Abstract
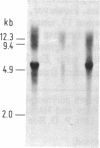
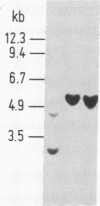
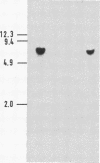
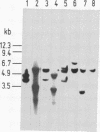
We describe a method for isolating cosmid clones randomly from mouse chromosome 17. A cosmid library was constructed from the mouse-Chinese hamster cell line R4 4-1 that contains a limited amount of mouse DNA (chromosomes 17 and 18 and some other unidentified material) on a Chinese hamster background. The library was screened with the murine repetitive sequence probe pMBA14, which selectively hybridizes with mouse DNA. The mouse-derived cosmid clones thus identified were individually hybridized with DNA from the mouse-Syrian hamster cell line JS17 containing all mouse chromosomes except chromosome 17 on a Syrian hamster background. We deduced that the cosmid clones that contained sequences absent in JS17 were derived from mouse chromosome 17. One of the chromosome 17-derived cosmid clones, 3-4-1 (located proximal to the T122/T66C segment) was found to be highly polymorphic among European wild-mouse populations and may be a useful probe to elucidate the evolution and migration of Mus species. The randomly isolated mouse-derived cosmid clones can also be screened for the presence of functional genes. Using testicular cDNA as a probe, a testis-specific gene was cloned from mouse chromosome 17.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Young B. D., Elles R. G., Hill M. E., Williamson R. Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):374–376. doi: 10.1038/293374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Cohen D. I., Nielsen E. A., Steinmetz M., Paul W. E., Hood L. Cell-type-specific cDNA probes and the murine I region: the localization and orientation of Ad alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2194–2198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Characterization of a highly repetitive family of DNA sequences in the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):5003–5013. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.5003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox H. S., Martin G. R., Lyon M. F., Herrmann B., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Silver L. M. Molecular probes define different regions of the mouse t complex. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90309-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Keys C., VarsanyiBreiner A., Kao F. T., Jones C., Puck T. T., Housman D. Isolation and localization of DNA segments from specific human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B., Bućan M., Mains P. E., Frischauf A. M., Silver L. M., Lehrach H. Genetic analysis of the proximal portion of the mouse t complex: evidence for a second inversion within t haplotypes. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Evans E. P., Jarvis S. E., Sayers I. t-Haplotypes of the mouse may involve a change in intercalary DNA. Nature. 1979 May 3;279(5708):38–42. doi: 10.1038/279038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F. Transmission ratio distortion in mouse t-haplotypes is due to multiple distorter genes acting on a responder locus. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):621–628. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90393-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. E., Pravtcheva D. D., Day C., Ruddle F. H., Jones P. P. Murine invariant chain gene: chromosomal assignment and segregation in recombinant inbred strains. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(2):193–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00563518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhme D., Fox H., Herrmann B., Frischauf A. M., Edström J. E., Mains P., Silver L. M., Lehrach H. Molecular clones of the mouse t complex derived from microdissected metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Steege D. A., Juricek D. K., Summers W. P., Ruddle F. H. A herpes simplex virus 1 integration site in the mouse genome defined by somatic cell genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):455–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymura J. M., Wabl M. R., Klein J. Mouse mitochondrial superoxide dismutase locus is on chromosome 17. Immunogenetics. 1981;14(3-4):231–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00342192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]