Abstract
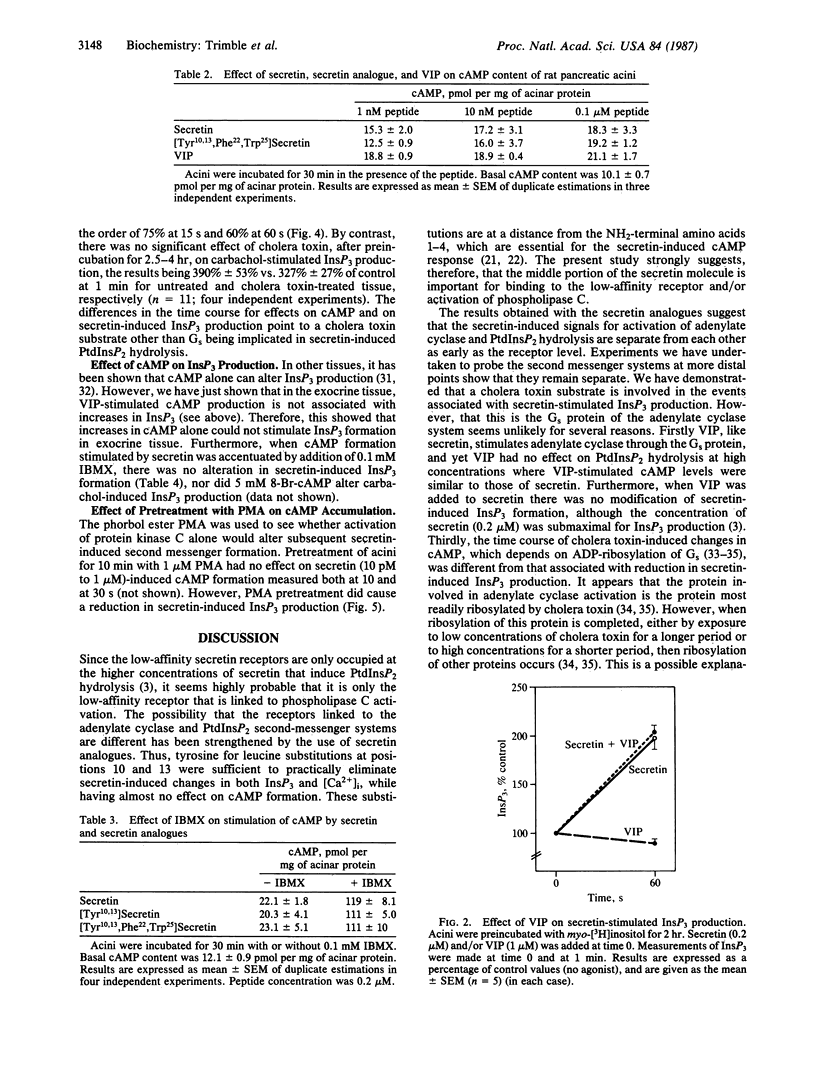
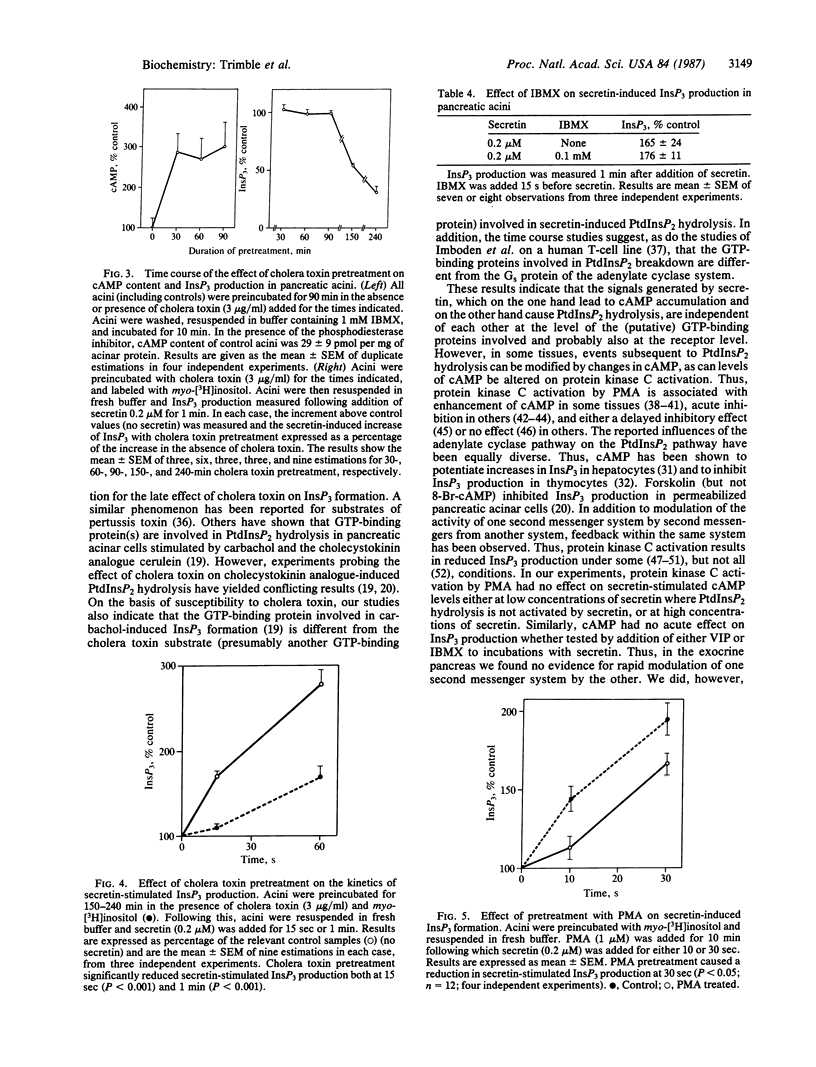
In rat pancreatic acinar tissue adenylate cyclase is stimulated by low concentrations of secretin, while higher concentrations also activate phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate hydrolysis. By the use of the secretin analogues [Tyr10,13]secretin and [Tyr10,13,Phe22,Trp25]secretin, we have shown that substitution of tyrosine for leucine at positions 10 and 13 was sufficient to reduce the ability of the peptide to stimulate the production of inositol trisphosphate and the increases in cytosolic free calcium, while the ability to stimulate cAMP is little affected and the peptide remained a full agonist. Incubation with cholera toxin caused increases in cAMP, which were maximal after 30 min. Cholera toxin treatment also resulted in a marked reduction of secretin-stimulated inositol trisphosphate production, but this required a much more prolonged treatment (150-240 min), suggesting that different cholera toxin substrates were involved. Activation of protein kinase C with the phorbol ester phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate had no effect on secretin-induced cAMP formation, nor was secretin-stimulated inositol trisphosphate formation altered by further increases in cAMP. These results indicate that the mechanisms by which secretin stimulates adenylate cyclase and activates phospholipase C in acinar tissue are completely independent.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. D., Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Enhancement of adenylate cyclase activity in S49 lymphoma cells by phorbol esters. Putative effect of C kinase on alpha s-GTP-catalytic subunit interaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2625–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette B. M., Collen M. J., Adachi H., Jensen R. T., Gardner J. D. Receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and secretin on rat pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 1):G710–G717. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.6.G710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Bocckino S. B., Waynick L. E., Exton J. H. Role of a guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein in the hydrolysis of hepatocyte phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate by calcium-mobilizing hormones and the control of cell calcium. Studies utilizing aluminum fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14477–14483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on the hepatic calcium-mobilizing activity of aluminum fluoride and glucagon. Modulation by cAMP and phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11056–11063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone R., Halban P. A., Gjinovci A., Trimble E. R. A new, rapid, method for preparation of dispersed pancreatic acini. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):621–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2260621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone R., Pozzan T., Wollheim C. B. Caerulein and carbamoylcholine stimulate pancreatic amylase release at resting cytosolic free Ca2+. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):139–143. doi: 10.1042/bj2350139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Pfeuffer T. Mechanism of cholera toxin action: covalent modification of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Mechanism of adenylate cyclase activation by cholera toxin: inhibition of GTP hydrolysis at the regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronin M. J., Summers S. T., Sortino M. A., Hewlett E. L. Protein kinase C enhances growth hormone releasing factor (1-40)-stimulated cyclic AMP levels in anterior pituitary. Actions of somatostatin and pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13932–13935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Rottman A. J., Natarajan S., Bodanszky M. Interaction of secretin5-27 and its analogues with hormone receptors on pancreatic acini. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 3;583(4):491–503. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Meren R. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins catalyzed by cholera toxin: basis of the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Guanine nucleotides decrease the free [Ca2+] required for secretion of serotonin from permeabilized blood platelets. Evidence of a role for a GTP-binding protein in platelet activation. