Abstract
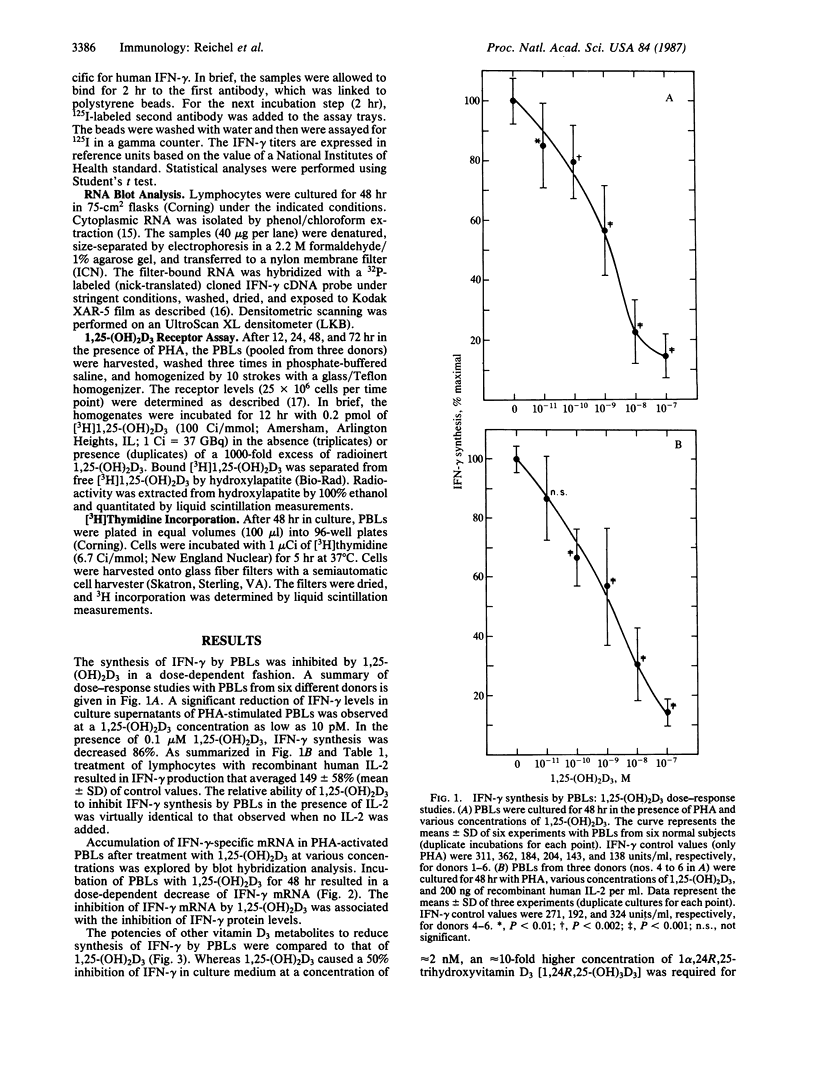
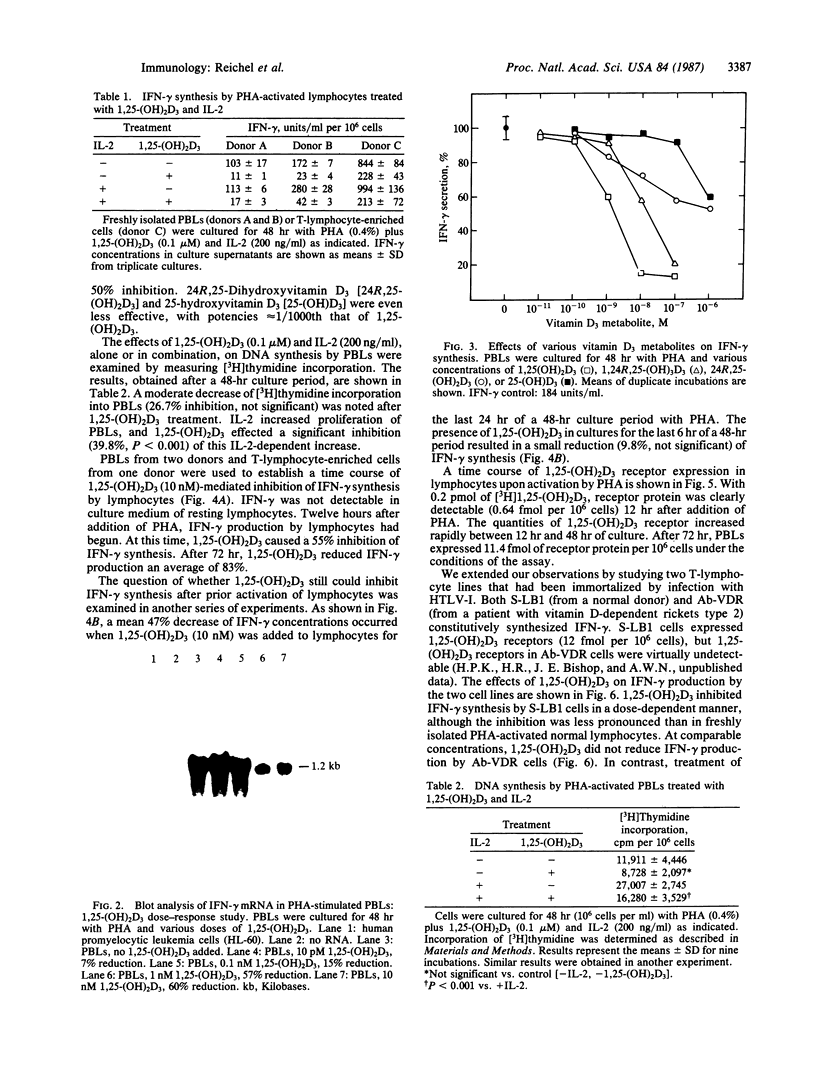
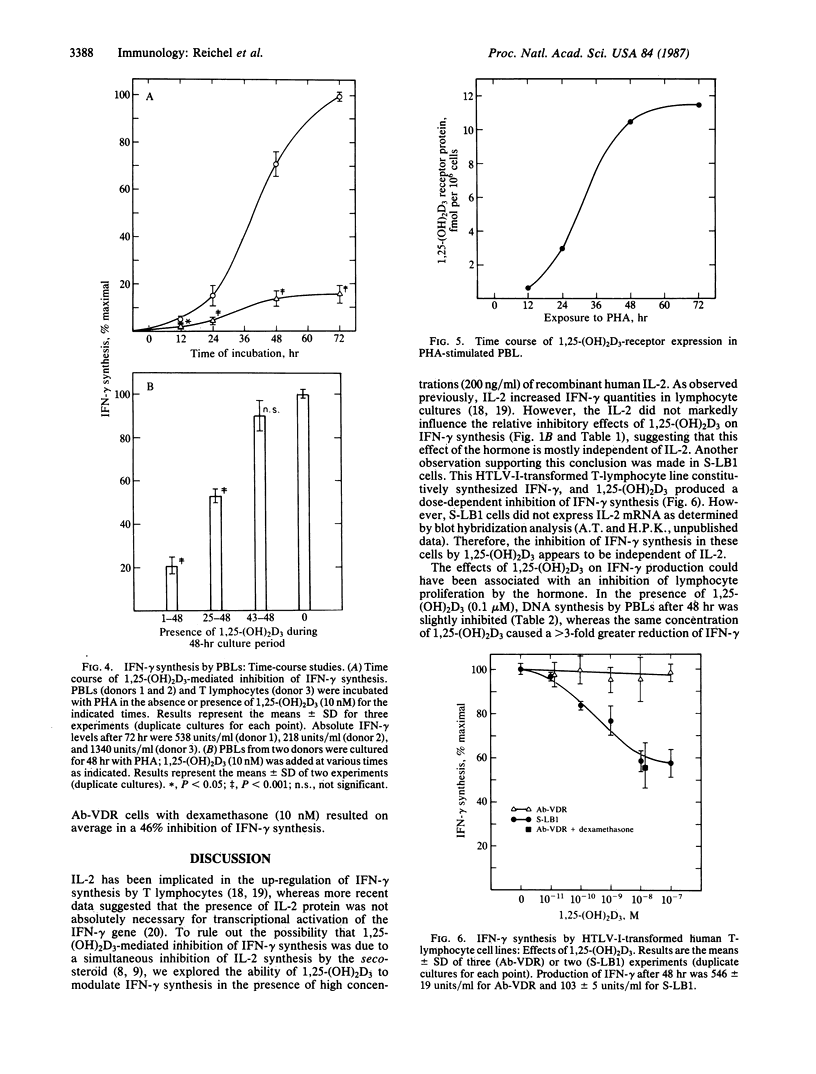
1 alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25-(OH)2D3], the biologically active metabolite of vitamin D3, inhibited synthesis of gamma-interferon (IFN-gamma) by phytohemagglutinin-activated peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs). A significant reduction of IFN-gamma protein levels in PBL culture medium was achieved with a physiologic 1,25-(OH)2D3 concentration (0.1 nM). 1,25-(OH)2D3 also inhibited accumulation of IFN-gamma mRNA in activated PBLs in a dose-dependent fashion. The ability of 1,25-(OH)2D3 to modulate IFN-gamma protein synthesis was unaltered in the presence of high concentrations of recombinant human interleukin 2. The suppression of IFN-gamma synthesis by PBLs was specific for 1,25-(OH)2D3; the potencies of other vitamin D3 metabolites were correlated with their affinities for the cellular 1,25-(OH)2D3 receptor. The time course of 1,25-(OH)2D3 receptor expression in phytohemagglutinin-activated PBLs was correlated with the time course of 1,25-(OH)2D3-mediated inhibition of IFN-gamma synthesis. In selected experiments, T-lymphocyte-enriched cell preparations were utilized. In these experiments, 1,25-(OH)2D3 was equally active as in PBL preparations. Finally, we examined the effects of 1,25-(OH)2D3 on the constitutive IFN-gamma production by two human T-lymphocyte lines transformed by human T-lymphotropic virus type I. The cell lines were established from a normal donor (cell line S-LB1) and from a patient with vitamin D-dependent rickets type 2 (cell line Ab-VDR). IFN-gamma synthesis by S-LB1 cells was inhibited in a dose-dependent fashion by 1,25-(OH)2D3, whereas IFN-gamma synthesis by Ab-VDR cells was not altered by 1,25-(OH)2D3. The data presented in this study provide further evidence for a role of 1,25-(OH)2D3 in immunoregulation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Shavit Z., Teitelbaum S. L., Reitsma P., Hall A., Pegg L. E., Trial J., Kahn A. J. Induction of monocytic differentiation and bone resorption by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5907–5911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla A. K., Amento E. P., Clemens T. L., Holick M. F., Krane S. M. Specific high-affinity receptors for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: presence in monocytes and induction in T lymphocytes following activation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Dec;57(6):1308–1310. