Abstract
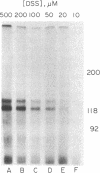
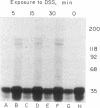
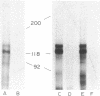
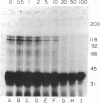
Erythropoietin (Epo) is a glycoprotein hormone that regulates erythroid development and interacts with surface receptors on developing erythroid cells. In this laboratory, a cell system with a relatively pure population of erythroid cells that respond to Epo has been developed. Immature erythroid cells are obtained from the spleens of mice infected with the anemia strain of Friend virus. The binding of 125I-labeled Epo (125I-Epo) to plasma membranes from these cells was studied in this investigation. 125I-Epo binding reached equilibrium within 20 min at 37 degrees C. Twenty percent of the receptors bound 125I-Epo with a Kd of 0.08 X 10(-9) M, while the remaining receptors bound the hormone with a Kd of 0.6 X 10(-9) M. In this study, a receptor for Epo was identified by cross-linking 125I-Epo to the receptor in intact cells and plasma membrane preparations using disuccinimidyl suberate. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed two labeled bands of 100 and 85 kDa. The 85-kDa band was more heavily labeled (65%) than the 100-kDa band. Both bands were equally decreased when increasing amounts of unlabeled Epo were included in the binding mixture, indicating a specific interaction of 125I-Epo with the receptor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bondurant M. C., Lind R. N., Koury M. J., Ferguson M. E. Control of globin gene transcription by erythropoietin in erythroblasts from friend virus-infected mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):675–683. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne J. K., Cohen A. M., Egrie J. C., Lai P. H., Lin F. K., Strickland T., Watson E., Stebbing N. Erythropoietin: gene cloning, protein structure, and biological properties. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):693–702. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. C., Sikkema D., Goldwasser E. Evidence for an erythropoietin receptor protein on rat bone marrow cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 25;57(2):399–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90944-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn K., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. III. Identification of a platelet-derived growth factor receptor by affinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5172–5176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koury M. J., Bondurant M. C., Duncan D. T., Krantz S. B., Hankins W. D. Specific differentiation events induced by erythropoietin in cells infected in vitro with the anemia strain of Friend virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):635–639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koury M. J., Bondurant M. C., Mueller T. J. The role of erythropoietin in the production of principal erythrocyte proteins other than hemoglobin during terminal erythroid differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Feb;126(2):259–265. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041260216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koury M. J., Sawyer S. T., Bondurant M. C. Splenic erythroblasts in anemia-inducing Friend disease: a source of cells for studies of erythropoietin-mediated differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Dec;121(3):526–532. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz S. B., Goldwasser E. Specific binding of erythropoietin to spleen cells infected with the anemia strain of Friend virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7574–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Guillette B. J., Czech M. P., Morgan C. J., Bradshaw R. A. Identification of a nerve growth factor receptor protein in sympathetic ganglia membranes by affinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9419–9424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Like B. Cellular receptors for type beta transforming growth factor. Ligand binding and affinity labeling in human and rodent cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2636–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The molecular biology and functions of the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):257–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misiti J., Spivak J. L. Erythropoiesis in vitro. Role of calcium. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1573–1579. doi: 10.1172/JCI109618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Peterson L. Identification of distinct receptors for two hemopoietic growth factors (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and multipotential colony-stimulating factor) by chemical cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12384–12389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paglin S., Jamieson J. D. Covalent crosslinking of angiotensin II to its binding sites in rat adrenal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3739–3743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. The subunit structure of the high affinity insulin receptor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked receptor complex in fat cell and liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1722–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawyler A. J., Roelofsen B., Wirtz K. W., Op den Kamp J. A. (poly) Phosphoinositide phosphorylation is a marker for plasma membrane in Friend erythroleukaemic cells. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 1;148(1):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Koury M. J., Bondurant M. C. Large-scale procurement of erythropoietin-responsive erythroid cells: assay for biological activity of erythropoietin. Methods Enzymol. 1987;147:340–352. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)47123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Krantz S. B. Transferrin receptor number, synthesis, and endocytosis during erythropoietin-induced maturation of Friend virus-infected erythroid cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9187–9195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon M., Klausner R. D., Cullen B. R., Chizzonite R., Leonard W. J. Novel interleukin-2 receptor subunit detected by cross-linking under high-affinity conditions. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):859–863. doi: 10.1126/science.3095922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood J. B., Goldwasser E. A radioimmunoassay for erythropoietin. Blood. 1979 Oct;54(4):885–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]