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 20;174(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth C. M., Whetton A. D., Kinsella A. R., Houslay M. D. The phorbol ester, TPA inhibits glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):38–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashida H., Streaty R. A., Klee W., Nirenberg M. Bradykinin-activated transmembrane signals are coupled via No or Ni to production of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, a second messenger in NG108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):942–946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Phillips W. J. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates GTP hydrolysis by membranes from GH4C1 rat pituitary tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6183–6187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth E. B., Ukena D., Daly J. W. The protein kinase C activator phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate enhances cyclic AMP accumulation in pheochromocytoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 3;196(1):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Shoback D. M., Pattison G., Stobo J. D. Cholera toxin inhibits the T-cell antigen receptor-mediated increases in inositol trisphosphate and cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5673–5677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Ishitoya J., Takenawa T. Inhibition of inositol phospholipids metabolism and calcium mobilization by cyclic AMP-increasing agents and phorbol ester in neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1272–1278. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80315-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher D. J., Pessin J. E., Ruoho A. E., Johnson G. L. Phorbol ester induces desensitization of adenylate cyclase and phosphorylation of the beta-adrenergic receptor in turkey erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4316–4320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Kozawa O., Kaibuchi K., Katada T., Ui M., Takai Y. Direct evidence for involvement of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein in chemotactic peptide-stimulated formation of inositol bisphosphate and trisphosphate in differentiated human leukemic (HL-60) cells. Reconstitution with Gi or Go of the plasma membranes ADP-ribosylated by pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11558–11562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima I., Shibata H., Ogata E. Phorbol ester inhibits angiotensin-induced activation of phospholipase C in adrenal glomerulosa cells. Its implication in the sustained action of angiotensin. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):253–258. doi: 10.1042/bj2370253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Olson C. V., Grewal I. S., Scott S. J. A pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein in the human neutrophil regulates multiple receptors, calcium mobilization, and lectin-induced capping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8643–8647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M., Svoboda M., Furnelle J., Christophe J. Solubilization from rat pancreatic plasma membranes of a cholecystokinin (CCK) agonist-receptor complex interacting with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins coexisting in the same macromolecular system. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):611–617. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-2956.1985.00611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Fain J. N. 5-Methyltryptamine stimulates phospholipase C-mediated breakdown of exogenous phosphoinositides by blowfly salivary gland membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16052–16055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Charest R., Bocckino S. B., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Inhibition of hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic effects and binding by phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2844–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Taylor C. W., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr Evidence suggesting that a novel guanine nucleotide regulatory protein couples receptors to phospholipase C in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):337–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2360337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojsov S., Merrifield R. B. An improved synthesis of crystalline mammalian glucagon. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):601–605. