Abstract
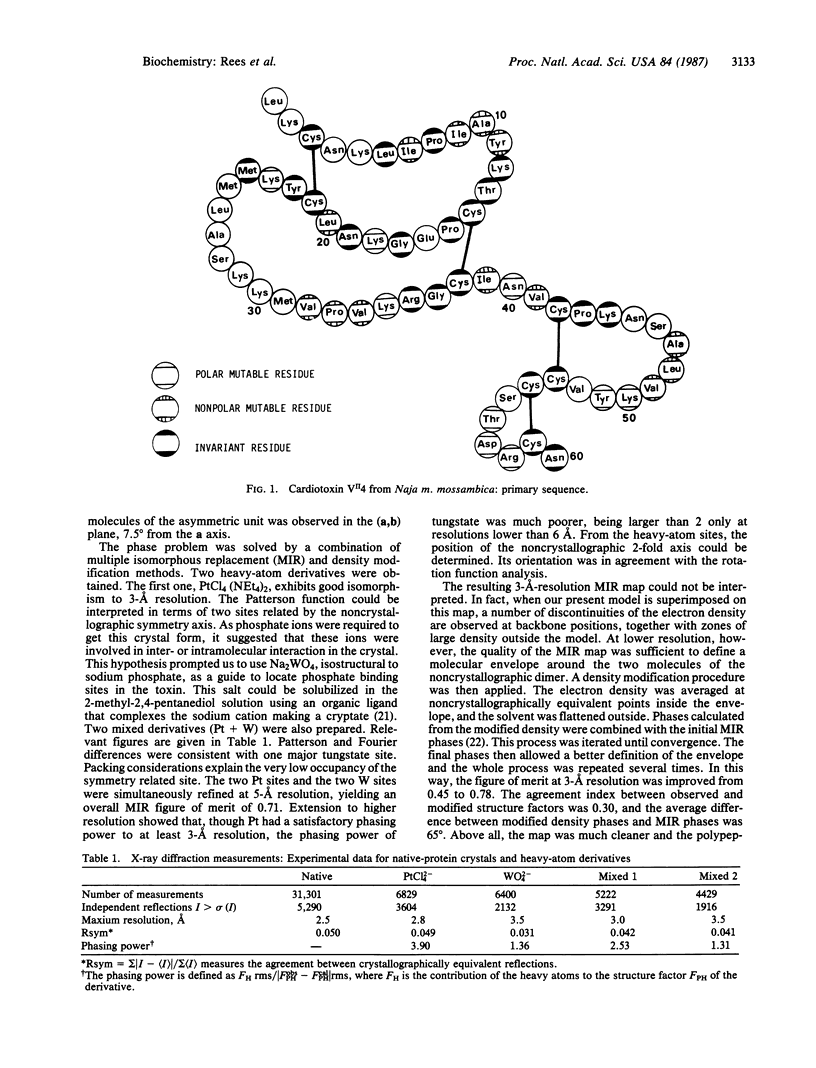
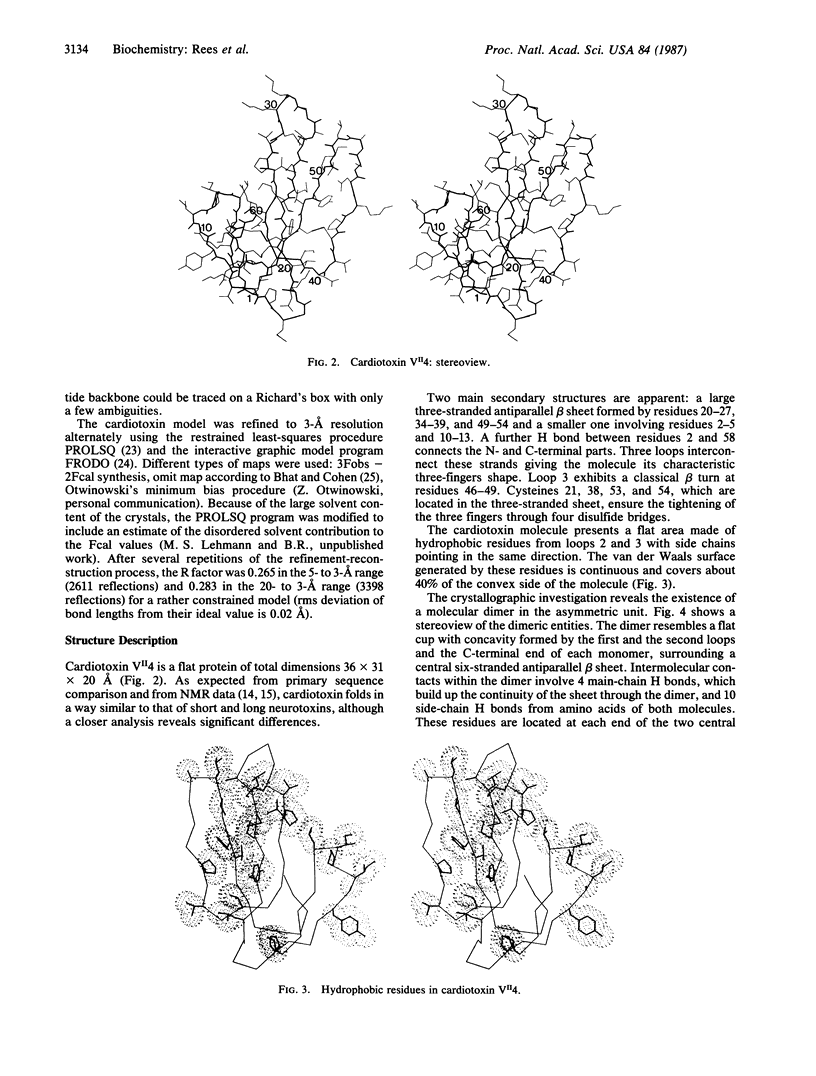
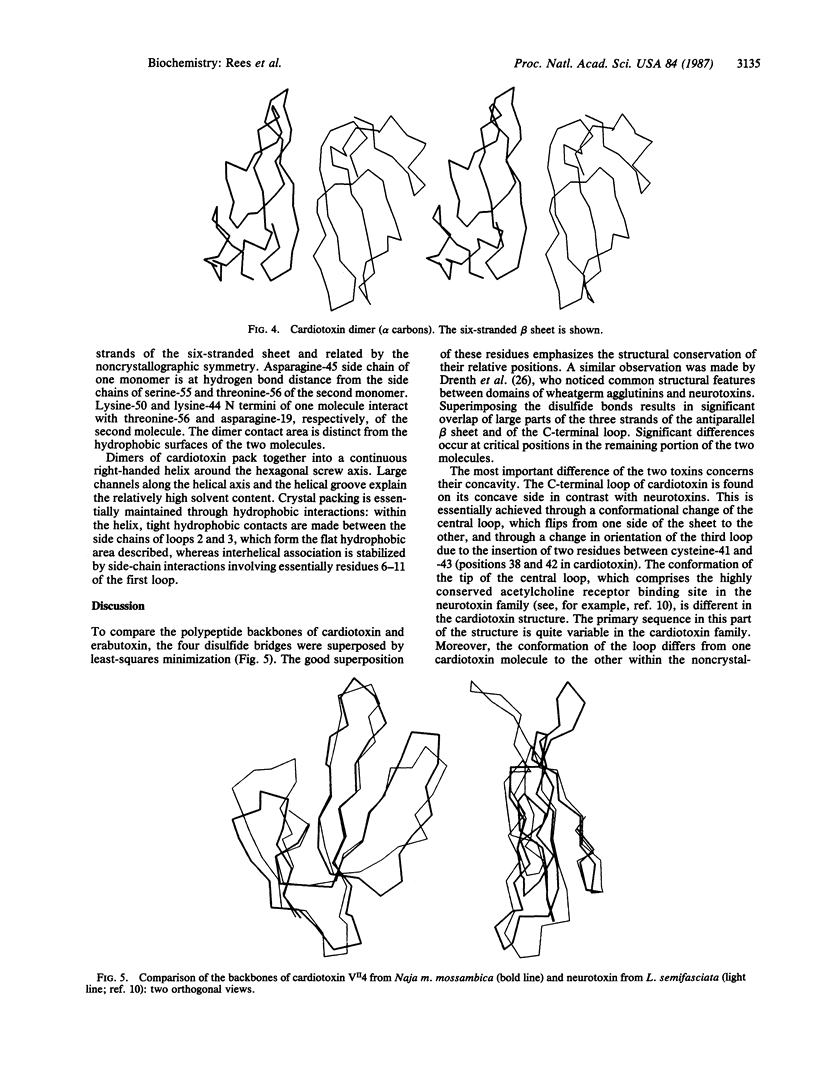
Cardiotoxin VII4 from Naja mossambica mossambica crystallizes in space group P61 (a = b = 73.9 A; c = 59.0 A) with two molecules of toxin (molecular mass = 6715 Da) in the asymmetric unit. The structure was solved by using a combination of multiple isomorphous replacement and density modification methods. Model building and least-squares refinement led to an agreement factor of 27% for a data set to 3-A resolution prior to any inclusion of solvent molecules. The topology of the molecule is similar to that found in short and long snake neurotoxins, which block the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Major differences occur in the conformation of the central loop, resulting in a change in the concavity of the molecule. Hydrophobic residues are clustered in two distinct areas. The existence of stable dimeric entities in the crystalline state, with the formation of a six-stranded antiparallel beta sheet, may be functionally relevant.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bougis P., Rochat H., Piéroni G., Verger R. Penetration of phospholipid monolayers by cardiotoxins. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4915–4920. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenth J., Low B. W., Richardson J. S., Wright C. S. The toxin-agglutinin fold. A new group of small protein structures organized around a four-disulfide core. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2652–2655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourcq J., Faucon J. F., Bernard E., Pezolet M., Tessier M., van Rietschoten J., Delori P., Rochat H. Structure-function relationships for cardiotoxins interacting with phospholipids. Toxicon. 