Abstract
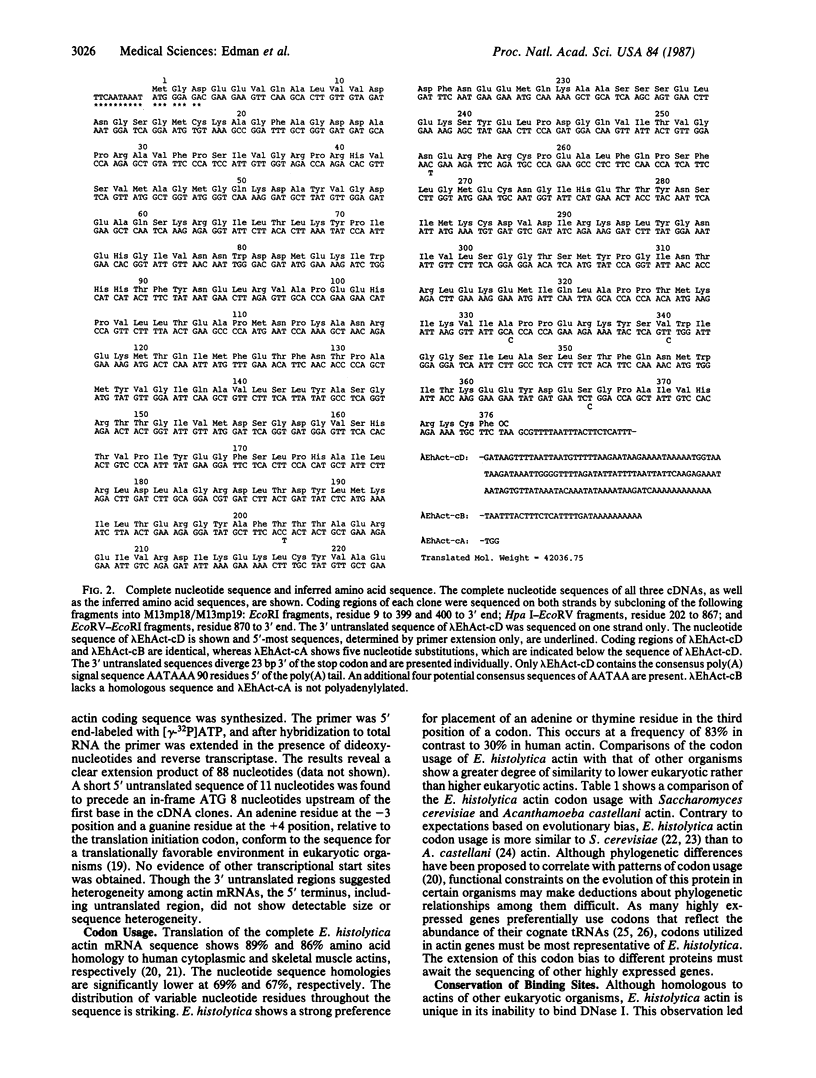
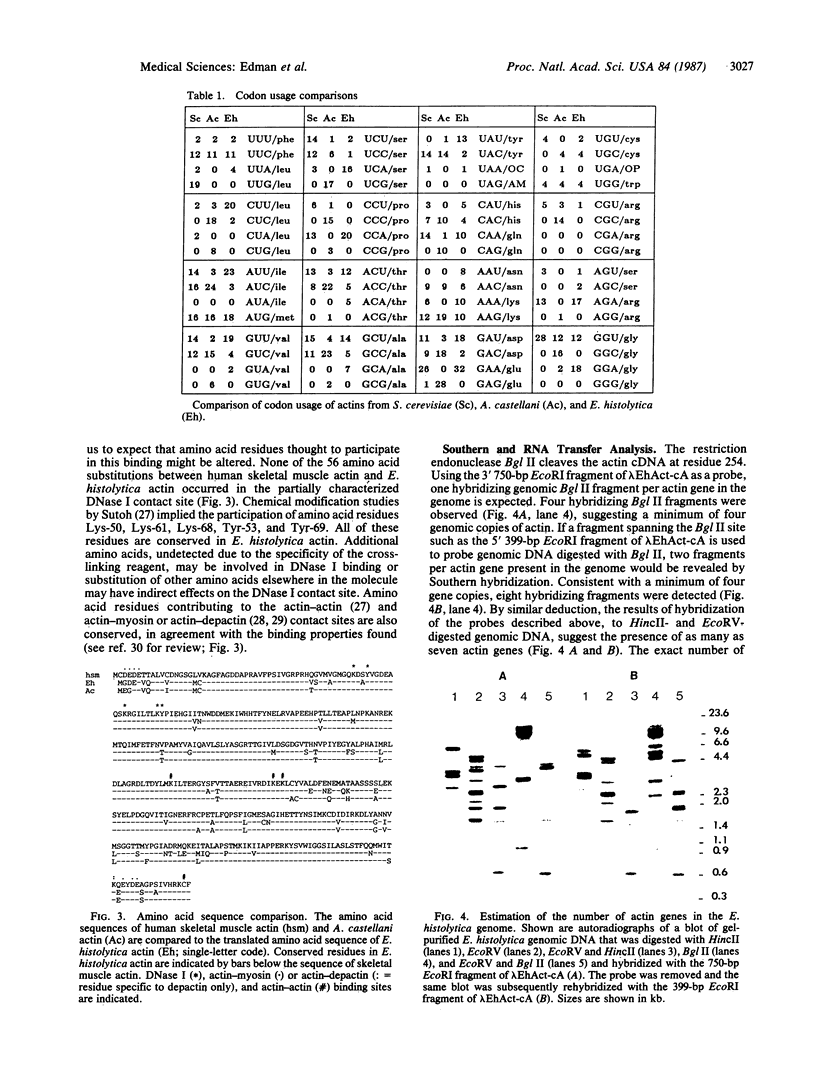
Invasiveness of Entamoeba histolytica strains that cause acute amoebiasis is characterized by aggressive behavior associated with cell motility and actin function. Analysis of actin genes from E. histolytica was initiated by devising methods for the isolation of biologically active nucleic acids, which allowed the preparation of cDNA and genomic DNA libraries. E. histolytica actin-encoding cDNAs and genomic clones have been isolated from libraries prepared from the virulent HM1:IMSS strain using a heterologous actin probe. Nucleotide sequence analysis of three independent cDNA clones and one genomic clone reveals a highly unusual codon bias and the absence of intervening sequences in E. histolytica actin. The coding sequence of the genomic clone is identical to that of two of the three cDNA clones. These represent at least two distinct mRNAs differing only by five silent changes in the protein coding sequence. Multiple genomic copies of the actin gene can be detected by Southern hybridization. E. histolytica actin exhibits a higher degree of homology to cytoplasmic than to muscle actin. Although the protein has been shown not to bind DNase I, the inferred amino acid sequence indicates conservation of all residues implied to participate in this binding.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albach R. A., Prachayasittikul V., Heebner G. M. Isolation and characterization of RNA of Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Jul;12(3):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey G. B., Day D. B., Gasque J. W. Rapid polymerization of Entamoeba histolytica actin induced by interaction with target cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):546–558. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupples C. G., Pearlman R. E. Isolation and characterization of the actin gene from Tetrahymena thermophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5160–5164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen J. L., Neubauer M. G., Degen S. J., Seyfried C. E., Morris D. R. Regulation of protein synthesis in mitogen-activated bovine lymphocytes. Analysis of actin-specific and total mRNA accumulation and utilization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12153–12162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903: from xenic to axenic cultivation. J Protozool. 1986 Feb;33(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A. Multigene families encoding actin and tubulin. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):6–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90494-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadasi H. Isolated Entamoeba histolytica actin does not inhibit DNAse-I activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):158–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91953-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Gautier C. Codon usage in bacteria: correlation with gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7055–7074. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L. Amebiasis: introduction, current status, and research questions. