Abstract
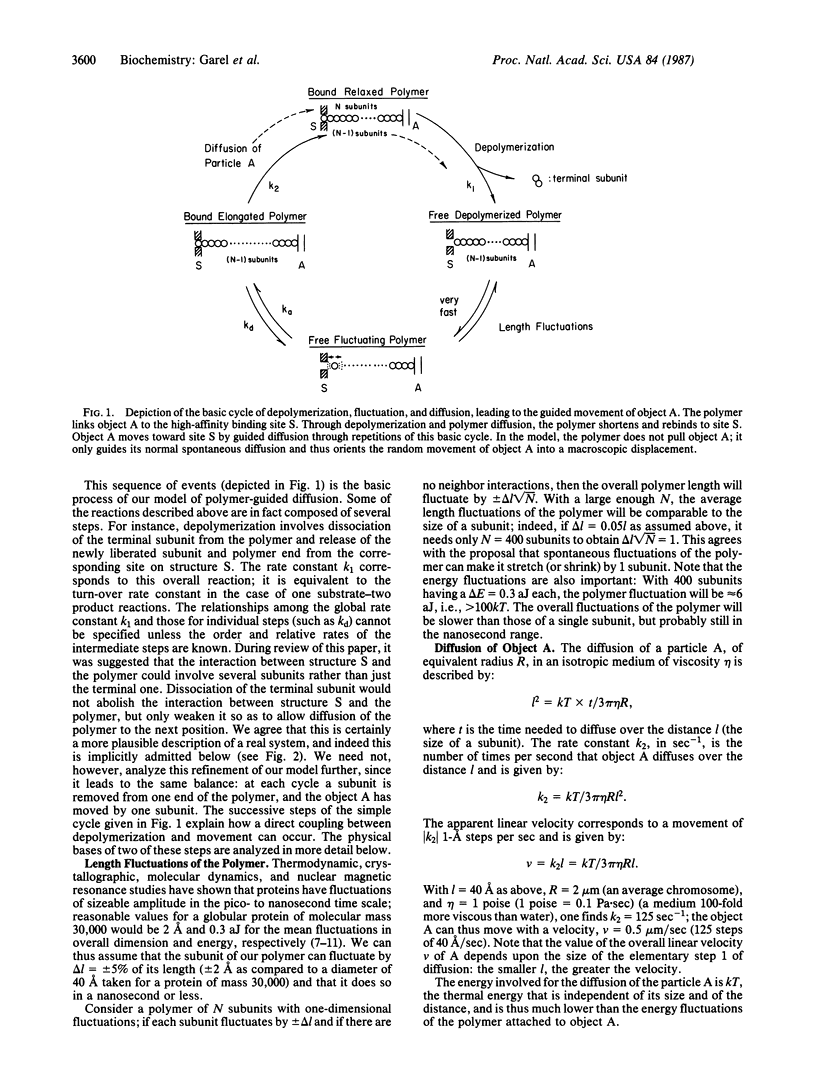
We propose a motility mechanism that may result in the displacement of objects within the cell. The mechanism, which we call polymer-guided diffusion, involves a microscopic cycle of polymer association and dissociation from a lateral binding site. Reassociation occurs at the polymer subunit adjacent to that which has just dissociated, thus generating an apparent sliding movement. The displacement involves only free diffusion and the spontaneous fluctuations of the polymer; the movement thus requires no other energy sources than thermal energy and the energy originally required for the formation of the polymer. In this manner polymer-associated organelles can be guided (inevitably) by diffusional processes toward a final destination. The specific example of the anaphase movement of chromosomes poleward is detailed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artymiuk P. J., Blake C. C., Grace D. E., Oatley S. J., Phillips D. C., Sternberg M. J. Crystallographic studies of the dynamic properties of lysozyme. Nature. 1979 Aug 16;280(5723):563–568. doi: 10.1038/280563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajer A. S., Cypher C., Molè-Bajer J., Howard H. M. Taxol-induced anaphase reversal: evidence that elongating microtubules can exert a pushing force in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6569–6573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajer A. S. Functional autonomy of monopolar spindle and evidence for oscillatory movement in mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):33–48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B., Karplus M. Harmonic dynamics of proteins: normal modes and fluctuations in bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6571–6575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cande W. Z. Inhibition of spindle elongation in permeabilized mitotic cells by erythro-9-[3-(2-hydroxynonyl)] adenine. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):700–701. doi: 10.1038/295700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cande W. Z. Nucleotide requirements for anaphase chromosome movements in permeabilized mitotic cells: anaphase B but not anaphase A requires ATP. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90370-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. Thermodynamic fluctuations in protein molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2740–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaban B. B., Forer A. The kinetic polarities of spindle microtubules in vivo, in crane-fly spermatocytes. I. Kinetochore microtubules that re-form after treatment with colcemid. J Cell Sci. 1985 Nov;79:1–37. doi: 10.1242/jcs.79.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaban B. B., Forer A. The kinetic polarities of spindle microtubules in vivo, in crane-fly spermatocytes. II. Kinetochore microtubules in non-treated spindles. J Cell Sci. 1985 Nov;79:39–65. doi: 10.1242/jcs.79.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Euteneuer U., McIntosh J. R. Structural polarity of kinetochore microtubules in PtK1 cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):338–345. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Euteneuer U., Ris H., Borisy G. G. Polarity of kinetochore microtubules in Chinese hamster ovary cells after recovery from a colcemid block. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):202–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frauenfelder H., Petsko G. A., Tsernoglou D. Temperature-dependent X-ray diffraction as a probe of protein structural dynamics. Nature. 1979 Aug 16;280(5723):558–563. doi: 10.1038/280558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G. J., Sammak P. J., Borisy G. G. Chromosomes move poleward in anaphase along stationary microtubules that coordinately disassemble from their kinetochore ends. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;104(1):9–18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Kirschner M. W. Subunit treadmilling of microtubules or actin in the presence of cellular barriers: possible conversion of chemical free energy into mechanical work. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):490–494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job D., Fischer E. H., Margolis R. L. Rapid disassembly of cold-stable microtubules by calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job D., Rauch C. T., Fischer E. H., Margolis R. L. Recycling of cold-stable microtubules: evidence that cold stability is due to substoichiometric polymer blocks. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):509–515. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karplus M., McCammon J. A. Dynamics of proteins: elements and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:263–300. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith C. H., Ratan R., Maxfield F. R., Bajer A., Shelanski M. L. Local cytoplasmic calcium gradients in living mitotic cells. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):848–850. doi: 10.1038/316848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren R., Hammes G. G. A kinetic study of protein-protein interactions. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):1165–1171. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levison S. A., Kierszenbaum F., Dandliker W. B. Salt effects on antigen-antibody kinetics. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 20;9(2):322–331. doi: 10.1021/bi00804a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Job D., Pabion M., Rauch C. T. Sliding of STOP proteins on microtubules: a model system for diffusion-dependent microtubule motility. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;466:306–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb38402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Rauch C. T., Job D. Purification and assay of a 145-kDa protein (STOP145) with microtubule-stabilizing and motility behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):639–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L., Keifer B. I. Mitotic mechanism based on intrinsic microtubule behaviour. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):450–452. doi: 10.1038/272450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T., Evans L., Schulze E., Kirschner M. Sites of microtubule assembly and disassembly in the mitotic spindle. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):515–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90283-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICKLAS R. B. CHROMOSOME VELOCITY DURING MITOSIS AS A FUNCTION OF CHROMOSOME SIZE AND POSITION. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:SUPPL–SUPPL:135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICKLAS R. B. CHROMOSOME VELOCITY DURING MITOSIS AS A FUNCTION OF CHROMOSOME SIZE AND POSITION. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:SUPPL–SUPPL:135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas R. B., Staehly C. A. Chromosome micromanipulation. I. The mechanics of chromosome attachment to the spindle. Chromosoma. 1967;21(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00330544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabion M., Job D., Margolis R. L. Sliding of STOP proteins on microtubules. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6642–6648. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Bourgeois S., Cohn M. The lac repressor-operator interaction. 3. Kinetic studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):401–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze E., Kirschner M. Microtubule dynamics in interphase cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1020–1031. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltys B. J., Borisy G. G. Polymerization of tubulin in vivo: direct evidence for assembly onto microtubule ends and from centrosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1682–1689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telzer B. R., Haimo L. T. Decoration of spindle microtubules with Dynein: evidence for uniform polarity. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):373–378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valberg P. A., Albertini D. F. Cytoplasmic motions, rheology, and structure probed by a novel magnetic particle method. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):130–140. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., Means A. R. Tubulin and calmodulin. Effects of microtubule and microfilament inhibitors on localization in the mitotic apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):624–634. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt P. L., Ris H., Borisy G. G. Origin of kinetochore microtubules in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Chromosoma. 1980;81(3):483–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00368158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