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Okajima F., Ui M. Inhibition by islet-activating protein of a chemotactic peptide-induced early breakdown of inositol phospholipids and Ca2+ mobilization in guinea pig neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15771–15780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Pertussis toxin inhibits thrombin-induced activation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Na+/H+ exchange in hamster fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):55–60. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J. Tumour promotor 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate inhibits angiotensin II-induced inositol phosphate production and cytosolic Ca2+ rise in rat renal mesangial cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 28;203(2):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80755-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebois R. V., Patel J. Phorbol ester causes desensitization of gonadotropin-responsive adenylate cyclase in a murine Leydig tumor cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8026–8031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberecht P., Waelbroeck M., Camus J. C., De Neef P., Christophe J. Importance of disulfide bonds in receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and secretin in rat pancreatic plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 27;773(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberecht P., Waelbroeck M., Noyer M., Chatelain P., De Neef P., König W., Christophe J. Characterization of secretin and vasoactive intestinal peptide receptors in rat pancreatic plasma membranes using the native peptides, secretin-(7-27) and five secretin analogues. Digestion. 1982;23(3):201–210. doi: 10.1159/000198728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. J., Applebury M. L., Sternweis P. C. Relationships within the family of GTP-binding proteins isolated from bovine central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16242–16249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara O., Knecht M., Catt K. J. Inhibition of gonadotropin-induced granulosa cell differentiation by activation of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8518–8522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturani E., Vicentini L. M., Zippel R., Toschi L., Pandiella-Alonso A., Comoglio P. M., Meldolesi J. PDGF-induced receptor phosphorylation and phosphoinositide hydrolysis are unaffected by protein kinase C activation in mouse Swiss 3T3 and human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden D., Vanecek J., Klein D. C., Thomas T. P., Anderson W. B. Activation of protein kinase C potentiates isoprenaline-induced cyclic AMP accumulation in rat pinealocytes. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):359–361. doi: 10.1038/314359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Merritt J. E., Putney J. W., Jr, Rubin R. P. A guanine nucleotide-dependent regulatory protein couples substance P receptors to phospholipase C in rat parotid gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90919-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P. Mitogens increase phosphorylation of phosphoinositides in thymocytes. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):462–465. doi: 10.1038/312462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble E. R., Bruzzone R., Biden T. J., Farese R. V. Secretin induces rapid increases in inositol trisphosphate, cytosolic Ca2+ and diacylglycerol as well as cyclic AMP in rat pancreatic acini. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):257–261. doi: 10.1042/bj2390257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuis J. D., Demers L. M. An inhibitory role for the protein kinase C pathway in ovarian steroidogenesis. Studies with cultured swine granulosa cells. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2390505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicentini L. M., Di Virgilio F., Ambrosini A., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Tumor promoter phorbol 12-myristate, 13-acetate inhibits phosphoinositide hydrolysis and cytosolic Ca2+ rise induced by the activation of muscarinic receptors in PC12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):310–317. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Murphy G. J., Hruby V. J., Houslay M. D. Activation of two signal-transduction systems in hepatocytes by glucagon. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):68–71. doi: 10.1038/323068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


