Abstract
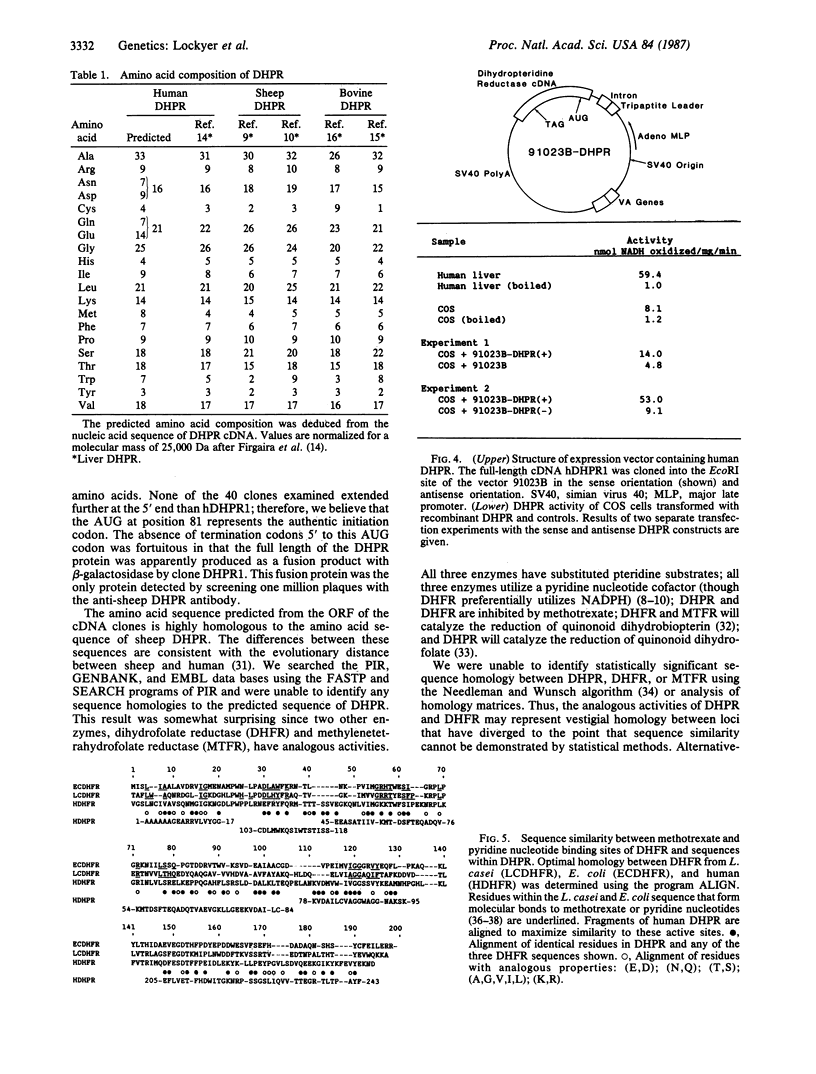
Dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR; EC 1.6.99.7) catalyzes the NADH-mediated reduction of quinonoid dihydrobiopterin and is an essential component of the pterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylating systems. A cDNA for human DHPR was isolated from a human liver cDNA library in the vector lambda gt11 using a monospecific antibody against sheep DHPR. The nucleic acid sequence and amino acid sequence of human DHPR were determined from a full-length clone. A 112 amino acid sequence of sheep DHPR was obtained by sequencing purified sheep DHPR. This sequence is highly homologous to the predicted amino acid sequence of the human protein. Gene transfer of the recombinant human DHPR into COS cells leads to expression of DHPR enzymatic activity. These results indicate that the cDNA clone identified by antibody screening is an authentic and full-length cDNA for human DHPR.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolin J. T., Filman D. J., Matthews D. A., Hamlin R. C., Kraut J. Crystal structures of Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus casei dihydrofolate reductase refined at 1.7 A resolution. I. General features and binding of methotrexate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13650–13662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewster T. G., Moskowitz M. A., Kaufman S., Breslow J. L., Milstien S., Abroms I. F. Dihydropteridine reductase deficiency associated with severe neurologic disease and mild hyperphenylalaninemia. Pediatrics. 1979 Jan;63(1):94–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Gamble C. L., Izaguirre C. A., Minden M. D., Mak T. W., McCulloch E. A. Detection of genes coding for human differentiation markers by their transient expression after DNA transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):146–150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheema S., Soldin S. J., Knapp A., Hofmann K. T., Scrimgeour K. G. Properties of purifed quinonoid dihydropterin reductase. Can J Biochem. 1973 Sep;51(9):1229–1239. doi: 10.1139/o73-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craine J. E., Hall E. S., Kaufman S. The isolation and characterization of dihydropteridine reductase from sheep liver. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6082–6091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filman D. J., Bolin J. T., Matthews D. A., Kraut J. Crystal structures of Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus casei dihydrofolate reductase refined at 1.7 A resolution. II. Environment of bound NADPH and implications for catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13663–13672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firgaira F. A., Choo K. H., Cotton R. G., Danks D. M. Heterogeneity of the molecular defect in human dihydropteridine reductase deficiency. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):677–682. doi: 10.1042/bj1980677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firgaira F. A., Cotton R. G., Danks D. M. Isolation and characterization of dihydropteridine reductase from human liver. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 1;197(1):31–43. doi: 10.1042/bj1970031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa H. Dihydropteridine reductase from bovine liver. Purification, crystallization, and isolation of a binary complex with NADH. J Biochem. 1977 Jan;81(1):169–177. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S. STUDIES ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE PRIMARY OXIDATION PRODUCT FORMED FROM TETRAHYDROPTERIDINES DURING PHENYLALAMINE HYDROXYLATION. