Abstract
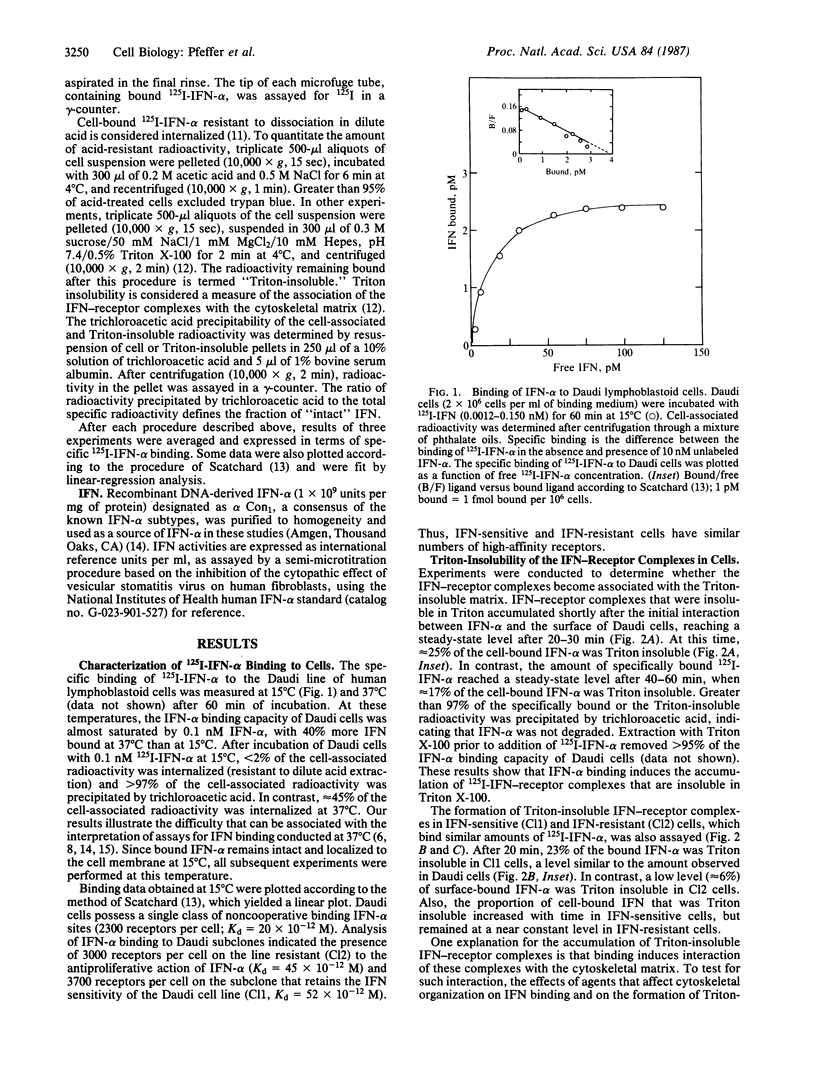
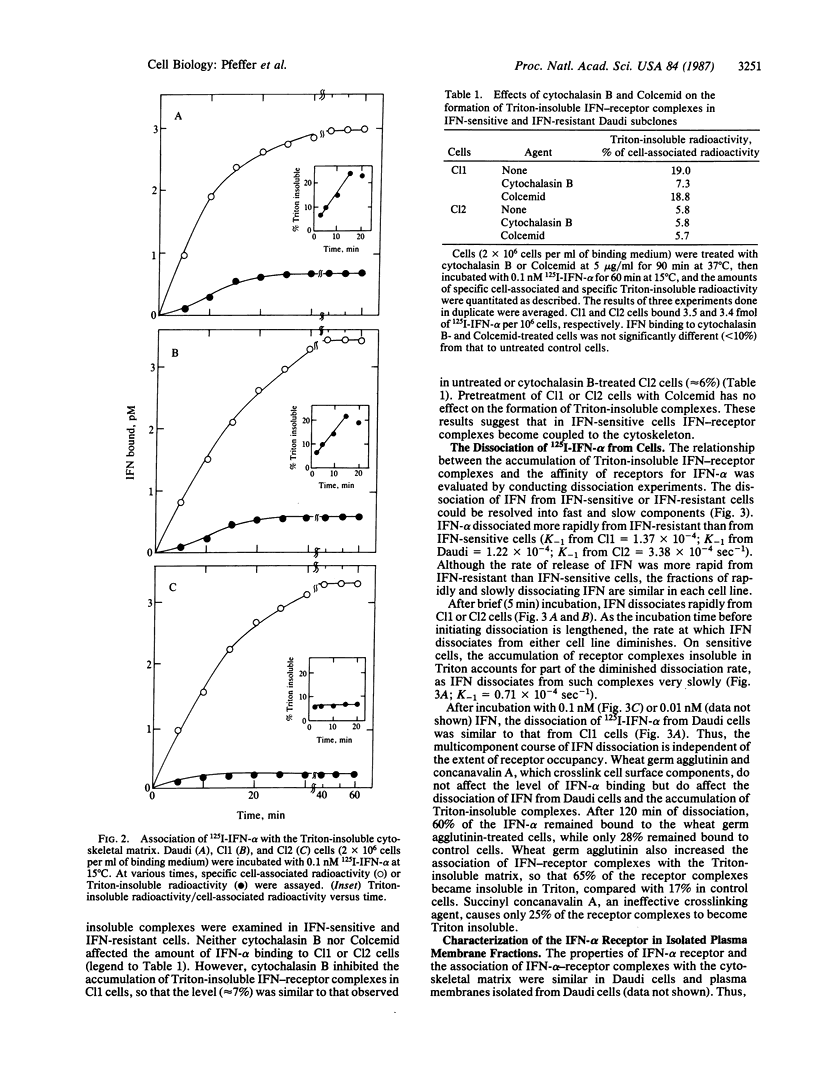
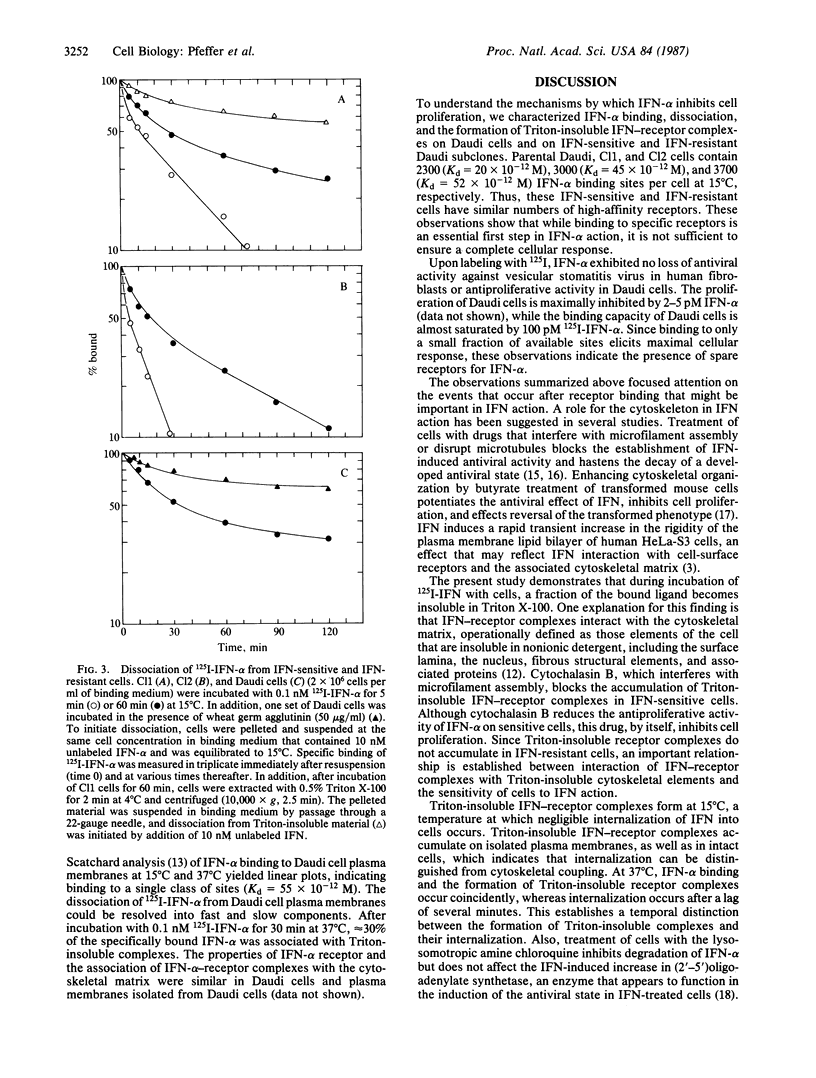
Human Daudi lymphoblastoid cells, which are highly sensitive to the antiproliferative action of human leukocyte alpha-interferon (IFN-alpha), and IFN-resistant and IFN-sensitive Daudi subclones (Cl2 and Cl1, respectively), contain 2300 (Kd = 20 X 10(-12) M), 3000 (Kd = 45 X 10(-12) M), and 3700 (Kd = 52 X 10(-12) M) IFN-alpha binding sites per cell, respectively. Thus, these IFN-sensitive and IFN-resistant cells have similar numbers of high-affinity IFN-alpha receptors. IFN-receptor complexes that are insoluble in Triton X-100 accumulate in IFN-sensitive but not in IFN-resistant cells. The ligand-induced accumulation of Triton-insoluble complexes in IFN-sensitive cells was inhibited by cytochalasin B. This suggests that the solubility change of IFN-receptor complexes results from their interaction with the cytoskeletal matrix. The dissociation of IFN-alpha from IFN-sensitive and IFN-resistant cells can be resolved into fast and slow components. IFN-alpha dissociates more slowly from IFN-sensitive cells than from IFN-resistant cells. Very slow dissociation of IFN-alpha from Triton-insoluble complexes correlates with this difference. These observations suggest that IFN-receptor complexes become coupled to the cytoskeletal matrix in IFN-sensitive but not in IFN-resistant cells, and that such interaction is an important element in the mechanism of the antiproliferative action of IFN-alpha on Daudi cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A., Strander H., Cantell K. Sensitivity of the Epstein-Barr virus transformed human lymphoid cell lines to interferon. J Gen Virol. 1975 Aug;28(2):207–217. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-2-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M., Mogensen K. E. Interferon receptors. Interferon. 1983;5:1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Duerr A., Solomon F., Penman S. The outer boundary of the cytoskeleton: a lamina derived from plasma membrane proteins. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):859–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeade M. F., Chany C. Effect of sodium butyrate on the antiviral and anticellular action of interferon in normal and MSV-transformed cells. Int J Cancer. 