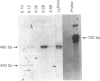
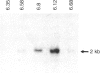
Abstract
Interaction of human gamma-interferon (IFN-gamma) with a cell-surface receptor is known to be essential for the cell to become resistant to viral infection. Here we demonstrate that IFN-gamma, when present inside the cell, is also capable of inducing a permanent antiviral state. Mouse cells transformed with a truncated human cDNA encoding a mature IFN-gamma protein lacking the signal peptide accumulate high levels of intracellular human IFN-gamma. Not only do these cells acquire a permanent resistance to viral infection, they also exhibit all the biochemical characteristics normally observed after exposure to exogenous IFN. The observed loss of species specificity normally associated with IFN-gamma suggests that this restriction is strictly dependent on the interaction of the molecule with the cell-surface receptor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Human interferon-gamma is internalized and degraded by cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6497–6502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ankel H., Chany C., Galliot B., Chevalier M. J., Robert M. Antiviral effect of interferon covalently bound to sepharose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2360–2363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Evidence that types I and II interferons have different receptors. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):768–770. doi: 10.1038/294768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Faltynek C. R., D'Alessandro S. B., Baglioni C. Interaction of interferon with cellular receptors. Internalization and degradation of cell-bound interferon. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13291–13296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Mechti N., Piechaczyk M., Lebleu B., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Increased rate of degradation of c-myc mRNA in interferon-treated Daudi cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4896–4899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Samanta H., Farrell P. J., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and RNA degradation. Isolation of homogeneous pppA(2'p5'A)n-1 synthetase from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3813–3816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff E., Falcoff R., Lebleu B., Revel M. Correlation between the antiviral effect of interferon treatment and the inhibition of in vitro mRNA translation in noninfected L cells. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):421–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.421-430.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Fogler W. E., Kleinerman E. S., Saiki I. Abrogation of species specificity for activation of tumoricidal properties in macrophages by recombinant mouse or human interferon-gamma encapsulated in liposomes. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4289–4296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M. Interferon binding: the first step in establishment of antiviral activity. Science. 1967 Jun 30;156(3783):1760–1761. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3783.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Pennica D., Yelverton E., Najarian R., Simonsen C. C., Derynck R., Sherwood P. J., Wallace D. M., Berger S. L. Expression of human immune interferon cDNA in E. coli and monkey cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):503–508. doi: 10.1038/295503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Sokawa Y. Microinjection of interferon and 2',5'-oligoadenylate into mouse L cells and their effects on virus growth. J Biochem. 1982 Jun;91(6):2021–2028. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huez G., Silhol M., Lebleu B. Microinjected interferon does not promote an antiviral response in Hela cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91273-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonak G. J., Knight E., Jr Selective reduction of c-myc mRNA in Daudi cells by human beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1747–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Differential regulation of interferon-induced mRNAs and c-myc mRNA by alpha- and gamma-interferons. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 2;153(2):367–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E. pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A: an inhibitor of protein synthesis synthesized with an enzyme fraction from interferon-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Cawthon M. L., Kabat D. Improved methods for purification and assay of eukaryotic messenger ribonucleic acids and ribosomes. Quantitative analysis of their interaction in a fractionated reticulocyte cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6077–6084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushnaryov V. M., MacDonald H. S., Debruin J., Lemense G. P., Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. Internalization and transport of mouse beta-interferon into the cell nucleus. J Interferon Res. 1986 Jun;6(3):241–245. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushnaryov V. M., MacDonald H. S., Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. Murine interferon-beta receptor-mediated endocytosis and nuclear membrane binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3281–3285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Mengheri E., Esteban M. Induction of an antiviral response by interferon requires thymidine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):26–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen B., Steinmetz M., McMillan M., Pierres M., Hood L. Expression of I-Ak class II genes in mouse L cells after DNA-mediated gene transfer. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):440–443. doi: 10.1038/305440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlin G., Revel M., Wallach D. The interferon-induced enzyme oligo-isoadenylate synthetase: rapid determination of its in vitro products. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):190–196. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Hatat D., Abadie A., Wallach D., Revel M., Fellous M. Differential regulation of HLA-DR mRNAs and cell surface antigens by interferon. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1585–1589. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancéau J., Lewis J. A., Sondermeyer P., Beranger F., Falcoff R., Vaquero C. Expression of extracellular and intracellular human IFN-gamma in mouse L cells transformed with the human IFN-gamma cDNA gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):894–901. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaquero C., Sanceau J., Sondermeyer P., Falcoff R. Kinetics of messenger accumulation coding for IFN gamma, related to modifications in the poly(A) RNA population of activated human lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2629–2640. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Sharp J. A., Summers W. C. Nucleotide sequence of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wietzerbin J., Gaudelet C., Aguet M., Falcoff E. Binding and cross-linking of recombinant mouse interferon-gamma to receptors in mouse leukemic L1210 cells; interferon-gamma internalization and receptor down-regulation. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2451–2455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wietzerbin J., Stefanos S., Lucero M., Falcoff E., O'Malley J. A., Sulkowski E. Physico-chemical characterization and partial purification of mouse immune interferon. J Gen Virol. 1979 Sep;44(3):773–781. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-3-773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Arnheiter H. Studies of the interferon receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1984;24(2):259–278. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(84)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Arnheiter H., Zur Nedden D., Fitzgerald D. J., Willingham M. C. Human interferon alpha enters cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]