Abstract
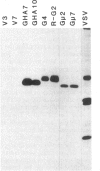
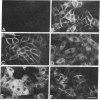
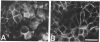
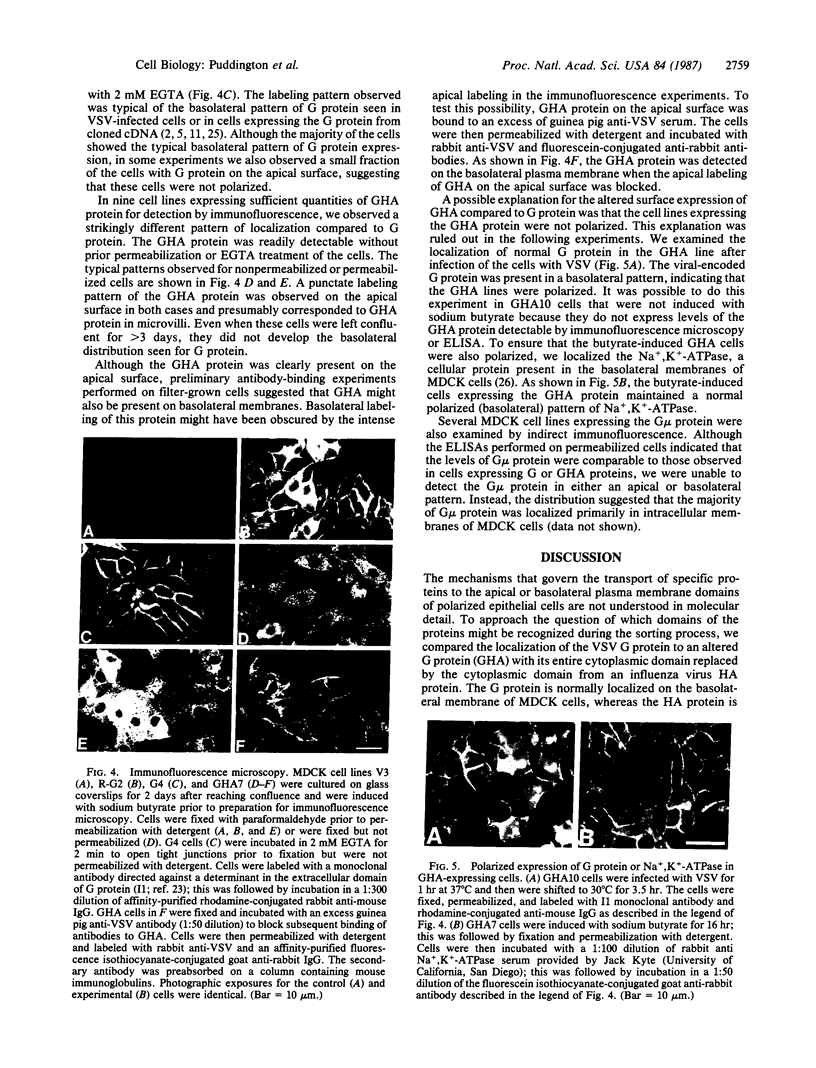
The envelope glycoprotein (G protein) of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is transported to the basolateral plasma membrane of polarized epithelial cells, whereas the hemagglutinin glycoprotein (HA protein) of influenza virus is transported to the apical plasma membrane. To determine if the cytoplasmic domain of VSV G protein might be important in directing G protein to the basolateral membrane, we derived polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cell lines expressing G protein or G protein with its normal cytoplasmic domain replaced with the cytoplasmic domain from an influenza HA protein (GHA protein). Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy showed that G protein was present primarily on basolateral surfaces, whereas the GHA protein was present on the apical and basolateral membranes. These results suggest that the cytoplasmic domain can be an important determinant directing polarized expression of an integral membrane protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chabanas A., Khoury E., Goeltz P., Froussard P., Gjerset R., Dod B., Eisen H., Lawrence J. J. Effects of butyric acid on cell cycle regulation and induction of histone H1(0) in mouse cells and tissue culture. Inducibility of H1 (0)in the late S-G2 phase of the cell cycle. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkiewicz R. Z., Smith A., Bergmann J. E., Rose J. K. Isolation of stable mouse cell lines that express cell surface and secreted forms of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1381–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D., Bravo R., Simons K. An enzymatic assay reveals that proteins destined for the apical or basolateral domains of an epithelial cell line share the same late Golgi compartments. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):297–307. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03629.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S., von Bonsdorff C. H., Simons K. Vesicular stomatitis virus infects and matures only through the basolateral surface of the polarized epithelial cell line, MDCK. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Howard B. H., Reeves R. Expression of recombinant plasmids in mammalian cells is enhanced by sodium butyrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7631–7648. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb T. A., Gonzalez A., Rizzolo L., Rindler M. J., Adesnik M., Sabatini D. D. Sorting and endocytosis of viral glycoproteins in transfected polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1242–1255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondor-Koch C., Bravo R., Fuller S. D., Cutler D., Garoff H. Exocytotic pathways exist to both the apical and the basolateral cell surface of the polarized epithelial cell MDCK. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancois L., Lyles D. S. The interaction of antibody with the major surface glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Analysis of neutralizing epitopes with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1982 Aug;121(1):157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancois L. Protection against lethal viral infection by neutralizing and nonneutralizing monoclonal antibodies: distinct mechanisms of action in vivo. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):208–214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.208-214.