Abstract
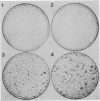
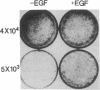
A peptide secreted by some tumor cells in vitro imparts anchorage-independent growth to normal rat kidney (NRK) cells and has been termed transforming growth factor type alpha (TGF-alpha). To directly investigate the transforming properties of this factor, the human sequence coding for TGF-alpha was placed under the control of either a metallothionein promoter or a retroviral long terminal repeat. These constructs failed to induce morphological transformation upon transfection of NIH 3T3 cells, whereas viral oncogenes encoding a truncated form of its cognate receptor, the EGF receptor, or another growth factor, sis/platelet-derived growth factor 2, efficiently induced transformed foci. When NIH 3T3 clonal sublines were selected by transfection of TGF-alpha expression vectors in the presence of a dominant selectable marker, they were shown to secrete large amounts of TGF-alpha into the medium, to have downregulated EGF receptors, and to be inhibited in growth by TGF-alpha monoclonal antibody. These results indicated that secreted TGF-alpha interacts with its receptor at a cell surface location. Single cell-derived TGF-alpha-expressing sublines grew to high saturation density in culture. However, when plated as single cells on contact-inhibited monolayers of NIH 3T3 cells, they failed to form colonies, whereas v-sis- and v-erbB-transfected cells formed transformed colonies under the same conditions. Moreover, TGF-alpha-expressing sublines were not tumorigenic in nude mice. These and other results imply that TGF-alpha exerts a growth-promoting effect on the entire NIH 3T3 cell population after secretion into the medium but little, if any, effect on the individual cell synthesizing this factor. It is concluded that the normal coding sequence for TGF-alpha is not a direct-acting oncogene when overexpressed in NIH 3T3 cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J., Freeman A. E. Human sarcoma cells in culture. Identification by colony-forming ability on monolayers of normal cells. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Jul;61(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K. Biphasic effects of type beta transforming growth factor on epidermal growth factor receptors in NRK fibroblasts. Functional consequences for epidermal growth factor-stimulated mitosis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9613–9617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Stoscheck C. M., Preston Y. A., DeLarco J. E. Antibodies to the epidermal growth factor receptor block the biological activities of sarcoma growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5627–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Goeddel D. V., Ullrich A., Gutterman J. U., Williams R. D., Bringman T. S., Berger W. H. Synthesis of messenger RNAs for transforming growth factors alpha and beta and the epidermal growth factor receptor by human tumors. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):707–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Roberts A. B., Winkler M. E., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-alpha: precursor structure and expression in E. coli. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90550-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit A., Igarashi H., Chiu I. M., Srinivasan A., Yaniv A., Tronick S. R., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Expression of the normal human sis/PDGF-2 coding sequence induces cellular transformation. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit A., Pierce J. H., Kraus M. H., Di Fiore P. P., Pennington C. Y., Aaronson S. A. Mammalian cell transformation by a murine retrovirus vector containing the avian erythroblastosis virus erbB gene. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):19–28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.19-28.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. A., Metcalf D., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., Gonda T. J. Expression of a hemopoietic growth factor cDNA in a factor-dependent cell line results in autonomous growth and tumorigenicity. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leal F., Williams L. T., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Evidence that the v-sis gene product transforms by interaction with the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1985 Oct 18;230(4723):327–330. doi: 10.1126/science.2996133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Rochford R., Todaro G. J., Villarreal L. P. Developmental expression of rat transforming growth factor-alpha mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3644–3646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Rose T. M., Webb N. R., Todaro G. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for rat transforming growth factor-alpha. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):489–491. doi: 10.1038/313489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Todaro G. J. Rat transforming growth factor type 1: structure and relation to epidermal growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 9;223(4640):1079–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6320373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Twardzik D. R., De Larco J. E., Stephenson J. R., Todaro G. J. Transforming growth factors produced by retrovirus-transformed rodent fibroblasts and human melanoma cells: amino acid sequence homology with epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4684–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Epidermal growth factor-like transforming growth factor. II. Interaction with epidermal growth factor receptors in human placenta membranes and A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13614–13620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. J., Marquardt H., Todaro G. J., Gallis B., Casnellie J. E., Bornstein P., Krebs E. G. Transforming growth factor and epidermal growth factor stimulate the phosphorylation of a synthetic, tyrosine-containing peptide in a similar manner. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14628–14631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Leal F., Pierce J. H., Aaronson S. A. The v-sis/PDGF-2 transforming gene product localizes to cell membranes but is not a secretory protein. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1783–1792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Lindquist P. B., Bringman T. S., Goeddel D. V., Derynck R. Expression in rat fibroblasts of a human transforming growth factor-alpha cDNA results in transformation. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90747-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Winkler M. E., Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: a more potent angiogenic mediator than epidermal growth factor. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1250–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.2422759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Todaro G. J. Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 9;303(15):878–880. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010093031511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Function of the retrovirus long terminal repeat. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90367-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., De Larco J. E., Cohen S. Transformation by murine and feline sarcoma viruses specifically blocks binding of epidermal growth factor to cells. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):26–31. doi: 10.1038/264026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Fryling C., De Larco J. E. Transforming growth factors produced by certain human tumor cells: polypeptides that interact with epidermal growth factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5258–5262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardzik D. R. Differential expression of transforming growth factor-alpha during prenatal development of the mouse. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 1):5413–5416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe L. G., Deinhardt F., Theilen G. H., Rabin H., Kawakami T., Bustad L. K. Induction of tumors in marmoset monkeys by simian sarcoma virus, type 1 (Lagothrix): a preliminary report. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Nov;47(5):1115–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Growth factors from murine sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4001–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]