1982;20(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufton M. J., Hider R. C. Conformational properties of the neurotoxins and cytotoxins isolated from Elapid snake venoms. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;14(2):113–171. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontecilla-Camps J. C., Almassy R. J., Suddath F. L., Watt D. D., Bugg C. E. Three-dimensional structure of a protein from scorpion venom: a new structural class of neurotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6496–6500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulik-Krzywicki T., Balerna M., Vincent J. P., Lazdunski M. Freeze-fracture study of cardiotoxin action on axonal membrane and axonal membrane lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 22;643(1):101–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosur R. V., Wider G., Wüthrich K. Sequential individual resonance assignments in the 1H nuclear-magnetic-resonance spectrum of cardiotoxin VII2 from Naja mossambica mossambica. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;130(3):497–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louw A. I. Snake venom toxins. The complete amino acid sequence of cytotoxin VII4 from the venom of Naja mossambica mossambica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 18;58(4):1022–1029. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. W., Preston H. S., Sato A., Rosen L. S., Searl J. E., Rudko A. D., Richardson J. S. Three dimensional structure of erabutoxin b neurotoxic protein: inhibitor of acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2991–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. Acetylcholine receptors. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 Jul;7(3):283–399. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARKAR N. K. Action mechanism of cobra venom, cardiotoxin and allied substances on muscle contraction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Nov;78(2):469–471. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz W. E., Moonen C., Kumar A., Lazdunski M., Visser L., Carlsson F. H., Wüthrich K. 1H nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies of the conformation of cardiotoxin VII2 from Naja mossambica mossambica. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;120(3):467–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A. Three-dimensional structure of neurotoxin a from venom of the Philippines sea snake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):971–974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Balerna M., Lazdunski M. Properties of association of cardiotoxin with lipid vesicles and natural membranes. A fluorescence study. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jan 1;85(1):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Schweitz H., Chicheportiche R., Fosset M., Balerna M., Lenoir M. C., Lazdunski M. Molecular mechanism of cardiotoxin action on axonal membranes. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3171–3175. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Schweitz H., Chicheportiche R., Fosset M., Balerna M., Lenoir M. C., Lazdunski M. Molecular mechanism of cardiotoxin action on axonal membranes. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3171–3175. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkinshaw M. D., Saenger W., Maelicke A. Three-dimensional structure of the "long" neurotoxin from cobra venom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2400–2404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Yang C. C. Crystallographic studies of snake venom proteins from Taiwan cobra (Naja nana atra). Cardiotoxin-analogue III and phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9279–9282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