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-6-1308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla A. K., Amento E. P., Serog B., Glimcher L. H. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits antigen-induced T cell activation. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1748–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., McKinney S., Liu V., Kung P. C., Vilcek J., Le J. Use of monoclonal antibodies as sensitive and specific probes for biologically active human gamma-interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5219–5222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Amatruda T., Ikekawa N., Kobayashi Y., DeLuca H. F. Induction of macrophage differentiation of human normal and leukemic myeloid stem cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its fluorinated analogues. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5624–5628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Sequential expression of genes involved in human T lymphocyte growth and differentiation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1593–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire J. M., Adams J. S., Kermani-Arab V., Bakke A. C., Sakai R., Jordan S. C. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses human T helper/inducer lymphocyte activity in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3032–3035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire J. M., Adams J. S., Sakai R., Jordan S. C. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses proliferation and immunoglobulin production by normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):657–661. doi: 10.1172/JCI111465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Koeffler H. P., Donaldson C. A., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced differentiation in a human promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL-60): receptor-mediated maturation to macrophage-like cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):391–398. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murao S., Gemmell M. A., Callaham M. F., Anderson N. L., Huberman E. Control of macrophage cell differentiation in human promyelocytic HL-60 leukemia cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1983 Oct;43(10):4989–4996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W., Roth J., Orci L. The vitamin D endocrine system: steroid metabolism, hormone receptors, and biological response (calcium binding proteins). Endocr Rev. 1982 Fall;3(4):331–366. doi: 10.1210/edrv-3-4-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provvedini D. M., Tsoukas C. D., Deftos L. J., Manolagas S. C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors in human leukocytes. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1181–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.6310748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reem G. H., Yeh N. H. Interleukin 2 regulates expression of its receptor and synthesis of gamma interferon by human T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):429–430. doi: 10.1126/science.6429853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby W. F., Stacy T., Fanger M. W. Inhibition of T lymphocyte mitogenesis by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol). J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1451–1455. doi: 10.1172/JCI111557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Provvedini D. M., Manolagas S. C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: a novel immunoregulatory hormone. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1438–1440. doi: 10.1126/science.6427926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Henriksen-Destefano D., Siegel D., Klion A., Robb R. J., Le J. Regulation of IFN-gamma induction in human peripheral blood cells by exogenous and endogenously produced interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1851–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wecksler W. R., Norman A. W. An hydroxylapatite batch assay for the quantitation of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-receptor complexes. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 15;92(2):314–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90664-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




