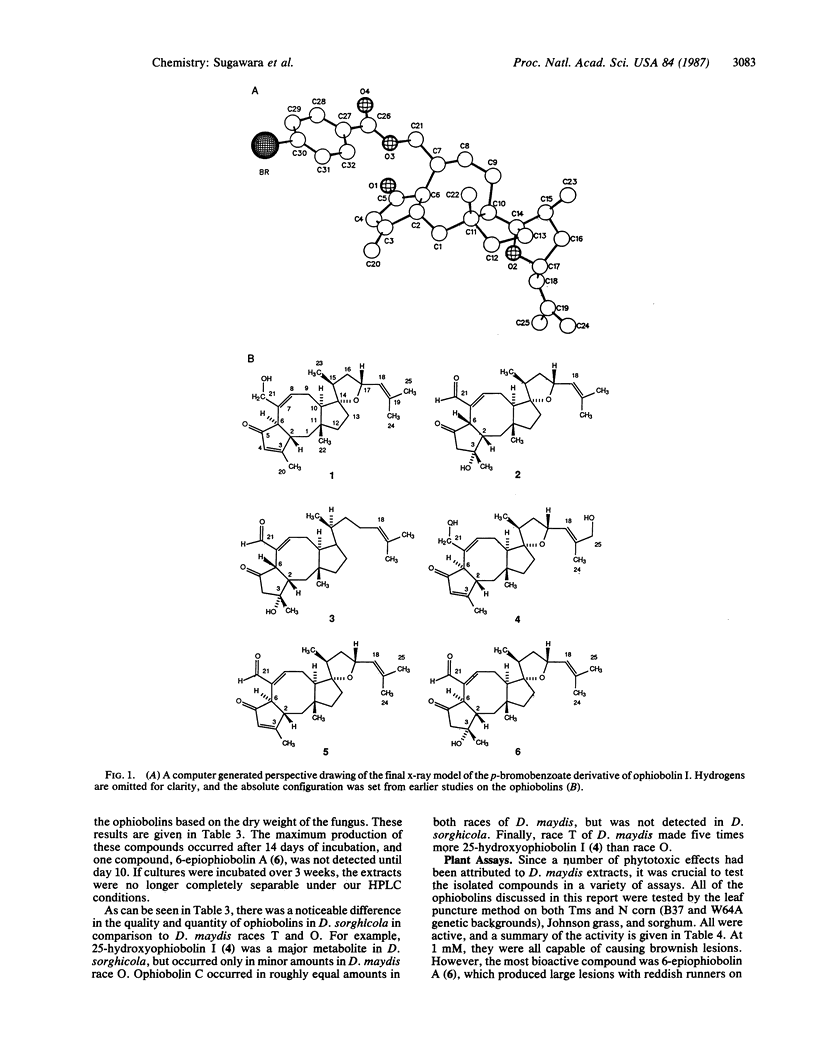
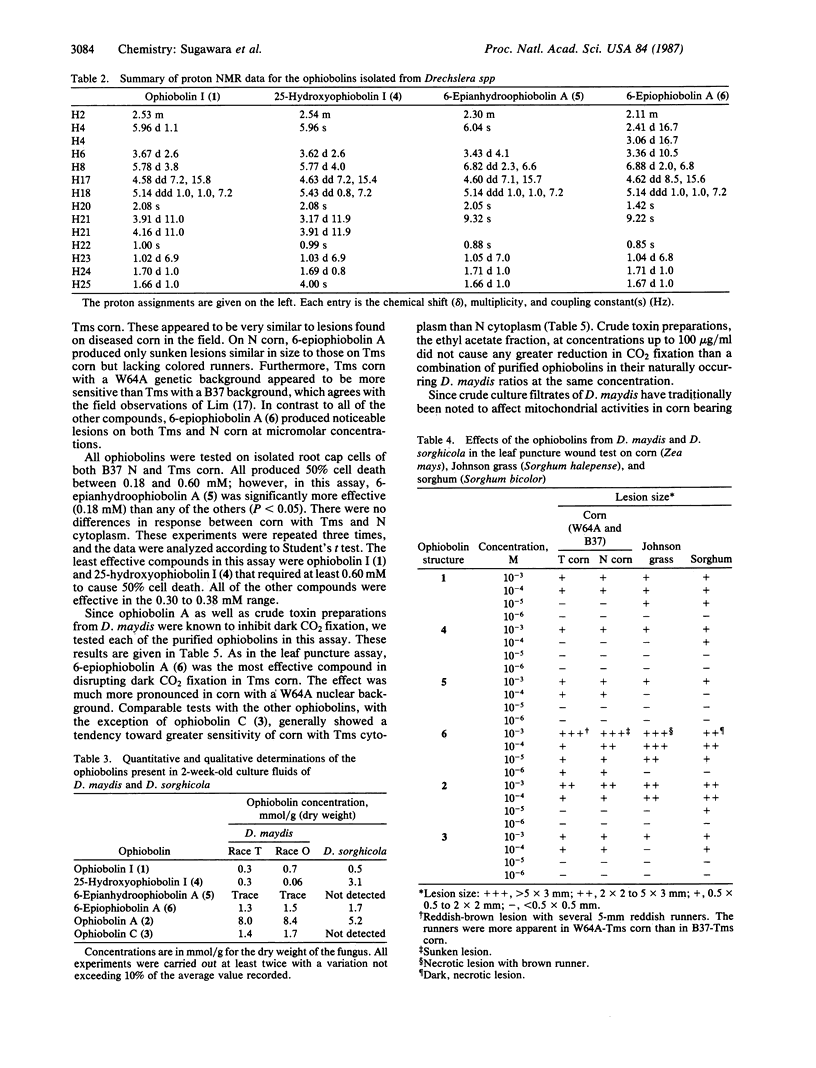
Abstract
Drechslera maydis, the causal agent of Southern corn leaf blight, and Drechslera sorghicola, the causal agent of leaf spot on Johnson grass, produce a series of phytotoxic sesterterpenoids. These sesterterpenoids belong to the ophiobolin family. One of them, ophiobolin I, was characterized by x-ray diffraction and served as a crucial reference compound for characterizing four other ophiobolins. All of the ophiobolins studied produce characteristic lesions on host plants at concentrations of 1 mM to 1 μM. The ophiobolin characterized as 6-epiophiobolin A is selectively toxic to corn bearing Texas-male-sterile (Tms) cytoplasm when assayed in a dark CO2 fixation assay. It is plausible that these ophiobolins had a role in the 1970 corn-blight epidemic in North America.
Keywords: corn blight, fungal metabolites, plant disease, sesterterpenoids, ophiobolins
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhullar B. S., Daly J. M., Rehfeld D. W. Inhibition of Dark CO(2) Fixation and Photosynthesis in Leaf Discs of Corn Susceptible to the Host-specific Toxin Produced by Helminthosporium maydis, Race T. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jul;56(1):1–7. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr A. L., Karr D. B., Strobel G. A. Isolation and Partial Characterization of Four Host-specific Toxins of Helminthosporium maydis (Race T). Plant Physiol. 1974 Feb;53(2):250–257. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.2.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. R., Koeppe D. E. Mode of Methomyl and Bipolaris maydis (race T) Toxin in Uncoupling Texas Male-Sterile Cytoplasm Corn Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1985 Apr;77(4):912–916. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.4.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung P. C., Taylor W. A., Wang J. H., Tipton C. L. Role of calmodulin inhibition in the mode of action of ophiobolin a. Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):303–308. