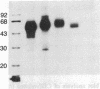
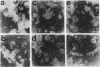
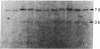
Abstract
A cDNA encoding the CD2 antigen has been isolated by a highly efficient technique based on transient expression in COS cells and adherence of cells expressing surface antigen to antibody-coated dishes. COS cells expressing a CD2 cDNA isolated by this method readily formed rosettes with sheep as well as human and other mammalian erythrocytes. Pretreatment of transfected COS cells with anti-CD2 antibody, or pretreatment of human erythrocytes with anti-LFA-3 antibody, abolished rosette formation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach J. F., Dormont J., Dardenne M., Balner H. In vitro rosette inhibition by antihuman antilymphocyte serum. Correlation with skin graft prolongation in subhuman primates. Transplantation. 1969 Sep;8(3):265–280. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196909000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxley G., Bishop G. B., Cooper A. G., Wortis H. H. Rosetting of human red blood cells to thymocytes and thymus-derived cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Nov;15(3):385–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard A., Gelin C., Raynal B., Pham D., Gosse C., Boumsell L. Phenomenon of human T cells rosetting with sheep erythrocytes analyzed with monoclonal antibodies. "Modulation" of a partially hidden epitope determining the conditions of interaction between T cells and erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1317–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain P., Gordon J., Willetts W. A. Rosette formation by peripheral lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):681–688. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs R. R., Gurner B. W., Wilson A. B., Holm G., Lindgren B. Rosette-formation between human lymphocytes and sheep red cells not involving immunoglobulin receptors. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(5-6):658–663. doi: 10.1159/000230390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard F. D., Ledbetter J. A., Wong J., Bieber C. P., Stinson E. B., Herzenberg L. A. A human T lymphocyte differentiation marker defined by monoclonal antibodies that block E-rosette formation. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2117–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen K. S., Johansen T. S., Talmage D. W. T cell rosette formation in primates, pigs, and guinea pigs. The influence of immunosuppresive agents. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1974 Aug;54(2):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(74)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun M., Martin P. J., Hansen J. A., Brown M. A., Siadak A. W., Nowinski R. C. Identification of a human T lymphocyte surface protein associated with the E-rosette receptor. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):207–212. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata M., Parnes J. R., Herzenberg L. A. Transcriptional control of HLA-A,B,C antigen in human placental cytotrophoblast isolated using trophoblast- and HLA-specific monoclonal antibodies and the fluorescence-activated cell sorter. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):633–651. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krensky A. M., Sanchez-Madrid F., Robbins E., Nagy J. A., Springer T. A., Burakoff S. J. The functional significance, distribution, and structure of LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3: cell surface antigens associated with CTL-target interactions. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little P. F., Treisman R., Bierut L., Seed B., Maniatis T. Plasmid vectors for the rapid isolation and transcriptional analysis of human beta-globin gene alleles. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Dec;1(5):473–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. J., Longton G., Ledbetter J. A., Newman W., Braun M. P., Beatty P. G., Hansen J. A. Identification and functional characterization of two distinct epitopes on the human T cell surface protein Tp50. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):180–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalet V., Fournier C. Human autologous rosette-forming cells. III. Binding of erythrocytes from different species to the T-cell receptors for autologous red blood cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Nov;96(1):126–136. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flynn K., Knott L. J., Russul-Saib M., Abdul-Gaffar R., Morgan G., Beverley P. C., Linch D. C. CD2 and CD3 antigens mobilize Ca2+ independently. Eur J Immunol. 1986 May;16(5):580–584. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flynn K., Krensky A. M., Beverley P. C., Burakoff S. J., Linch D. C. Phytohaemagglutinin activation of T cells through the sheep red blood cell receptor. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):686–687. doi: 10.1038/313686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flynn K., Russul-Saib M., Ando I., Wallace D. L., Beverley P. C., Boylston A. W., Linch D. C. Different pathways of human T-cell activation revealed by PHA-P and PHA-M. Immunology. 1986 Jan;57(1):55–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Martinez-Maza O. Is the E receptor on human T lymphocytes a "negative signal receptor"? J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2479–2485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Tadmori W., Kamoun M., Koretzky G., Nowell P. C. Suppression of interleukin 2 receptor acquisition by monoclonal antibodies recognizing the 50 KD protein associated with the sheep erythrocyte receptor on human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1631–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. High-frequency transfer of cloned herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences to mammalian cells by protoplast fusion. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;1(8):743–752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.8.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell W. A., Brown M. H., Dunne J., Owen M. J., Crumpton M. J. Molecular cloning of the human T-lymphocyte surface CD2 (T11) antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8718–8722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Luce G. E., Quinones R., Gress R. E., Springer T. A., Sanders M. E. Two antigen-independent adhesion pathways used by human cytotoxic T-cell clones. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):262–264. doi: 10.1038/323262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman D. J., Milman G. Short-term, high-efficiency expression of transfected DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1641–1643. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbi W., Greaves M. F., Schneider C., Koubek K., Janossy G., Stein H., Kung P., Goldstein G. Monoclonal antibodies OKT 11 and OKT 11A have pan-T reactivity and block sheep erythrocyte "receptors". Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):81–86. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. Y., Chouaib S., Dupont B. A common pathway for T lymphocyte activation involving both the CD3-Ti complex and CD2 sheep erythrocyte receptor determinants. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1097–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]