Abstract
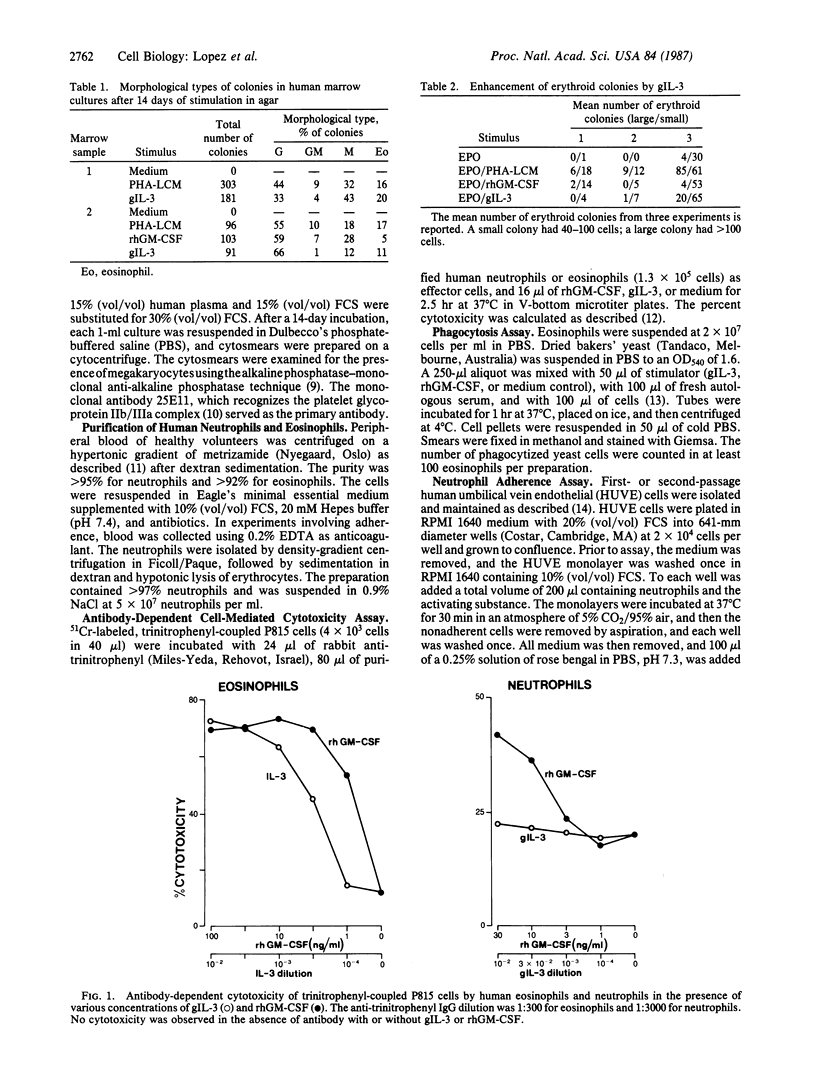
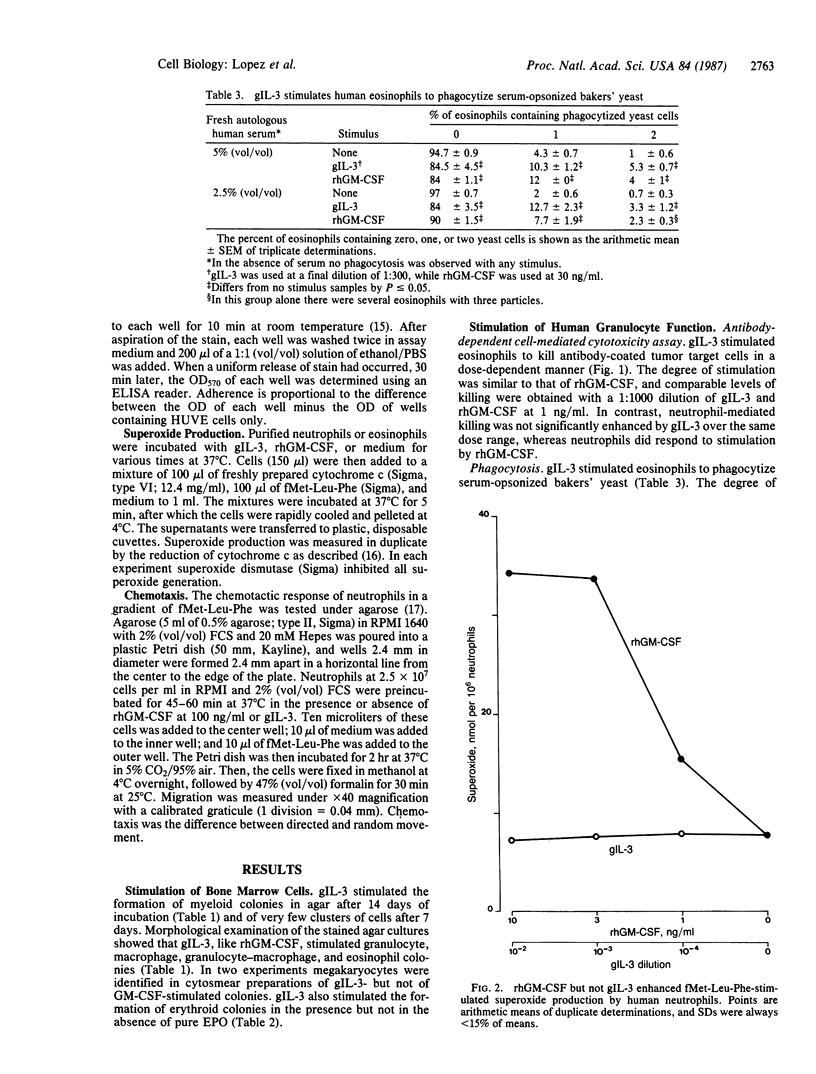
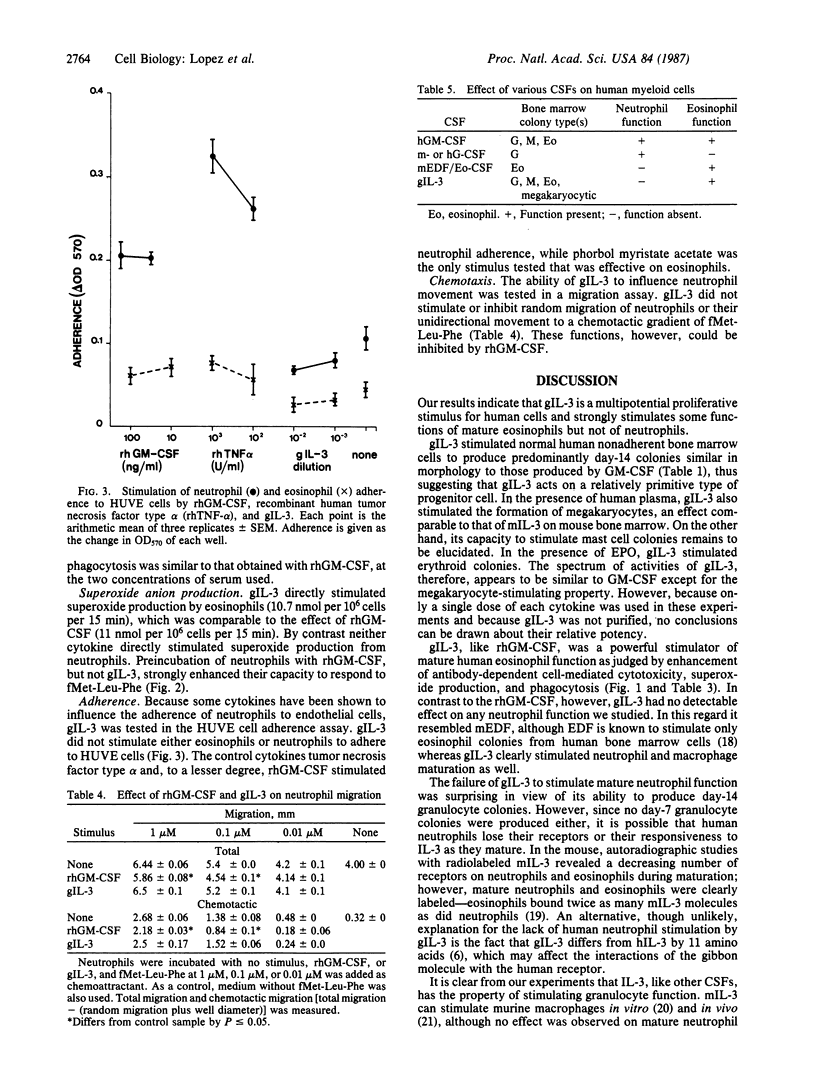
Cloned gibbon interleukin 3 (gIL-3) was found to stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of human bone marrow cells to produce day-14 granulocyte, macrophage, granulocyte-macrophage, and eosinophil colonies in semisolid agar. In the presence of normal human plasma, gIL-3 stimulated megakaryocytes. In methylcellulose cultures, it stimulated erythroid colonies in the presence, but not in the absence, of erythropoietin. When mature human leukocytes were used, gIL-3 stimulated the function of purified mature eosinophils as measured by the capacity to kill antibody-coated target cells, to produce superoxide anions, and to phagocytize opsonized yeast particles in a manner similar to recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. In contrast, gIL-3 did not significantly stimulate any of the neutrophil functions tested, whereas human recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor was active in these assays. Among cytokines that are active on human hematopoietic cells, gIL-3 thus has a distinct set of functions and may predict the range of actions of the human molecule.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burns G. F., Cosgrove L., Triglia T., Beall J. A., López A. F., Werkmeister J. A., Begley C. G., Haddad A. P., d'Apice A. J., Vadas M. A. The IIb-IIIa glycoprotein complex that mediates platelet aggregation is directly implicated in leukocyte adhesion. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong A. S., Parish C. R. Nonimmune lymphocyte-macrophage interaction. II. Evidence that the interaction involves sulfated polysaccharide recognition. Cell Immunol. 1985 May;92(2):277–289. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Kent S. B., Schrader J. W. Purification to apparent homogeneity of a factor stimulating the growth of multiple lineages of hemopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7488–7494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapper R. M., Vairo G., Hamilton J. A., Clark-Lewis I., Schrader J. W. Stimulation of bone marrow-derived and peritoneal macrophages by a T lymphocyte-derived hemopoietic growth factor, persisting cell-stimulating factor. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):859–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. L., Metcalf D., Nicola N. A., Johnson G. R. Purification of a multipotential colony-stimulating factor from pokeweed mitogen-stimulated mouse spleen cell conditioned medium. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6579–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emotion and immunity. Lancet. 1985 Jul 20;2(8447):133–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. C., Hapel A. J., Ymer S., Cohen D. R., Johnson R. M., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Molecular cloning of cDNA for murine interleukin-3. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):233–237. doi: 10.1038/307233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophils to umbilical vein endothelium by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8667–8671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Oroszlan S., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Fitch F., Prystowsky M. B., Goldwasser E., Schrader J. W., Palaszynski E. Biologic properties of homogeneous interleukin 3. I. Demonstration of WEHI-3 growth factor activity, mast cell growth factor activity, p cell-stimulating factor activity, colony-stimulating factor activity, and histamine-producing cell-stimulating factor activity. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Begley C. G., Williamson D. J., Warren D. J., Vadas M. A., Sanderson C. J. Murine eosinophil differentiation factor. An eosinophil-specific colony-stimulating factor with activity for human cells. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1085–1099. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J., Gamble J. R., Begley C. G., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Waltersdorph A., Wong G., Clark S. C., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates in vitro mature human neutrophil and eosinophil function, surface receptor expression, and survival. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1220–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI112705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Begley C. G., Johnson G. R., Nicola N. A., Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J. Effects of purified bacterially synthesized murine multi-CSF (IL-3) on hematopoiesis in normal adult mice. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):46–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Begley C. G., Johnson G. R., Nicola N. A., Vadas M. A., Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J., Wong G. G., Clark S. C., Wang E. A. Biologic properties in vitro of a recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):37–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Binding of iodinated multipotential colony-stimulating factor (interleukin-3) to murine bone marrow cells. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Aug;128(2):180–188. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., O'Garra A., Warren D. J., Klaus G. G. Eosinophil differentiation factor also has B-cell growth factor activity: proposed name interleukin 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):437–440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne K. J., Richardson B. A., Taverne J., Williamson D. J., Vadas M. A., Butterworth A. E. A comparison of eosinophil-activating factor (EAF) with other monokines and lymphokines. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Sep;16(9):1143–1149. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., David J. R., Butterworth A., Pisani N. T., Siongok T. A. A new method for the purification of human eosinophils and neutrophils, and a comparison of the ability of these cells to damage schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1228–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Activation of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of human neutrophils and eosinophils by separate colony-stimulating factors. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):795–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., Nicola N., Lopez A. F., Metcalf D., Johnson G., Pereira A. Mononuclear cell-mediated enhancement of granulocyte function in man. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):202–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veith M. C., Butterworth A. E. Enhancement of human eosinophil-mediated killing of Schistosoma mansoni larvae by mononuclear cell products in vitro. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1828–1843. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Ciarletta A. B., Temple P. A., Chung M. P., Kovacic S., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Leary A. C., Kriz R., Donahue R. E., Wong G. G. Human IL-3 (multi-CSF): identification by expression cloning of a novel hematopoietic growth factor related to murine IL-3. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



