Abstract
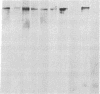
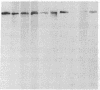
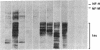
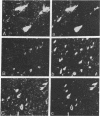
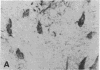
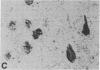
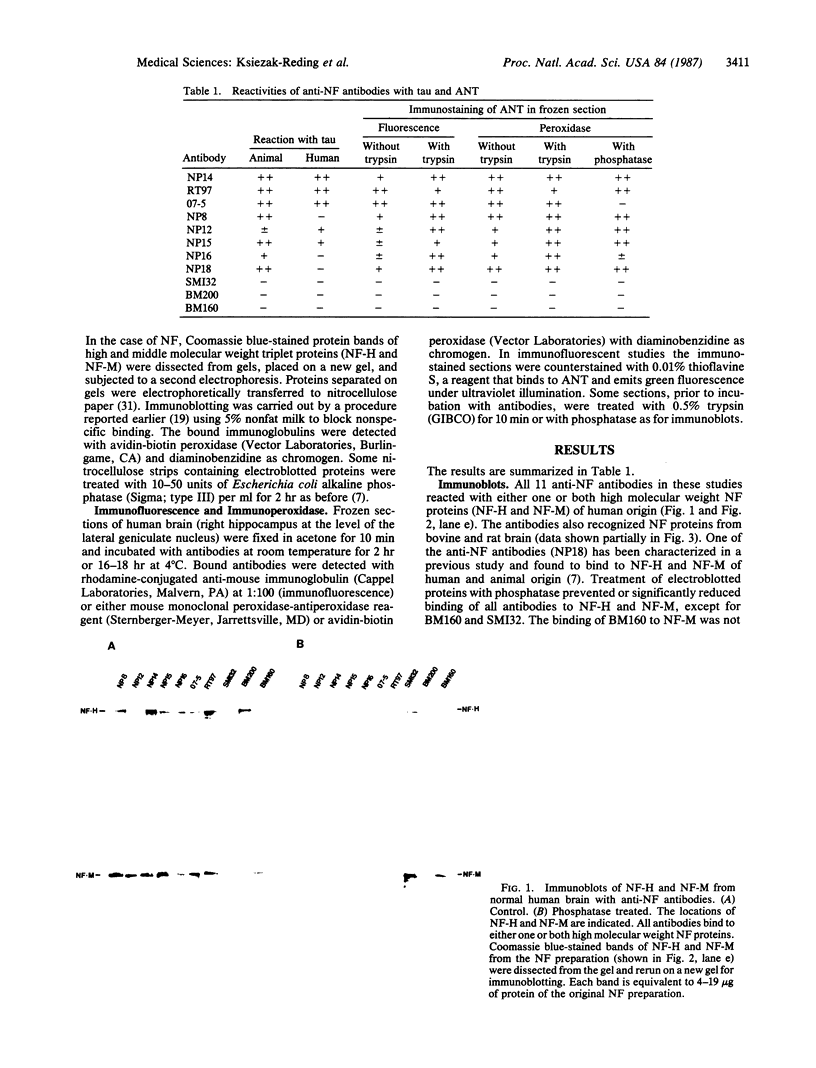
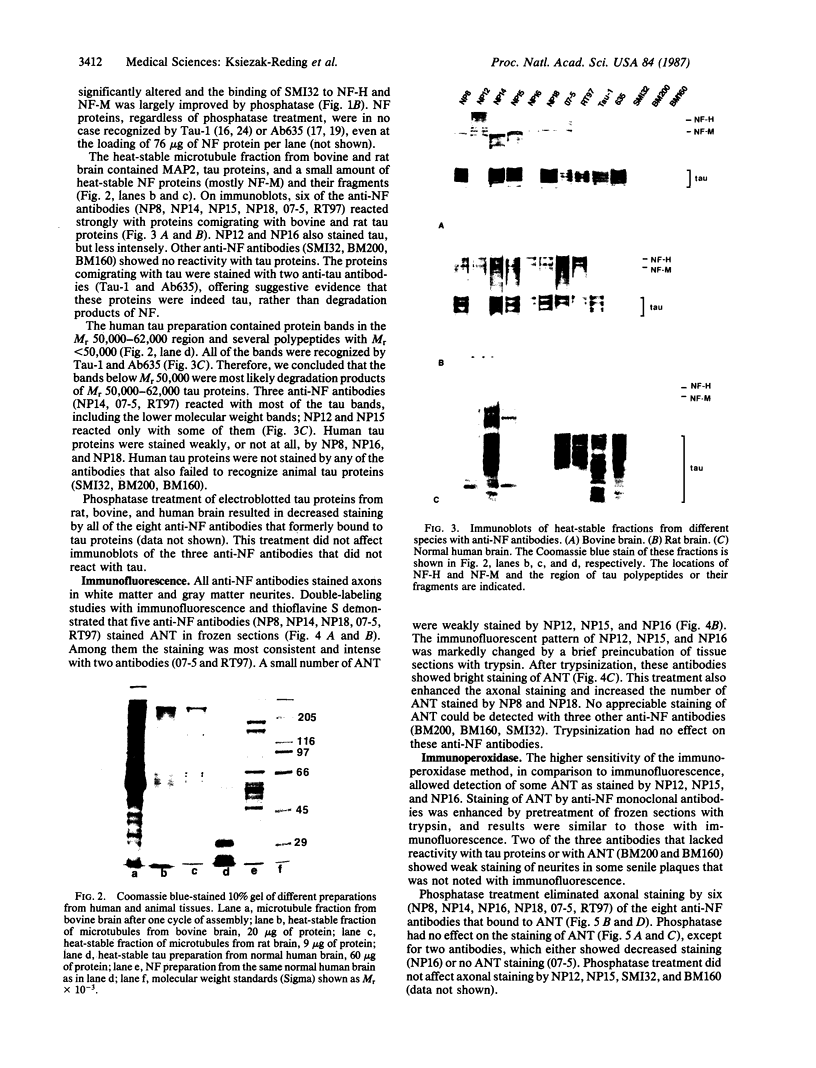
Eleven anti-neurofilament (anti-NF) monoclonal antibodies were studied for their reactivity with heat-stable, microtubule-associated proteins and Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles (ANT). On immunoblots of NF proteins, the antibodies recognized epitopes that were variably sensitive to Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Eight of the antibodies showed reactivity with ANT and decreased binding to electroblotted NF after phosphatase treatment. The same eight antibodies reacted with tau proteins from bovine and rat brain, binding to tau proteins was also substantially reduced by phosphatase. Of the eight antibodies that bound to animal tau proteins, five also bound to tau proteins from normal human brain. All of the antibodies that bound to animal tau proteins stained ANT in frozen tissue sections. Brief treatment of tissue sections with trypsin in most cases enhanced antibody binding to ANT. All antibodies that lacked reactivity with tau proteins failed to bind ANT. Phosphatase treatment of Alzheimer tissue sections did not change the immunoreactivity of ANT and neurites in senile plaques with ANT-reactive, anti-NF antibodies, except for two antibodies that showed decreased binding to ANT. In contrast, axonal staining was decreased or eliminated by phosphatase treatment, similar to the response of electroblotted NF and tau proteins. These results suggest that staining of ANT by anti-NF antibodies may be due to cross-reaction of anti-NF with epitopes in tau proteins, the epitopes in axons, NF, and tau are sensitive to the effect of phosphatase, whereas the majority of those in ANT are not, and some of the epitopes in ANT that are shared with NF and tau proteins are not readily accessible to antibody binding.
Full text
PDF
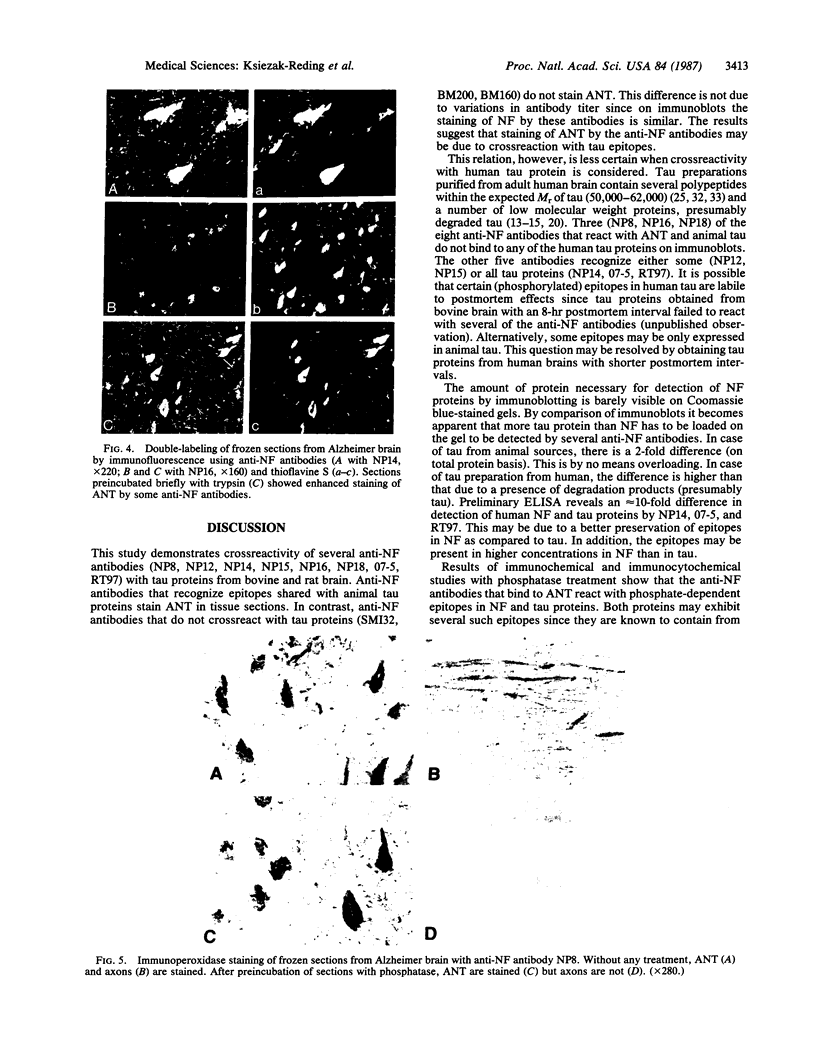

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderton B. H., Breinburg D., Downes M. J., Green P. J., Tomlinson B. E., Ulrich J., Wood J. N., Kahn J. Monoclonal antibodies show that neurofibrillary tangles and neurofilaments share antigenic determinants. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):84–86. doi: 10.1038/298084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder L. I., Frankfurter A., Rebhun L. I. The distribution of tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M., Shelanski M. L. Microheterogeneity of microtubule-associated tau proteins is due to differences in phosphorylation. J Neurochem. 1986 Nov;47(5):1517–1522. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. Physical and chemical properties of purified tau factor and the role of tau in microtubule assembly. