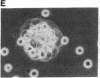
Abstract
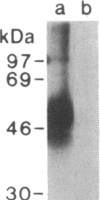
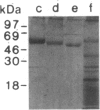
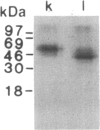
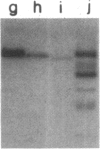
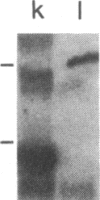
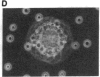
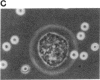
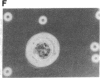
The T11 (CD2) sheep-erythrocyte-binding protein is a T-cell surface molecule involved in activation of T lymphocytes and thymocytes, including those lacking the T3-Ti antigen-receptor complex. The primary structure of T11 was deduced from protein microsequencing and cDNA cloning. The mature human protein appears to be divided into three domains: a hydrophilic 185 amino acid external domain bearing only limited homology to the T-cell surface protein T4 and the immunoglobulin kappa light chain variable region, a 25 amino acid hydrophobic transmembrane segment, and a 126 amino acid cytoplasmic domain rich in prolines and basic residues. Transfection of cDNAs encoding either the 1.7- or the 1.3-kilobase T11 mRNA into COS-1 cells resulted in expression of surface T11 epitopes as well as sheep-erythrocyte-binding capacity. The predicted structure is consistent with the possibility that T11 functions in signal transduction.
Full text
PDF


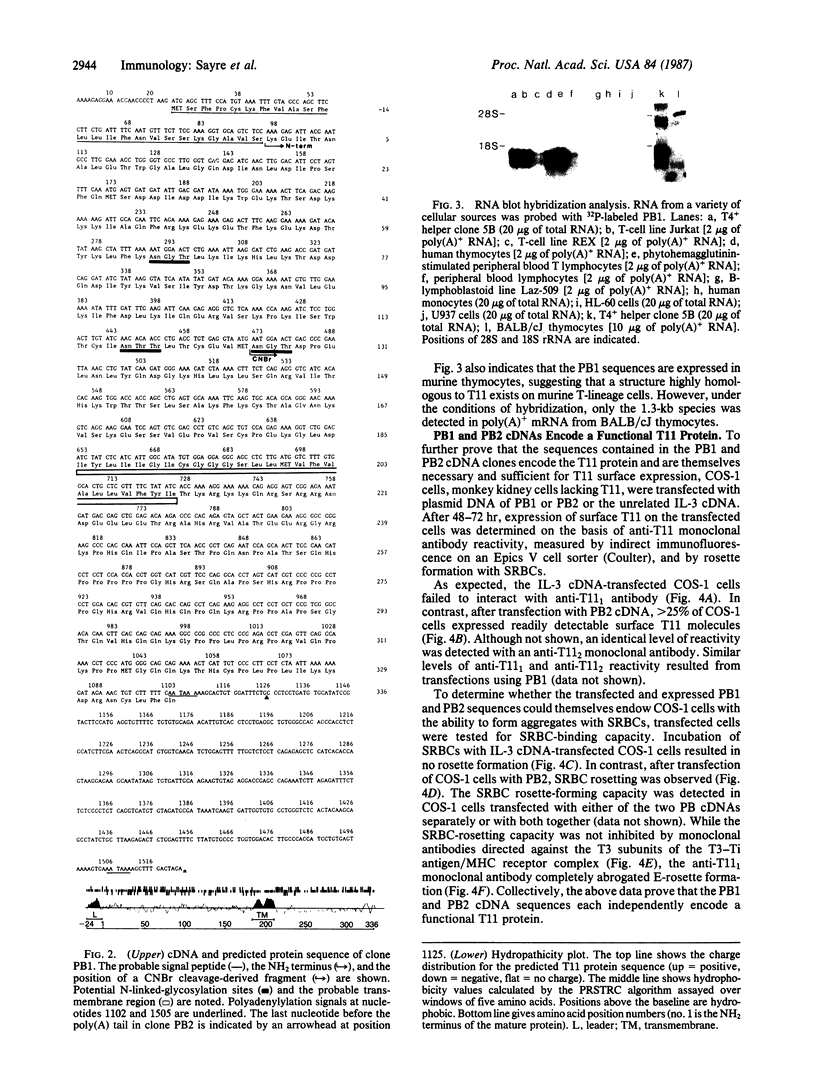

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acuto O., Meuer S. C., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Peptide variability exists within alpha and beta subunits of the T cell receptor for antigen. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1368–1373. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcover A., Weiss M. J., Daley J. F., Reinherz E. L. The T11 glycoprotein is functionally linked to a calcium channel in precursor and mature T-lineage cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2614–2618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard A., Gelin C., Raynal B., Pham D., Gosse C., Boumsell L. Phenomenon of human T cells rosetting with sheep erythrocytes analyzed with monoclonal antibodies. "Modulation" of a partially hidden epitope determining the conditions of interaction between T cells and erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1317–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain P., Gordon J., Willetts W. A. Rosette formation by peripheral lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):681–688. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs R. R., Gurner B. W., Wilson A. B., Holm G., Lindgren B. Rosette-formation between human lymphocytes and sheep red cells not involving immunoglobulin receptors. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(5-6):658–663. doi: 10.1159/000230390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. A., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Bensussan A., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Activation of human thymocytes via the 50KD T11 sheep erythrocyte binding protein induces the expression of interleukin 2 receptors on both T3+ and T3- populations. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):330–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold D. P., Puck J. M., Pettey C. L., Cho M., Coligan J., Woody J. N., Terhorst C. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding the 20K non-glycosylated polypeptide chain of the human T-cell receptor/T3 complex. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):431–434. doi: 10.1038/321431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Dowell D. L., Hensley L. L., Gore I., Metzgar R. S. Human T cell antigen expression by primate T cells. Science. 1982 Jan 15;215(4530):298–300. doi: 10.1126/science.6171885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard F. D., Ledbetter J. A., Wong J., Bieber C. P., Stinson E. B., Herzenberg L. A. A human T lymphocyte differentiation marker defined by monoclonal antibodies that block E-rosette formation. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2117–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T. The target structure for T11: a cell interaction molecule involved in T-cell activation? Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;126:165–172. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71152-7_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun M., Kadin M. E., Martin P. J., Nettleton J., Hansen J. A. A novel human T cell antigen preferentially expressed on mature T cells and shared by both well and poorly differentiated B cell leukemias and lymphomas. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):987–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Siu G., Hood L. E., Shastri N. The molecular genetics of the T-cell antigen receptor and T-cell antigen recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:529–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Mendes N. F., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Binding of sheep red blood cells to a large population of human lymphocytes. Nature. 1971 Apr 23;230(5295):531–532. doi: 10.1038/230531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R., Thomas Y., Maddon P. J., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and sequence of the gene encoding T8: a molecule defining functional classes of T lymphocytes. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luescher B., Bron C. Biosynthesis of mouse Thy-1 antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1084–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Littman D. R., Godfrey M., Maddon D. E., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the T cell surface protein T4: a new member of the immunoglobulin gene family. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. P., Deverson E. V. The amino acid sequence of a human kappa light chain. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):945–958. doi: 10.1042/bj1230945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Meuer S., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Levine H., Schlossman S. F. Antigen recognition by human T lymphocytes is linked to surface expression of the T3 molecular complex. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):735–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renugopalakrishnan V., Strawich E. S., Horowitz P. M., Glimcher M. J. Studies of the secondary structures of amelogenin from bovine tooth enamel. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4879–4887. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell W. A., Brown M. H., Dunne J., Owen M. J., Crumpton M. J. Molecular cloning of the human T-lymphocyte surface CD2 (T11) antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8718–8722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Luce G. E., Quinones R., Gress R. E., Springer T. A., Sanders M. E. Two antigen-independent adhesion pathways used by human cytotoxic T-cell clones. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):262–264. doi: 10.1038/323262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano R. F., Pratt J. C., Schmidt R. E., Ritz J., Reinherz E. L. Activation of cytolytic T lymphocyte and natural killer cell function through the T11 sheep erythrocyte binding protein. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):428–430. doi: 10.1038/317428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbi W., Greaves M. F., Schneider C., Koubek K., Janossy G., Stein H., Kung P., Goldstein G. Monoclonal antibodies OKT 11 and OKT 11A have pan-T reactivity and block sheep erythrocyte "receptors". Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):81–86. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Daley J. F., Hodgdon J. C., Reinherz E. L. Calcium dependency of antigen-specific (T3-Ti) and alternative (T11) pathways of human T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6836–6840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]