Abstract
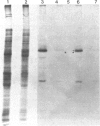
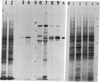
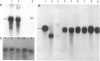
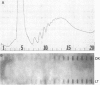
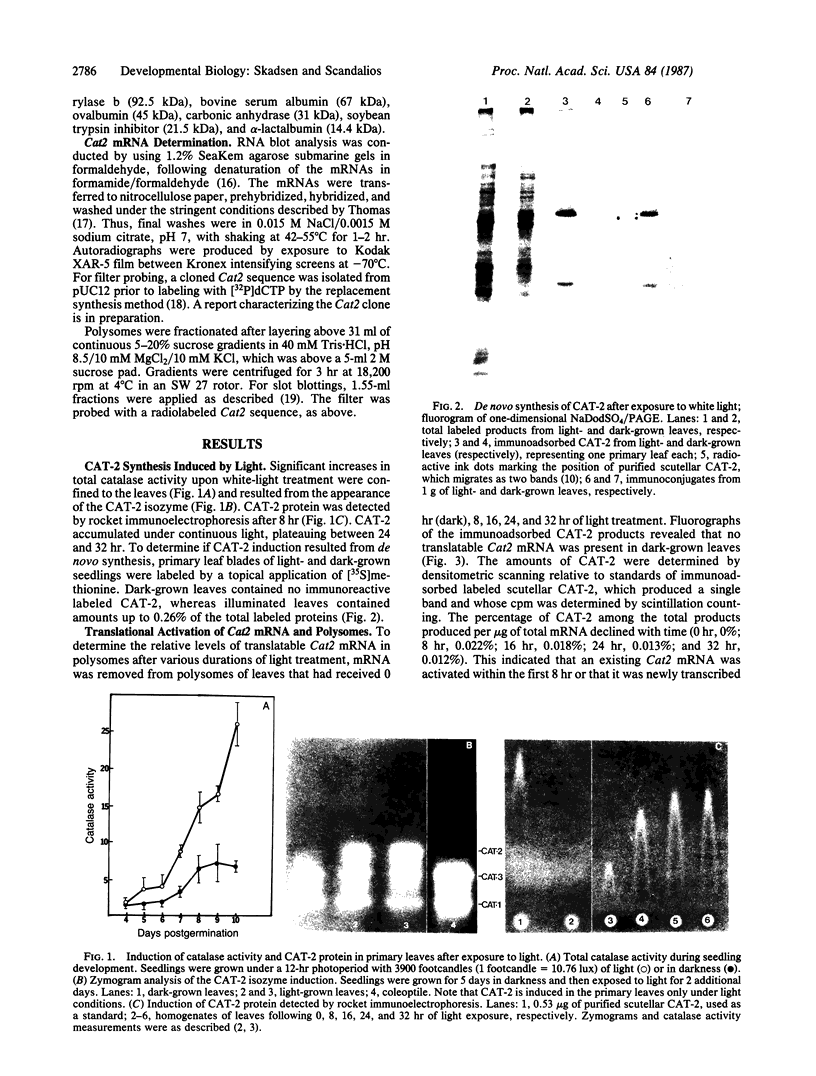
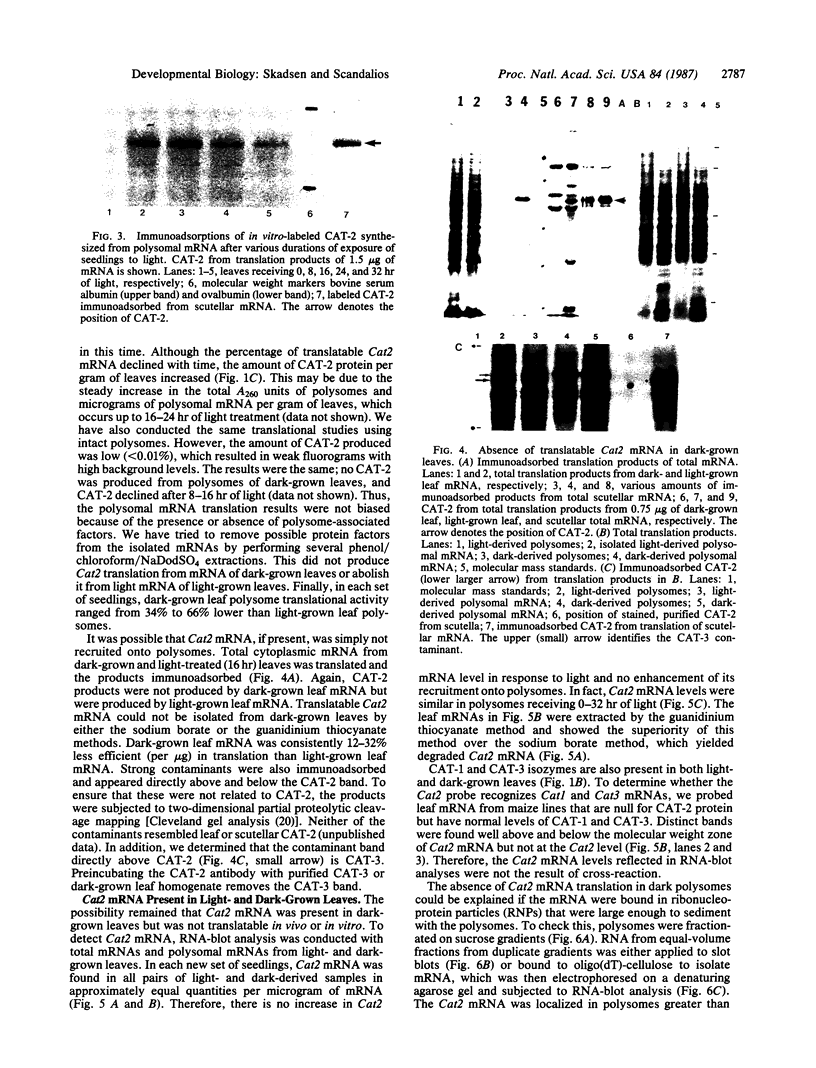
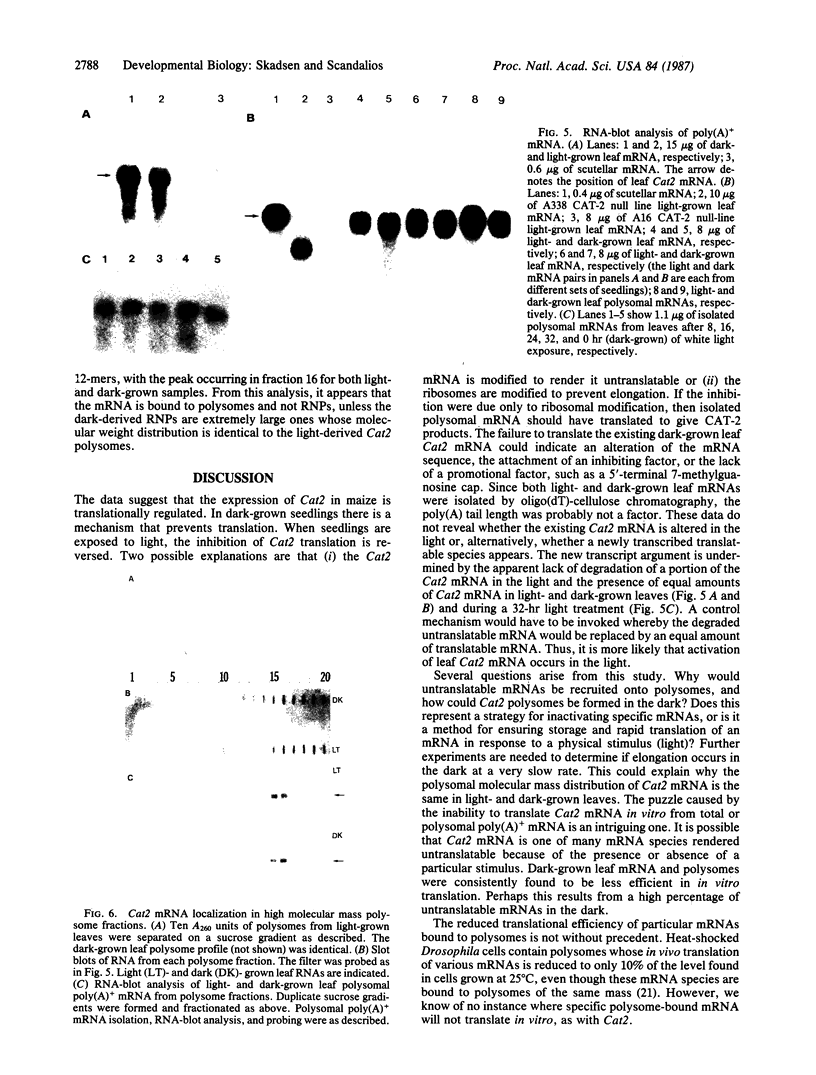
In dark-grown leaves of Zea mays, the catalase (H2O2:H2O2 oxidoreductase; EC 1.11.1.6; CAT) isozyme CAT-2 is absent. With continuous white light, CAT-2 protein levels increase (due to de novo synthesis) and plateau after 24 hr. When total poly(A)+ RNA (mRNA), polysomes, or isolated polysomal mRNA from light- and dark-treated leaves was translated in vitro, CAT-2 was detected only among the light-treated leaf products. A Cat2 clone was used to probe blots of total mRNA and polysomal mRNA from light- and dark-treated leaves. Cat2 mRNA was found in approximately equal quantities in both. Cat2 mRNA was equally distributed in identical high molecular weight fractions in polysomes from light- and dark-treated leaves and, therefore, was probably not sequestered in ribonucleoprotein particles in dark-grown leaves. The control of Cat2 expression appears to involve a unique form of translational inhibition in dark-grown leaves, preventing translation of the isolated mRNA and preventing polypeptide elongation. These results may have important implication in studies of translational control in other systems.