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 25;116(2):227–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cork L. C., Sternberger N. H., Sternberger L. A., Casanova M. F., Struble R. G., Price D. L. Phosphorylated neurofilament antigens in neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1986 Jan;45(1):56–64. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198601000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Caput D., Kirschner M. W. Studies on the expression of the microtubule-associated protein, tau, during mouse brain development, with newly isolated complementary DNA probes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1090–1097. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovaara I., Paetau A., Lehto V. P., Dahl D., Virtanen I., Palo J. Immunocytochemical studies of Alzheimer neuronal perikarya with intermediate filament antisera. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Dec;62(1-3):315–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Quinlan M., Tung Y. C., Zaidi M. S., Wisniewski H. M. Microtubule-associated protein tau. A component of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):6084–6089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Tung Y. C., Quinlan M., Wisniewski H. M., Binder L. I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog W., Weber K. Fractionation of brain microtubule-associated proteins. Isolation of two different proteins which stimulate tubulin polymerization in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Mushynski W. E. Multiple phosphorylation sites in mammalian neurofilament polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10467–10470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD M. ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE--AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPICAL STUDY. Brain. 1964 Jun;87:307–320. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Duffy L. K., Dowling M. M., Abraham C., McCluskey A., Selkoe D. J. Microtubule-associated protein 2: monoclonal antibodies demonstrate the selective incorporation of certain epitopes into Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7941–7945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Joachim C. L., Selkoe D. J. Microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4044–4048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Yen S. H. Two monoclonal antibodies recognize Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles, neurofilament, and microtubule-associated proteins. J Neurochem. 1987 Feb;48(2):455–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindwall G., Cole R. D. The purification of tau protein and the occurrence of two phosphorylation states of tau in brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12241–12245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luca F. C., Bloom G. S., Vallee R. B. A monoclonal antibody that cross-reacts with phosphorylated epitopes on two microtubule-associated proteins and two neurofilament polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1006–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. C., Brion J. P., Calvert R., Chin T. K., Eagles P. A., Downes M. J., Flament-Durand J., Haugh M., Kahn J., Probst A. Alzheimer's paired helical filaments share epitopes with neurofilament side arms. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):269–276. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukina N., Ihara Y. One of the antigenic determinants of paired helical filaments is related to tau protein. J Biochem. 1986 May;99(5):1541–1544. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukina N., Kosik K. S., Selkoe D. J. Recognition of Alzheimer paired helical filaments by monoclonal neurofilament antibodies is due to crossreaction with tau protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3415–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Rizzuto N., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Paired helical filaments from Alzheimer disease patients contain cytoskeletal components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3916–3920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasool C. G., Abraham C., Anderton B. H., Haugh M., Kahn J., Selkoe D. J. Alzheimer's disease: immunoreactivity of neurofibrillary tangles with anti-neurofilament and anti-paired helical filament antibodies. Brain Res. 1984 Sep 24;310(2):249–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Ihara Y., Salazar F. J. Alzheimer's disease: insolubility of partially purified paired helical filaments in sodium dodecyl sulfate and urea. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1243–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.6120571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Sternberger N. H. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of neurofilaments in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6126–6130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger N. H., Sternberger L. A., Ulrich J. Aberrant neurofilament phosphorylation in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4274–4276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolozin B. L., Pruchnicki A., Dickson D. W., Davies P. A neuronal antigen in the brains of Alzheimer patients. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):648–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3083509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Mirra S. S., Pollock N. J., Binder L. I. Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4040–4043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Lathangue N. B., McLachlan D. R., Smith B. J., Anderton B. H., Dowding A. J. Chromatin proteins share antigenic determinants with neurofilaments. J Neurochem. 1985 Jan;44(1):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Crowe A., Dickson D. W. Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. 1. Identification of polypeptides. Am J Pathol. 1985 Aug;120(2):282–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Dickson D. W., Crowe A., Butler M., Shelanski M. L. Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles contain unique epitopes and epitopes in common with the heat-stable microtubule associated proteins tau and MAP2. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jan;126(1):81–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]