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D. Apical membrane aminopeptidase appears at site of cell-cell contact in cultured kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4132–4136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Sorting of an apical plasma membrane glycoprotein occurs before it reaches the cell surface in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2131–2139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misek D. E., Bard E., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Biogenesis of epithelial cell polarity: intracellular sorting and vectorial exocytosis of an apical plasma membrane glycoprotein. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90460-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Kelly R. B. Secretory protein targeting in a pituitary cell line: differential transport of foreign secretory proteins to distinct secretory pathways. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1773–1781. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer S., Fuller S. D., Simons K. Intracellular sorting and basolateral appearance of the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):470–476. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
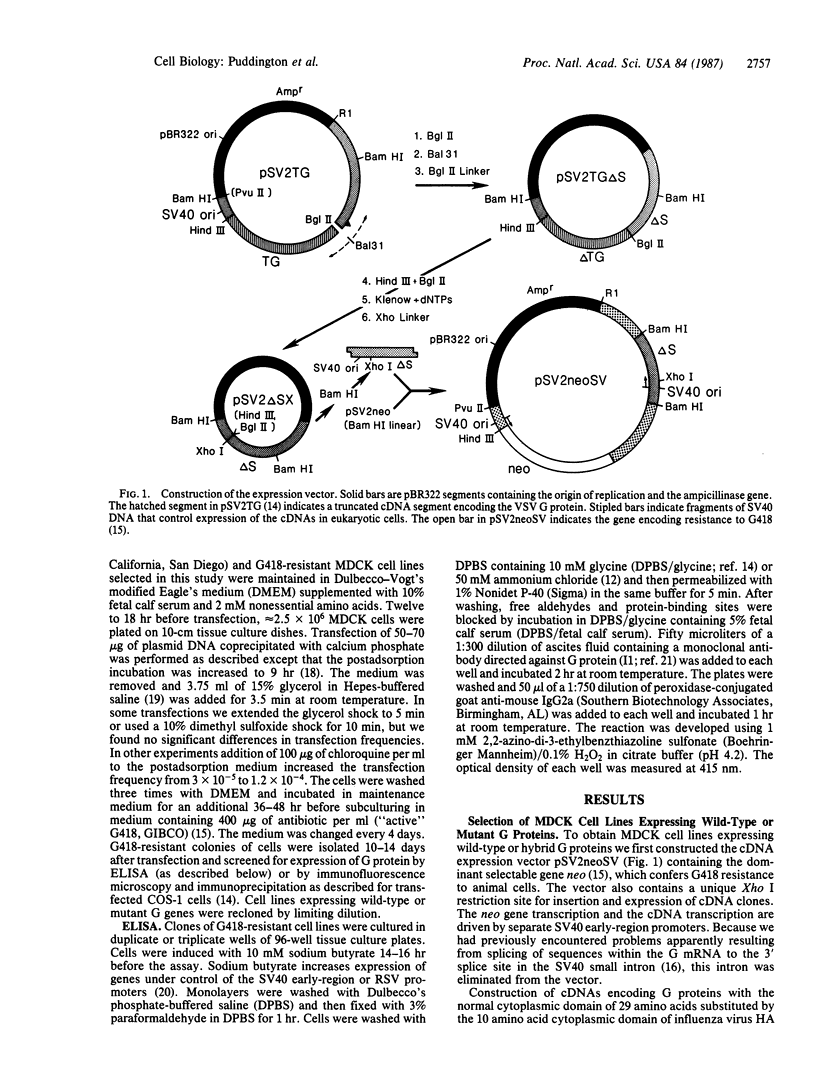
- Puddington L., Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. Cytoplasmic domains of cellular and viral integral membrane proteins substitute for the cytoplasmic domain of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein in transport to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2147–2157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Ivanov I. E., Plesken H., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Sabatini D. D. Viral glycoproteins destined for apical or basolateral plasma membrane domains traverse the same Golgi apparatus during their intracellular transport in doubly infected Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1304–1319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Ivanov I. E., Plesken H., Sabatini D. D. Polarized delivery of viral glycoproteins to the apical and basolateral plasma membranes of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells infected with temperature-sensitive viruses. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):136–151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Boulan E., Pendergast M. Polarized distribution of viral envelope proteins in the plasma membrane of infected epithelial cells. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Boulan E., Sabatini D. D. Asymmetric budding of viruses in epithelial monlayers: a model system for study of epithelial polarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Altered cytoplasmic domains affect intracellular transport of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. G., Compans R. W., Giusti L., Davis A. R., Nayak D. P., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Influenza virus hemagglutinin expression is polarized in cells infected with recombinant SV40 viruses carrying cloned hemagglutinin DNA. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Fuller S. D. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. B., Compans R. W., Earl P., Moss B. Surface expression of viral glycoproteins is polarized in epithelial cells infected with recombinant vaccinia viral vectors. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):237–245. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04204.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]