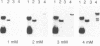Abstract
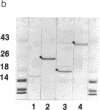
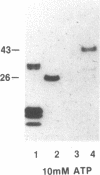
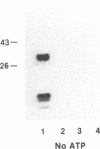
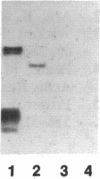
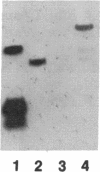
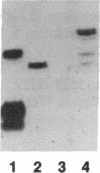
We have previously shown that the mos gene product, p40mos, produced in Escherichia coli binds ATP and has ATPase activity. In the present study, we investigated the DNA-binding properties of p40mos and two mos deletion mutant proteins. Nitrocellulose blot protein-DNA binding assays showed that p40mos binds DNA in the presence of Mg2+-ATP and certain other nucleoside triphosphates. Ninety percent of the p40mos-bound DNA is dissociated if the complex is washed in the presence of 1 M NaCl or in the absence of ATP. p40mos-DNA binding is not observed in the presence of AMP or the nonhydrolyzable ATP analog adenosine 5'-[beta, gamma-methylene]-triphosphate; however, in the presence of ADP, p40mos binds DNA at 20% of the level that is observed with ATP. An N-terminal-deletion mutant protein, p19mos, has no DNA-binding activity, whereas a C-terminal-deletion mutant protein, p25mos, does. p25mos contains the ATP-binding domain, binds DNA in the presence of either ADP or ATP, and shows 5% and 45% binding (relative to that in the presence of ATP) in the presence of AMP and adenosine 5'-[beta, gamma-methylene]triphosphate, respectively. These results suggest that the N-terminal domain of p40mos is responsible for nucleoside triphosphate-mediated DNA binding. We also observed differential histone-DNA binding in the presence and absence of ATP.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K., Kornberg A. Mechanism of dnaB protein action. II. ATP hydrolysis by dnaB protein dependent on single- or double-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5253–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Cary K., Scheller A., Basilico C., Israel M. A., Prives C. A subclass of polyomavirus middle tumor antigen binds to DNA cellulose. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):157–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.157-164.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunte T., Greiser-Wilke I., Moelling K. The transforming protein of the MC29-related virus CMII is a nuclear DNA-binding protein whereas MH2 codes for a cytoplasmic RNA-DNA binding polyprotein. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1087–1092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Hager L., Dulbecco R. Simian virus 40 T antigen binds to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3754–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castora F. J., Kelly W. G. ATP inhibits nuclear and mitochondrial type I topoisomerases from human leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1680–1684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Gaudray P., May E., Cuzin F. The nucleotide binding site detected by affinity labeling in the large T proteins of polyoma and SV40 viruses is distinct from their ATPase catalytic site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15196–15203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Sippel A. E. Subnuclear localization of proteins encoded by the oncogene v-myb and its cellular homolog c-myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):62–69. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloetzer W. S., Maxwell S. A., Arlinghaus R. B. P85gag-mos encoded by ts110 Moloney murine sarcoma virus has an associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):412–416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautenberger J. A., Court D., Papas T. S. High-level expression in Escherichia coli of the carboxy-terminal sequences of the avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29) v-myc protein. Gene. 1983 Jul;23(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell S. A., Arlinghaus R. B. Serine kinase activity associated with Maloney murine sarcoma virus-124-encoded p37mos. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):321–333. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins W. K., Roberts M. P., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H. Use of a protein-blotting procedure and a specific DNA probe to identify nuclear proteins that recognize the promoter region of the transferrin receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6741–6744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Nigg E. A., Hunter T. The transforming protein of Moloney murine sarcoma virus is a soluble cytoplasmic protein. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Verma I. M., Hunter T. Detection of a transforming gene product in cells transformed by Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):417–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentz M., Vatev R., Goldthwait D. A. The effect of preincubation of HeLa cell nuclei with ATP on the degradation of mononucleosomal DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5513–5529. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Leder P. Nuclear localization and DNA binding properties of a protein expressed by human c-myc oncogene. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):718–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6463648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Barnet B., Scheller A., Khoury G., Jay G. Discrete regions of simian virus 40 large T antigen are required for nonspecific and viral origin-specific DNA binding. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):73–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.73-82.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Beck Y., Shure H. DNA binding properties of simian virus 40 T-antigens synthesized in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):689–696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.689-696.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Vande Woude G. F. Expression of c-mos proto-oncogene transcripts in mouse tissues. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):516–518. doi: 10.1038/315516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos M., Butel J. S. Association of SV40 large tumor antigen and cellular proteins on the surface of SV40-transformed mouse cells. Virology. 1982 Jul 15;120(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Lapis P., Vande Woude G. F., Papas T. High-level expression vectors to synthesize unfused proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;42(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Vande Woude G. F. Nucleotide sequence and biochemical activities of the Moloney murine sarcoma virus strain HT-1 mos gene. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):144–152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.144-152.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptides by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: further data concerning resolving power and general considerations. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jun;29(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Galleshaw J. A., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome of a murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt B., Vakalopoulou E., Fanning E. Allosteric control of simian virus 40 T-antigen binding to viral origin DNA. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):765–772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.765-772.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R. A., Shatzman A. R., Rosenberg M. Expression and characterization of the human c-myc DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):448–456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickett R., Isenberg I. The interaction of histone IV with nucleoside triphosphates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2687–2690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishart W. L., Broach J. R., Ohtsubo E. ATP-dependent specific binding of Tn3 transposase to Tn3 inverted repeats. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):556–558. doi: 10.1038/314556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]