1979 Sep 15;24(3):314–318. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeade M. F., Chany C. Inhibition of interferon action by cytochalasin B, colchicine, and vinblastine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Dec;153(3):501–504. doi: 10.3181/00379727-153-39578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Evidence that types I and II interferons have different receptors. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):768–770. doi: 10.1038/294768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Faltynek C. R., D'Alessandro S. B., Baglioni C. Interaction of interferon with cellular receptors. Internalization and degradation of cell-bound interferon. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13291–13296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Hochman P. S., Unanue E. R. Ligand-induced association of surface immunoglobulin with the detergent-insoluble cytoskeletal matrix of the B lymphocyte. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1198–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L. Recycling receptors: the round-trip itinerary of migrant membrane proteins. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):663–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chany C., Rousset S., Bourgeade M. F., Mathieu D., Grégoire A. Role of receptors and the cytoskeleton in reverse transformation and steroidogenesis induced by interferon. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;350:254–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb20626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corin R. E., Donner D. B. Insulin receptors convert to a higher affinity state subsequent to hormone binding. A two-state model for the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):104–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Dansylcadaverine inhibits internalization of 125I-epidermal growth factor in BALB 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1239–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Naemura J. R., Sklar L. A., Cochrane C. G., Painter R. G. Rapid modulation of N-formyl chemotactic peptide receptors on the surface of human granulocytes: formation of high-affinity ligand-receptor complexes in transient association with cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1378–1387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landreth G. E., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor receptors on PC12 cells: ligand-induced conversion from low- to high-affinity states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4751–4755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landreth G. E., Williams L. K., Rieser G. D. Association of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase with the detergent-insoluble cytoskeleton of A431 cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1341–1350. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaleb M. L., Donner D. B. Affinity of the hepatic insulin receptor is influenced by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11051–11057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Landsberger F. R., Tamm I. Beta-interferon-induced time-dependent changes in the plasma membrane lipid bilayer of cultured cells. J Interferon Res. 1981;1(4):613–620. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Tamm I. Effects of beta interferon on concanavalin A binding and size of HeLa cells. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(3):431–440. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Wang E., Tamm I. Interferon effects on microfilament organization, cellular fibronectin distribution, and cell motility in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1980 Apr;85(1):9–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. L., Bothwell M. A. Nerve growth factor receptors on PC12 cells: evidence for two receptor classes with differing cytoskeletal association. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):867–874. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S., Taylor P. Functional consequences of agonist-mediated state transitions in the cholinergic receptor. Studies in cultured muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3315–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Pfeffer L. M., Tamm I. Interferon increases the abundance of submembranous microfilaments in HeLa-S3 cells in suspension culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6281–6285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