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:332–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S. THE STRUCTURE OF THE PHENYLALANINE-HYDROXYLATION COFACTOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1085–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S. The enzymatic conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):511–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S., Holtzman N. A., Milstien S., Butler L. J., Krumholz A. Phenylketonuria due to a deficiency of dihydropteridine reductase. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 16;293(16):785–790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510162931601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. Phenylketonuria and its variants. Adv Hum Genet. 1983;13:217–297. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8342-4_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korri K. K., Chippel D., Chauvin M. M., Tirpak A., Scrimgeour K. G. Quinonoid dihydropterin reductase from beef liver. Can J Biochem. 1977 Nov;55(11):1145–1152. doi: 10.1139/o77-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length complementary DNA clone and amino acid sequence of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):556–561. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D., Grenett H. E., DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Woo S. L. Gene transfer and expression of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.3856322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D., Grenett H. E., McGinnis-Shelnutt M., Woo S. L. Retroviral-mediated gene transfer of human phenylalanine hydroxylase into NIH 3T3 and hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):409–413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D. Somatic gene therapy for human disease: background and prospects. Part I. J Pediatr. 1987 Jan;110(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80278-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D. Somatic gene therapy for human disease: background and prospects. Part II. J Pediatr. 1987 Feb;110(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Ochs R. L., Reddy R., Cook R. G., Yeoman L. C., Tan E. M., Reichlin M., Busch H. Purification and partial characterization of a nucleolar scleroderma antigen (Mr = 34,000; pI, 8.5) rich in NG,NG-dimethylarginine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14304–14310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. A., Alden R. A., Bolin J. T., Freer S. T., Hamlin R., Xuong N., Kraut J., Poe M., Williams M., Hoogsteen K. Dihydrofolate reductase: x-ray structure of the binary complex with methotrexate. Science. 1977 Jul 29;197(4302):452–455. doi: 10.1126/science.17920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. G., Kaufman S. Characterization of the dihydropterin reductase activity of pig liver methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6014–6017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. S., Paterson B. M., Ricciardi R. P., Cohen L., Roberts B. E. Methods utilizing cell-free protein-synthesizing systems for the identification of recombinant DNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:650–674. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstien S., Kaufman S. Preparation of an antiserum to sheep liver dihydropteridine reductase. Methods Enzymol. 1980;66:723–725. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(80)66532-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichol C. A., Smith G. K., Duch D. S. Biosynthesis and metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin and molybdopterin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:729–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K. H., Simonsen V., Lind K. E. Dihydropteridine reductase. A method for the measurement of activity, and investigations of the specificity for NADH and NADPH. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jul;9(4):497–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R. J., Kaufman S. Dihydropteridine reductase may function in tetrahydrofolate metabolism. J Neurochem. 1978 Jul;31(1):115–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]