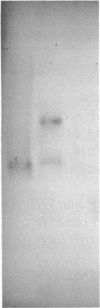
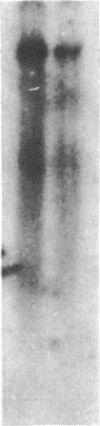
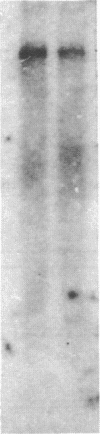
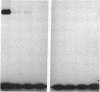
Abstract
The structural gene (fdhF) for the 80-kDa selenopolypeptide of formate dehydrogenase (formate:benzyl viologen oxidoreductase, EC 1.2.--.--) from Escherichia coli contains an in-frame UGA codon at amino acid position 140 that is translated. Translation of gene fusions between N-terminal parts of fdhF with lacZ depends on the availability of selenium in the medium when the hybrid gene contains the UGA codon; it is independent of the presence of selenium when an fdhF portion upstream of the UGA position is fused to lacZ. Transcription does not require the presence of selenium in either case. By localized mutagenesis, the UGA codon was converted into serine (UCA) and cysteine (UGC and UGU) codons. Each mutation relieved the selenium dependency of fdhF mRNA translation. Selenium incorporation was completely abolished in the case of the UCA insertion and was reduced to about 10% when the UGA was replaced by a cysteine codon. Insertion of UCA yielded an inactive fdhF gene product, while insertion of UGC and UGU resulted in polypeptides with lowered activities as components in the system formerly known as formate hydrogenlyase. Altogether the results indicate that the UGA codon at position 140 directs the cotranslational insertion of selenocysteine into the fdhF polypeptide chain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressureized atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):781–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.781-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Lactose genes fused to exogenous promoters in one step using a Mu-lac bacteriophage: in vivo probe for transcriptional control sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4530–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers I., Frampton J., Goldfarb P., Affara N., McBain W., Harrison P. R. The structure of the mouse glutathione peroxidase gene: the selenocysteine in the active site is encoded by the 'termination' codon, TGA. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1221–1227. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condell R. A., Tappel A. L. Amino acid sequence around the active-site selenocysteine of rat liver glutathione peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 20;709(2):304–309. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90472-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. C., Edwards E. S., DeMoss J. A. Resolution of distinct selenium-containing formate dehydrogenases from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1317–1324. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1317-1324.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crea R., Kraszewski A., Hirose T., Itakura K. Chemical synthesis of genes for human insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5765–5769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Clark A. J. Construction of an Hfr strain useful for transferring recA mutations between Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):529–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.529-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond A., Dudock B., Hatfield D. Structure and properties of a bovine liver UGA suppressor serine tRNA with a tryptophan anticodon. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzler W. A., Steffens G. J., Grossmann A., Kim S. M., Otting F., Wendel A., Flohé L. The amino-acid sequence of bovine glutathione peroxidase. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 Feb;365(2):195–212. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1984.365.1.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D., Diamond A., Dudock B. Opal suppressor serine tRNAs from bovine liver form phosphoseryl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6215–6219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Hershey J. W. A sensitive immunoblotting method for measuring protein synthesis initiation factor levels in lysates of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12836–12839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani T., Tachibana Y. Possible incorporation of phosphoserine into globin readthrough protein via bovine opal suppressor phosphoseryl-tRNA. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):162–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuber A. P., Orr E. C., Recny M. A., Schendel P. F., May H. D., Schauer N. L., Ferry J. G. Cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of the formate dehydrogenase genes from Methanobacterium formicicum. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):12942–12947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwkowski M. X., Stadtman T. C. Incorporation and distribution of selenium into thiolase from Clostridium kluyveri. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3140–3144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Birkmann A., Stadtman T. C., Böck A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the selenocysteine-containing polypeptide of formate dehydrogenase (formate-hydrogen-lyase-linked) from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4650–4654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]