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger D. G., Pardue M. L. The control of protein synthesis during heat shock in Drosophila cells involves altered polypeptide elongation rates. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandlee J. M., Scandalios J. G. Regulation of Cat1 gene expression in the scutellum of maize during early sporophytic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4903–4907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feierabend J., Beevers H. Developmental studies on microbodies in wheat leaves : I. Conditions influencing enzyme development. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jan;49(1):28–32. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber P. J., Becker W. M., Newcomb E. H. The development of microbodies and peroxisomal enzymes in greening bean leaves. J Cell Biol. 1973 Feb;56(2):500–518. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.2.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk M. M., Kirk D. L. Translational regulation of protein synthesis, in response to light, at a critical stage of Volvox development. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire D. M., Chan L., Smith L. C., Towle H. C., Dempsey M. E. Translational control of the circadian rhythm of liver sterol carrier protein. Analysis of mRNA sequences with a specific cDNA probe. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5435–5439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandalios J. G., Chang D. Y., McMillin D. E., Tsaftaris A., Moll R. H. Genetic regulation of the catalase developmental program in maize scutellum: Identification of a temporal regulatory gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5360–5364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skadsen R. W., Scandalios J. G. Evidence for processing of maize catalase 2 and purification of its messenger RNA aided by translation of antibody-bound polysomes. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2027–2032. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Sun S. M., Hall T. C. Complete nucleotide sequence of a French bean storage protein gene: Phaseolin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1897–1901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsaftaris A. S., Bosabalidis A. M., Scandalios J. G. Cell-type-specific gene expression and acatalasemic peroxisomes in a null Cat2 catalase mutant of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]