Abstract
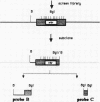
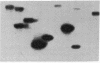
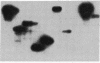
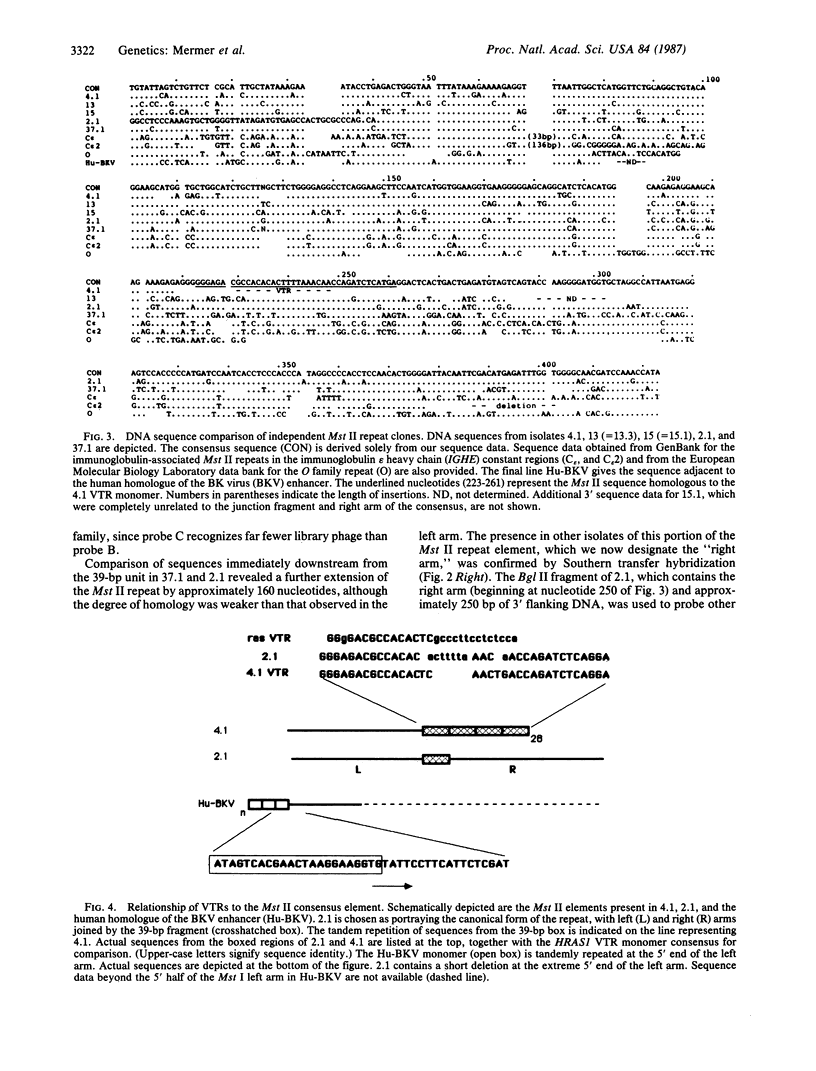
A family of short, interspersed repeats in the human genome, designated the Mst II family, is described. The canonical structure of the repeat consists of a 220-base-pair (bp) left arm joined to a 160-bp right arm by a 39-bp junction sequence. The right arm is absent in some isolates. Some homology with the "O" and "THE" (transposon-like element) families of repeats was observed, suggesting that the Mst II elements could be a subgroup of a SINE superfamily. The 39-bp junction sequence is tandemly repeated in one of our clones. The association of tandemly repetitive sequences with Mst II elements or the putative superfamily is probably nonrandom; a search of DNA sequence data bases revealed that approximately 80 bp of the Mst II left arm occurs immediately adjacent to the tandem repeat that comprises the human homologue to the BK virus enhancer. The fortuitous occurrence of a gene duplication event involving an Mst II repeat has allowed us to estimate a mutation rate for human DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Selby M. J., Rutter W. J. The highly polymorphic region near the human insulin gene is composed of simple tandemly repeating sequences. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):31–35. doi: 10.1038/295031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colb M., Yang-Feng T., Francke U., Mermer B., Parkinson D. R., Krontiris T. G. A variable tandem repeat locus mapped to chromosome band 10q26 is amplified and rearranged in leukocyte DNAs of two cancer patients. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):7929–7937. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.7929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S. E., Higgs D. R., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. Molecular basis of length polymorphism in the human zeta-globin gene complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5022–5026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisajima H., Nishida Y., Nakai S., Takahashi N., Ueda S., Honjo T. Structure of the human immunoglobulin C epsilon 2 gene, a truncated pseudogene: implications for its evolutionary origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2995–2999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Individual-specific 'fingerprints' of human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):76–79. doi: 10.1038/316076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krontiris T. G., DiMartino N. A., Colb M., Mitcheson H. D., Parkinson D. R. Human restriction fragment length polymorphisms and cancer risk assessment. J Cell Biochem. 1986;30(4):319–329. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240300405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krontiris T. G., DiMartino N. A., Colb M., Parkinson D. R. Unique allelic restriction fragments of the human Ha-ras locus in leukocyte and tumour DNAs of cancer patients. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):369–374. doi: 10.1038/313369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Battey J., Ney R., Kirsch I. R., Leder P. Duplication and deletion in the human immunoglobulin epsilon genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry H. M. Fossils and the mosaic nature of human evolution. Science. 1975 Oct 31;190(4213):425–431. doi: 10.1126/science.809842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Deka N., Schmid C. W., Misra R., Schindler C. W., Rush M. G., Kadyk L., Leinwand L. A transposon-like element in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):359–361. doi: 10.1038/316359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N., Kress M., Gruss P., Khoury G. BK viral enhancer element and a human cellular homolog. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):749–755. doi: 10.1126/science.6314501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L., Paulson K. E., Schmid C. W., Kadyk L., Leinwand L. Non-Alu family interspersed repeats in human DNA and their transcriptional activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2669–2690. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]