Abstract
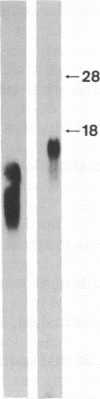
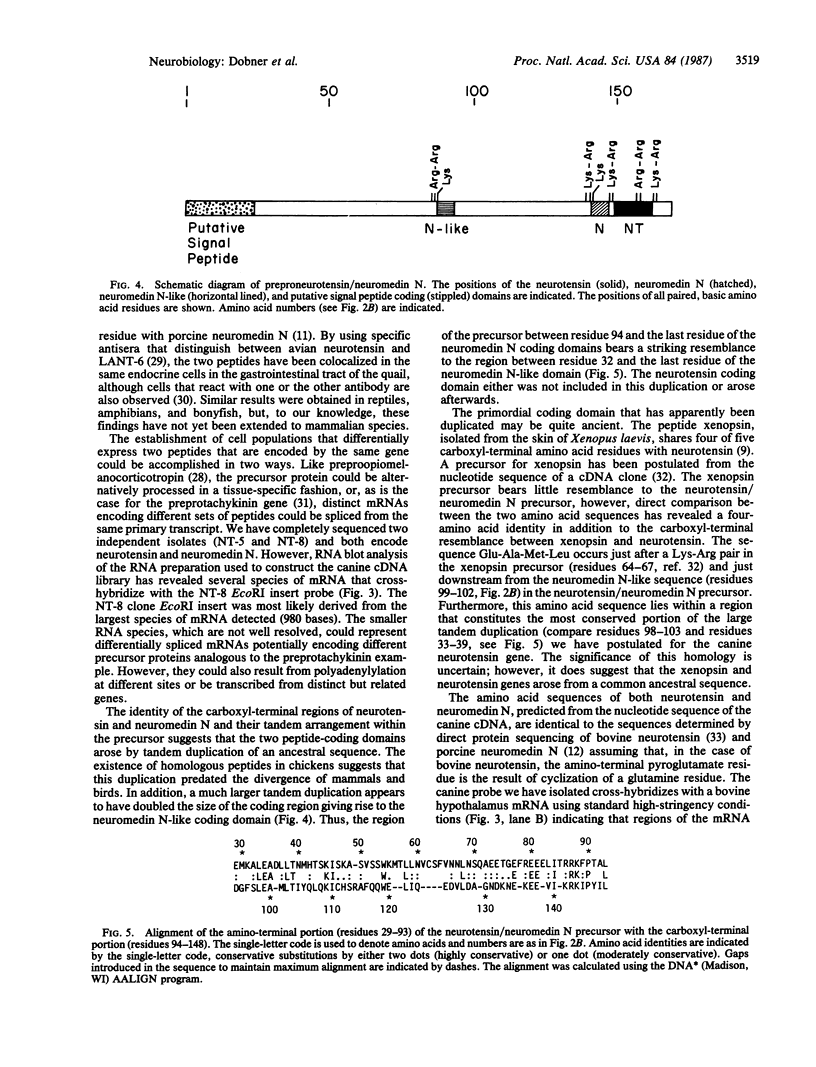
Cloned cDNAs encoding neurotensin were isolated from a cDNA library derived from primary cultures of canine enteric mucosa cells. Nucleotide sequence analysis has revealed the primary structure of a 170-amino acid precursor protein that encodes both neurotensin and the neurotensin-like peptide neuromedin N. The peptide-coding domains are located in tandem near the carboxyl terminus of the precursor and are bounded and separated by the paired, basic amino acid residues Lys-Arg. An additional coding domain, resembling neuromedin N, occurs immediately after an Arg-Arg basic amino acid pair located in the central region of the precursor. Additional amino acid homologies suggest that tandem duplications have contributed to the structure of the gene. RNA blot analysis, using the cloned cDNA probe, has revealed several mRNA species ranging in size from 500 to 980 nucleotides in the canine enteric mucosa. In contrast, a single RNA species of 1500 nucleotides was detected in bovine hypothalamus poly(A)+ RNA. The ability of the canine probe to cross-hybridize with bovine mRNA suggests that this probe can be used to isolate neurotensin/neuromedin N genes from other mammalian species.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki K., Tachibana S., Uchiyama M., Nakajima T., Yasuhara T. Isolation and structure of a new active peptide "Xenopsin" on the smooth muscle, especially on a strip of fundus from a rat stomach, from the skin of Xenopus laevis. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1973 Dec;21(12):2801–2804. doi: 10.1248/cpb.21.2801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong M. J., Parker M. C., Ferris C. F., Leeman S. E. Neurotensin stimulates [3H]oleic acid translocation across rat small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 1):G823–G829. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.6.G823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber D. L., Buchan A. M., Walsh J. H., Soll A. H. Isolated canine ileal mucosal cells in short-term culture: a model for study of neurotensin release. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):G374–G384. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.3.G374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R. E., Ferris C. F. Isolation, biological and chemical characterization, and synthesis of a neurotensin-related hexapeptide from chicken intestine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2475–2479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R. E., Ruane S. E., Ritsema R. S. Radioimmunoassay for Lys8, Asn9, neurotensin 8-13: tissue and subcellular distribution of immunoreactivity in chickens. Peptides. 1983 Jan-Feb;4(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(83)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Bhatnagar Y. M. Isolation, structure and biologic activity of chicken intestinal neurotensin. Peptides. 1980 Summer;1(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(80)90082-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Kitabgi P., Leeman S. E. The amino acid sequence of radioimmunoassayable neurotensin from bovine intestine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):7996–7998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. Characterization of radioimmunoassayable neurotensin in the rat. Its differential distribution in the central nervous system, small intestine, and stomach. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7045–7052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The amino acid sequence of a hypothalamic peptide, neurotensin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1907–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobner P. R., Kawasaki E. S., Yu L. Y., Bancroft F. C. Thyroid or glucocorticoid hormone induces pre-growth-hormone mRNA and its probable nuclear precursor in rat pituitary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2230–2234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Civelli O., Herbert E. Polyprotein gene expression: generation of diversity of neuroendocrine peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:665–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. F., Armstrong M. J., George J. K., Stevens C. A., Carraway R. E., Leeman S. E. Alcohol and fatty acid stimulation of neurotensin release from rat small intestine. Endocrinology. 1985 Mar;116(3):1133–1138. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-3-1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. A., Leeman S. E., Carraway R., Williams R. H. Isolation of human intestinal neurotensin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2476–2480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstaedter V., Feurle G. E., Forssmann W. G. Ultrastructural identification of a new cell type--the N-cell as the source of neurotensin in the gut mucosa. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Nov 23;184(4):445–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00220968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R. Studies on the selectivity of DNA precipitation by spermine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5493–5504. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge J., Langridge P., Bergquist P. L. Extraction of nucleic acids from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Apr;103(2):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeman S. E., Aronin N., Ferris C. Substance P and neurotensin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1982;38:93–132. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571138-8.50008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley T. J., Anagnou N. P., Pepe G., Nienhuis A. W. RNA processing errors in patients with beta-thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4775–4779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Neuromedin N: a novel neurotensin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):542–549. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Nakanishi S. Nucleotide sequences of cloned cDNAs for two types of bovine brain substance P precursor. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):32–36. doi: 10.1038/306032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke M. Neurotensin. Immunohistochemical localization in central and peripheral nervous system and in endocrine cells and its functional role as neurotransmitter and endocrine hormone. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 1985;16(1):1–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Crippa M. Xenopsin: the neurotensin-like octapeptide from Xenopus skin at the carboxyl terminus of its precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):380–384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]