Abstract
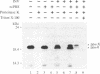
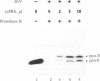
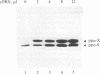
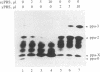
mRNA for prepro-alpha-factor (pp alpha), a yeast secretory glycoprotein, was translated in a wheat germ cell-free system that was posttranslationally supplemented either with inverted vesicles from the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli (INV) or with microsomes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A postribosomal supernatant (PRS) from E. coli was found to stimulate translocation of pp alpha across the INV membrane. A yeast PRS could substitute for its E. coli counterpart. Likewise, an E. coli PRS could substitute for a yeast PRS and stimulate translocation of pp alpha across yeast microsomal membranes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen L., Rhoads D., Tai P. C. Alkaline phosphatase and OmpA protein can be translocated posttranslationally into membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):973–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.973-980.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément J. M., Hofnung M. Gene sequence of the lambda receptor, an outer membrane protein of E. coli K12. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90392-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser T. H., Bruce B. J. Chicken ovalbumin is synthesized and secreted by Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5936–5940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M., Blobel G. Bovine opsin has more than one signal sequence. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):338–343. doi: 10.1038/318338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen W., Garcia P. D., Walter P. In vitro protein translocation across the yeast endoplasmic reticulum: ATP-dependent posttranslational translocation of the prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Schekman R., Thorner J. Glycosylation and processing of prepro-alpha-factor through the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg H. M., Fennick B. J., Vasicek T. J. Transport and cleavage of bacterial pre-beta-lactamase by mammalian microsomes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):1117–1119. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Blobel G. In vitro translocation of bacterial proteins across the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7421–7425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Blobel G. Protein export in Escherichia coli requires a soluble activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7737–7741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Ibrahimi I., Chang C. N., Walter P., Blobel G. A bacterial secretory protein requires signal recognition particle for translocation across mammalian endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11860–11863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggenkamp R., Kustermann-Kuhn B., Hollenberg C. P. Expression and processing of bacterial beta-lactamase in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4466–4470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J. A., Meyer D. I. Secretion in yeast: translocation and glycosylation of prepro-alpha-factor in vitro can occur via an ATP-dependent post-translational mechanism. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1031–1036. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04318.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Benson S. A., Emr S. D. Mechanisms of protein localization. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):313–344. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.313-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K., Kaufman J., Gilbert W. Bacteria mature preproinsulin to proinsulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3988–3992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K., Stahl S., Gilbert W. Eukaryotic signal sequence transports insulin antigen in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3369–3373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Blobel G. Secretory protein translocation in a yeast cell-free system can occur posttranslationally and requires ATP hydrolysis. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1543–1550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Chirico W. J., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the yeast microsomal membrane is stimulated by a soluble factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2629–2636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemel-Dreasen O., Zamir A. Secretion and processing of an immunoglobulin light chain in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]