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J., Koeppe D. E. Southern corn leaf blight: susceptible and resistant mitochondria. Science. 1971 Jul 2;173(3991):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3991.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozoe S., Morisaki M., Tsuda K., Iitaka Y., Takahashi N., Tamura S., Ishibashi K., Shirasaka M. The structure of ophiobolin, a C25 terpenoid having a novel skeleton. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Nov 5;87(21):4968–4970. doi: 10.1021/ja00949a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkerton F., Strobel G. Serinol as an activator of toxin production in attenuated cultures of Helminthosporium sacchari. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4007–4011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siedow J. N., Bickett D. M. Binding of butyl gallate to isolated mung bean mitochondria : relationship to inhibition of the alternative pathway. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jun;72(2):339–344. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel G. A. Phytotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:309–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara F., Strobel G., Fisher L. E., Van Duyne G. D., Clardy J. Bipolaroxin, a selective phytotoxin produced by Bipolaris cynodontis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8291–8294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Danko S. J., Daly J. M., Kono Y., Knoche H. W., Takeuchi S. Comparison of Activities of the Host-Specific Toxin of Helminthosporium maydis, Race T, and a Synthetic C(41) Analog. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):440–444. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatum L. A. The southern corn leaf blight epidemic. Science. 1971 Mar 19;171(3976):1113–1116. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3976.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipton C. L., Paulsen P. V., Betts R. E. Effects of ophiobolin a on ion leakage and hexose uptake by maize roots. Plant Physiol. 1977 May;59(5):907–910. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.5.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


