabir M. A. Insulin acutely increases phospholipids in the phosphatidate-inositide cycle in rat adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4042–4045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Cross G. A. Myristylation of the membrane form of a Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3011–3015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Haldar K., Cross G. A. Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein has a sn-1,2-dimyristyl glycerol membrane anchor at its COOH terminus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4963–4968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14547–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A., Duszenko M., Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Purification and characterization of a novel glycan-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15767–15771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sáinz J. A., Fain J. N. Effect of insulin, catecholamines and calcium ions on phospholipid metabolism in isolated white fat-cells. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):781–789. doi: 10.1042/bj1860781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He H. T., Barbet J., Chaix J. C., Goridis C. Phosphatidylinositol is involved in the membrane attachment of NCAM-120, the smallest component of the neural cell adhesion molecule. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2489–2494. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereld D., Krakow J. L., Bangs J. D., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. A phospholipase C from Trypanosoma brucei which selectively cleaves the glycolipid on the variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13813–13819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman T. W., Strohsnitter W., Scheid C. R., Schimmel R. J. Phosphatidic acid and phosphatidylinositol labelling in adipose tissue. Relationship to the metabolic effects of insulin and insulin-like agents. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):489–498. doi: 10.1042/bj2120489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezawa H., Yamanegi M., Taguchi R., Miyashita T., Ohyabu T. Studies on phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase (phospholipase C type) of Bacillus cereus. I. purification, properties and phosphatase-releasing activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 19;450(2):154–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. R., Murray E., Manolagas S., Olefsky J. M. Demonstration of insulin receptors and modulation of alkaline phosphatase activity by insulin in rat osteoblastic cells. Endocrinology. 1986 Oct;119(4):1786–1792. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-4-1786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. Non-lytic release of acetylcholinesterase from erythrocytes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80905-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. Specific release of plasma membrane enzymes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 20;508(3):565–570. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington S. R., Martin B. R. Insulin-stimulated phosphoinositide metabolism in isolated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11039–11045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser H., Oettgen H., Yeh E. T., Terhorst C., Low M. G., Benacerraf B., Rock K. L. Structural characterization of the TAP molecule: a phosphatidylinositol-linked glycoprotein distinct from the T cell receptor/T3 complex and Thy-1. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90593-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin stimulates the generation from hepatic plasma membranes of modulators derived from an inositol glycolipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Fox J. A., Sherline P., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin-stimulated hydrolysis of a novel glycolipid generates modulators of cAMP phosphodiesterase. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):967–972. doi: 10.1126/science.3016898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R. Insulin generates an enzyme modulator from hepatic plasma membranes: regulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and adenylate cyclase. Endocrinology. 1987 Mar;120(3):967–972. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-3-967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Sherline P., Fox J. A. Insulin-stimulated diacylglycerol production results from the hydrolysis of a novel phosphatidylinositol glycan. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1116–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaltiel S. Hydrophobic chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:69–96. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. M., Hales C. N. The effect of insulin on 32Pi incorporation into rat fat cell phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jan 23;337(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D., Uhing R. J., Blackmore P. F., Prpić V., Exton J. H. Insulin and epidermal growth factor do not affect phosphoinositide metabolism in rat liver plasma membranes and hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2011–2014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]