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):218–227. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer A., Levin M., Heilig R., Daegelen D., Kahn A., Mandel J. L. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human skeletal muscle alpha actin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3503–3516. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Aebi U., Pollard T. D. An actin-binding protein from Acanthamoeba regulates actin filament polymerization and interactions. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):455–459. doi: 10.1038/288455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaine B. P., Spear B. B. Nucleotide sequence of a macronuclear gene for actin in Oxytricha fallax. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):430–432. doi: 10.1038/295430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J., Aley S. The biochemistry and functional morphology of the Entamoeba. J Protozool. 1985 May;32(2):221–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meza I., Sabanero M., Cazares F., Bryan J. Isolation and characterization of actin from Entamoeba histolytica. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3936–3941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellen W., Gallwitz D. Actin genes and actin messenger RNA in Acanthamoeba castellanii. Nucleotide sequence of the split actin gene I. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 25;159(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Zakut R., Shani M., Neuman S., Levy Z., Yaffe D. The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1759–1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Guerrant R. L. Role of adherence in cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. Study with mammalian tissue culture cells and human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Grene J. D. The differentiation of invasive and non-invasive Entamoeba histolytica by isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(5):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Tuohy T. M., Mosurski K. R. Codon usage in yeast: cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5125–5143. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Actin-actin and actin-deoxyribonuclease I contact sites in the actin sequence. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 24;23(9):1942–1946. doi: 10.1021/bi00304a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Identification of myosin-binding sites on the actin sequence. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 20;21(15):3654–3661. doi: 10.1021/bi00258a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. Multiple polyadenylation sites in a mouse alpha-amylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2313–2323. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
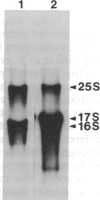
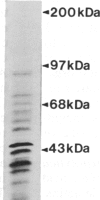
- Uyemura D. G., Brown S. S., Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural characterization of actin from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9088–9096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]